Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (19): 2973-2979.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.19.004
Previous Articles Next Articles
Unilateral pedicle screw fixation combined with translaminar facet screw fixation versus bilateral pedicle screw fixation for lower lumbar degenerative diseases: a 2-year follow-up
Jiang Wei1, Yuan Feng2
- 1Graduate School of Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou 221000, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou 221000, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Online:2017-07-08Published:2017-08-10 -
Contact:Yuan Feng, Professor, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou 221000, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Jiang Wei, Studying for master’s degree, Graduate School of Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou 221000, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:the Project of Jiangsu Provincial Department of Health, No. H201129
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Jiang Wei, Yuan Feng. Unilateral pedicle screw fixation combined with translaminar facet screw fixation versus bilateral pedicle screw fixation for lower lumbar degenerative diseases: a 2-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(19): 2973-2979.
share this article
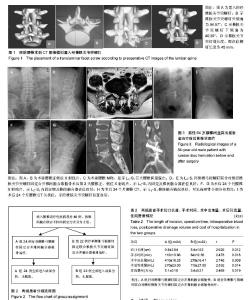
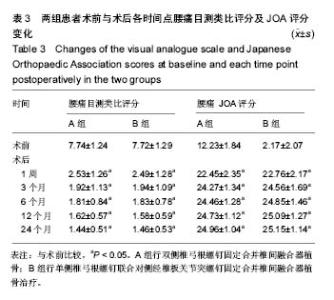
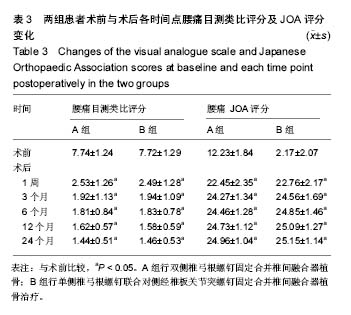
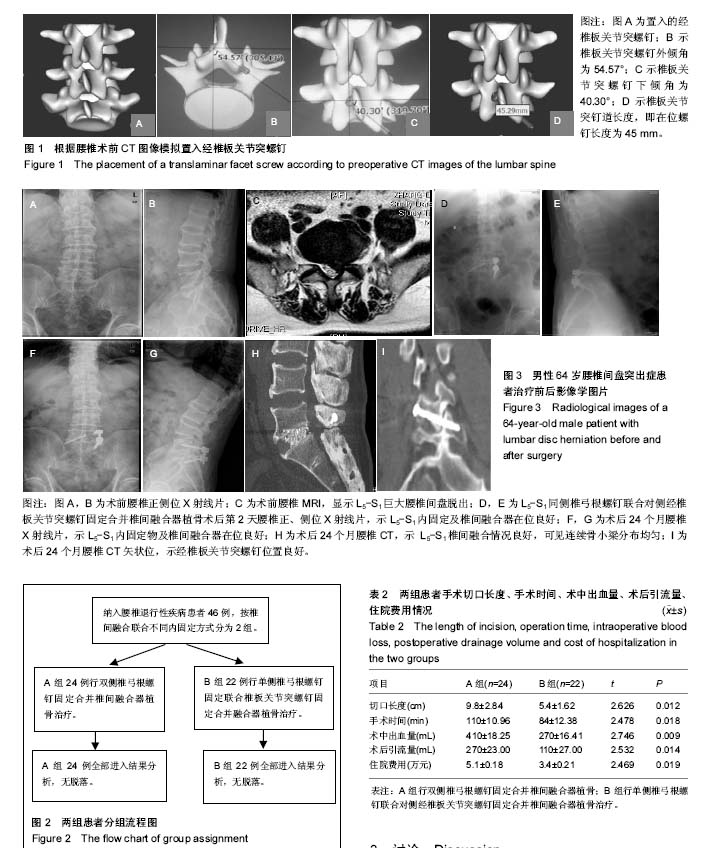
2.1 参与者数量分析 按意向性处理,纳入腰椎退行性疾病患者46例,按内固定方式分为2组,全部进入结果分析,无脱落。试验流程图见图2。 2.2 患者一般情况 2组患者手术切口长度、手术时间、术中出血量、术后引流量、住院费用比较见表2,结果显示,B组各项指标均优于A组,差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。表明单侧椎弓根螺钉联合对侧经椎板关节突螺钉固定合并椎间融合器植骨具有创伤小、手术时间短、术中出血量和术后引流量少、住院费用少等优点。 2.3 影像学评估 术后24个月的随访结果显示,固定节段椎弓根螺钉和经椎板关节突螺钉未出现松动、移位、断裂,CT显示椎板关节突螺钉位置良好。 末次随访时,手术节段A组椎间隙高度为(11.51± 1.62) mm,B组椎间隙高度为(11.39± 1.74) mm,与术前对比差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05),而2组间对比差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。根据Suk评分标准,除外2例(A组1例,B组1例)不能明确是否融合,其余44例均获得椎间融合。A组24例中融合23例,融合率为96%;B组22例中融合21例,融合率为96%,2组融合率比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。 2.4 目测类比评分及JOA评分 2组术后各时间点腰痛目测类比评分及JOA评分与术前比较差异均有显著性意义 (P < 0.05);术后各时间点腰痛目测类比评分及JOA评分2组间比较差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见表3。 末次随访时JOA评分A组为22-28分,平均24.7分,改善率为61%-90%;B组为23-28分,平均25.2分,改善率为62%-90%,2组改善率比较差异无显著性意义。 2.5 不良事件 行内固定联合椎间融合器植骨术治疗后2组均未见明显的不良反应,均未出现植入物宿主反应。 2.6 典型病例 男性患者,64岁,腰痛2年,加重伴左下肢放射痛半年,术前腰椎MRI显示L5-S1巨大腰椎间盘脱出,给予L5-S1同侧椎弓根螺钉联合对侧经椎板关节突螺钉固定合并椎间融合器植骨治疗,相关影像学图片见图3。"
| [1] Park P, Garton HJ, Gala VC, et al. Adjacent segment disease after lumbar or lumbosacral fusion:review of the literature. Spine.2004;29(17):1938-1944.[2] Magerl FP. Stabilization of the lower thoracic and lumbar spine with external skeletal fixation. Clin Orthop Relat Res.1984; 189:125-141.[3] Ferrara LA, Secor JL, Jin BH, et al. A biomechanical comparison of facet screw fixation and pedicle screw fixation:effects of short-term and long-term repetitive cycling. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2003;28(12):1226-1234.[4] Kim TH,Lee BH,Moon SH, et al. Comparison of adjacent segment degeneration after successful posterolateral fusion with unilateral or bilateral pedicle screw instrumentation: a minimum 10-year follow-up. Spine J. 2013 ;13(10):1208-1216.[5] Imagama S,Kawakami N,Matsubara Y, et al. Radiographic Adjacent Segment Degeneration at 5 Years After L4/5 Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion With Pedicle Screw Instrumentation: Evaluation by Computed Tomography and Annual Screening With Magnetic Resonance Imaging.Clin Spine Surg.2016;29(9):442-451.[6] Xie Y, Ma H, Li H, et al. Comparative study of unilateral and bilateral pedicle screw fixation in posterior lumbar interbody fusion. Orthopedics. 2012;35(10):1517-1523.[7] Minghua X, Yihui T,Minwei C. Comparison of unilateral versus bilateral instrumented transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion in degenerative lumbar disease. J Spine. 2012;12(3):209-215.[8] Deutsch H, Musacchio MJ. Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion with unilateral pedicle screw fixation. Neurosurg Focus. 2006;20:E10.[9] Goel VK,Lim TH,Gwon J.et al.Effects of an internal fixation device:a comprehensive biomechanical investigation. Spine. 1991;16(3 Suppl):155-161.[10] Mao L ,Yang HL,Tang TS. Postoperative back pain of opposite lumbosacral area attribute to unilateral fixation with diagonal cage-instrumented transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion. J Chin Orthopedic .2012;24:2260-2263.[11] Suk KS, Lee HM, Kim NH, et al. Unilateral versus bilateral pedicle screw fixation in lumbar spinal fusion. Spine. 2000; 25(14):1843-1847.[12] Reich SM,Kuflik P,Neuwirth M. Translaminar facet screw fixation in lumbar spine fusion. spine(Phila Pa 1976).1993; 18(4):444-449.[13] Kornblatt MD,Casey MP,Jacobs RR.Internal fixation in lumbosacral spine fusion.A biomechanical and clinical study. Clin Orthop Relat Res.1986;203:141-150.[14] Heggeness MH,Esses SI. Translaminar facet joint screw fixation for lumbar and lumbosacral fusion.A clinical and biomechanical study.Spine(Phila Pa 1976).1991;16(Suppl 6):S266-S269.[15] Deguchi M, Cheng BC, Sato K, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of translaminar facet joint fixation. A comparative study of poly-L-lactide pins, screws, and pedicle fixation.Spine(Phila Pa 1976).1998;23(12):1307-1312.[16] Eskander M,Brooks D,Ordway N,et al. Analysis of pedicle and translaminar facet fixation in a multisegment interbody fusion model.Spine(Phila Pa 1976).2007;32(7):E230-E235.[17] Apli M,Mannion AF,Grob D.Translaminar screw fixation of the lumbar spine:long-term outcome. Spine(Phila Pa 1976).2009; 34(14):1492-1498.[18] Jacobs RR,Montesano PX,Jackson RP. Enhancemem of lumbar spine fusion by use of translaminar facet joint screws. Spine(Phila Pa 1976).1989:14(1):12-15.[19] Shim CS,Lee SH,Jung B,et al. Fluoroscopically assisted percutaneous translaminar facet screw fixation following anterior lumbar interhody fusion: technical report.Spine(Phila Pa 1976).2005;30(7):838-843.[20] Wang M,Tang SJ,McGrady LM,et al. Biomechanical comparison of supplemental posterior fixations for two-level anterior lumbar interbody fusion.Proc Inst Mech Eng.2013; 227(3):245-250.[21] Zhan Y,Tian D. Do translaminar facet screws have the same stability as pedicle screws in two-level anterior lumbar interbody fusion? A biomechanical study.Turk Neurosurg. 2012;22(5):630-633. [22] Hou Y, Shen Y, Liu Z, et al. Which posterior instrumentation is better for two-level anterior lumbar interbody fusion: translaminar facet screw or pedicle screw?Arch Orthop Trauma Surg.2013;133(1):37-42. [23] Frantzides CT, Zeni TM, Phillips FM, et al. L5-S1 laparoseopic anterior interbody fusion. JSLS.2006;10:488-492.[24] Rick C,Sasso J, Burkus K,et al.Retrograde ejaculation after anterior lumbar interbody fusion.Spine.2003;28:1023.[25] Cao Y, Chen Z, Jiang C,et al. The combined use of unilateral pedicle screw and contralateral facet joint screw fixation in transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion.Eur Spine J.2015; 24(11):2607-2613.[26] 曾忠友,严卫锋,陈国军,等.单侧椎弓根螺钉联合对侧椎板关节突螺钉固定并椎间融合治疗下腰椎病变的临床观察[J].中华骨科杂志,2011,31(8):834-839.[27] 曾忠友,张建乔,严卫锋,等.椎板关节突螺钉瞄准器在治疗下腰椎退行性病变的临床应用[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2011,19(5): 378-381.[28] 曾忠友,吴鹏,宋永新,等.小切口单侧椎弓根螺钉联合对侧经皮椎板关节突螺钉固定并椎间融合治疗腰椎病变的并发症分析[J].中国骨伤,2016,29(3):232-241.[29] Liu F, Cao Y, Feng Z,et al. Comparison of three different posterior fixation techniques in transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for two-level lumbar degenerative diseases: At a mean follow up time of 46 months.Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2016 ;141:1-6. [30] Liu F, Jiang C, Cao Y, et al. Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion using unilateral pedicle screw fixation plus contralateral translaminar facet screw fixation in lumbar degenerative diseases. Indian J Orthop.2014 ;48(4):374-379. [31] Gong Z, Chen Z, Feng Z, et al. Finite element analysis of 3 posterior fixation techniques in the lumbar spine.Orthopedics. 2014 ;37(5):441-448. [32] Amoretti N, Amoretti ME, Hovorka I,et al. Percutaneous facet screw fixation of lumbar spine with CT and fluoroscopic guidance: a feasibility study.Radiology.2013; 268(2):548-555.[33] 毛克亚,王岩,肖嵩华,等.单侧微创经椎间孔腰椎体间融合术采用椎弓根螺钉结合经椎板关节突螺钉混合内固定可行性研究[J].中华外科杂志,2011,49(12):1067-1070.[34] Park SH,Park WM,Park CW, et al. Minimally invasive anterior lumbar interbody fusion followed by percutaneous translaminar facet screw fixation in elderly patients. J Neurosurg Spine.2009;10(6):610-616.[35] 陶勇,吴云乐,宗少晖,等. 基于有限元分析腰椎内固定的生物力学特征[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(13):1932-1938.[36] Chen SH,Lin SC,Tsai WC, et al. Biomechanical comparison of unilateral and bilateral pedicle screws fixation for transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion after decompressive surgery--a finite element analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2012;13:72.[37] 陆声,徐永清,丁自海,等. 经皮椎板关节突螺钉固定的应用解剖及影像学研究[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2006, 14(5):351-352. |
| [1] | Shi Bin, An Jing, Chen Long-gang, Zhang Nan, Tian Ye . Influencing factors for pain after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 993-997. |
| [2] | Wang Xian-xun. Impact of local compression cryotherapy combined with continuous passive motion on the early functional recovery after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 998-1003. |
| [3] | Yuan Wei, Zhao Hui, Ding Zhe-ru, Wu Yu-li, Wu Hai-shan, Qian Qi-rong. Association between psychological resilience and acute mental disorders after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1015-1019. |
| [4] | Chen Qun-qun, Qiao Rong-qin, Duan Rui-qi, Hu Nian-hong, Li Zhao, Shao Min. Acu-Loc®2 volar distal radius bone plate system for repairing type C fracture of distal radius [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1025-1030. |
| [5] | Huang Xiang-wang, Liu Hong-zhe. A new low elastic modulus of beta titanium alloy Ti2448 spinal pedicle screw fixation affects thoracic stability: biomechanical analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1031-1035. |
| [6] | Xie Qiang. Three-dimensional finite element model for biomechanical analysis of stress in knee inversion and external rotation after posterior cruciate ligament rupture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1036-1040. |
| [7] | He Ze-dong, Zhao Jing, Chen Liang-yu, Li Ke, Weng Jie. Multilevel finite element analysis on the biological tribology damage of water on bone tissue [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1041-1045. |
| [8] | Jiang Zi-wei, Huang Feng, Cheng Si-yuan, Zheng Xiao-hui, Sun Shi-dong, Zhao Jing-tao, Cong Hai-chen,Sun Han-qiao, Dong Hang. Design and finite element analysis of digital splint [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1052-1056. |
| [9] | Wang Fei, Liu Zhi-bin, Tao Hui-ren, Zhang Jian-hua, Li Chang-hong, Cao Qiang, Zheng Jun, Liu Yan-xiong, Qu Xiao-peng. Clinical efficacy of preoperative osteotomy designs using paper-cut technology versus photoshop software for ankylosing spondylitis with kyphosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1057-1063. |
| [10] | Li Peng, Li Hong-wei, Wang Shuang, Wang Hai-zhou. Digital anatomy of lumbar spinous process tilt angle of adults in northeast China: prodinding reference for pedicle screw insertion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1064-1068. |
| [11] | Li Hui, Ma Jun-yi, Ma Yuan, Zhu Xu . Establishment of a three-dimensional finite element model of ankylosing spondylitis kyphosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1069-1073. |
| [12] | Ling Guan-han, Ou Zhi-xue, Yao Lan, Wen Li-chun, Wang Guo-xiang, Lin Heng-feng. Establishment of simulating three-dimensional model of China-Japan Friendship Hospital Classification for L type osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1074-1079. |
| [13] | Fu Wei-min, Wang Ben-jie. Assessing the degree of necrotic femoral head, and association of blood supply with pathlogical changes: study protocol for a diagnostic animal trial [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1086-1091. |
| [14] | Zhang Wen-qiang, Ding Qian, Zhang Na. Associations between alpha angle and herniation pit on oblique axial magnetic resonance imaging in asymptomatic hip joints of adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1098-1103. |
| [15] | Sun Xiao-xin1, Zhou Wei2, Zuo Shu-ping3, Liu Hao1, Song Jing-feng1, Liang Chun-yu1. Morphological characteristics for the magnetic resonance imaging assessment of discoid lateral meniscal tears in children [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1104-1109. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||