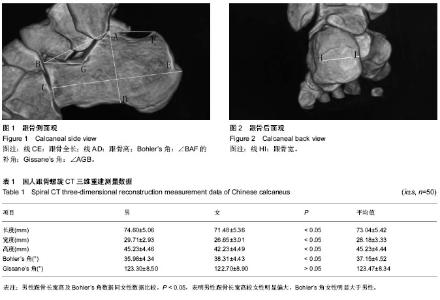
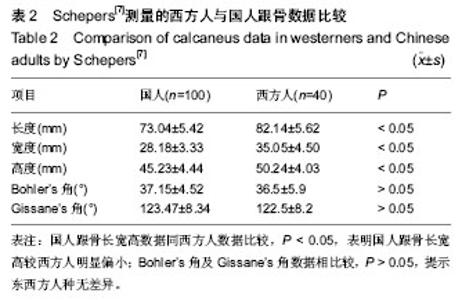
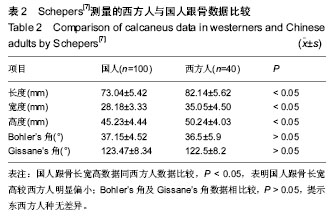
| [1] 王冰,杨春.跟骨前部的解剖测量与多层螺旋CT测量的比较研究及其临床意义[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2012,19(20):1868-1872.
[2] 孔德海,冯德香,刘万军.跟骨侧位X线片在跟骨骨折临床中的应用及临床体会[J].中国临床医学影像杂志,2011,22(6):445-446.
[3] 陈波,韩为清,葛琳娜,等,多层螺旋CT三维及多平面重建在跟骨骨折中的诊断价值[J].中外医疗,2010,29(10):174-176.
[4] 吴清武,岳军艳.多层螺旋CT三维重建技术在创伤性骨折中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(9):1688-1691.
[5] 金国鑫,郭文力.二次测量三维CT重建数据在脊柱侧弯矫形术中的应用[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2012,26(1):74-77.
[6] 冯敏,王书智,卢铃铨,等.螺旋CT三维重建在跟骨骨折中的应用[J].实用医技杂志,2004,11(15):1394-1395.
[7] Schepers T. Radiographic evaluation of calcaneal fractures: to measure or not to measure.Skeletal Radiol. 2007;36: 847-852.
[8] 俞光荣,燕晓宇.跟骨骨折治疗方法的选择[J].中华骨科杂志, 2006,26(2):134-141.
[9] Brunner A, Müller J, Regazzoni P, et al. Open Reduction and Internal Fixation of OTA Type C2–C4 Fractures of the Calcaneus with a Triple-plate Technique. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2012;(3):299-307.
[10] Wu Z,Su Y.Functional outcome of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures: a comparison between open reduction/internal fixation and a minimally invasive approach featured an anatomical plate and compression bolts.J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2012;73(3):743-751.
[11] 梅炯,俞光荣,朱辉,等.跟骨及其周围结构的临床解剖学研究[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2004,22(11):36-38.
[12] 李西成,张英泽.跟骨的解剖和螺旋CT三维测量及其临床意义[J].解剖与临床,2007,12(4):224-227.
[13] De Wall M.Percutaneous reduction and fixation of displaced intra-articular calcaneus fractures.J Orthop Trauma. 2010; 24(8):466-472.
[14] Fan WL, Sun HZ.Subtalar distraction osteogenesis for posttraumatic arthritis following intra-articular calcaneal fractures. Foot Ankle Int. 2013;34(3):398-402.
[15] Shuler FD.Wound-healing risk factor after open reduction and internal fixation of calcaneal fractures:Does correction of Bohler's angle alter outcomes? Orthop Clin N Am. 2001;32(1): 187-192.
[16] 王一民.跟骨Bohler's角的改变对跟骨应力影响的有限元分析[J].实用骨科杂志,2013,19(5):422-424.
[17] 刘峻滔.跟骨Bohler's角的改变对踝关节接触面积及压强影响的实验研究[J].滨州医学院学报,2011,34(3):198-200.
[18] Croaby LA.Intraarticular calcaneal fracture.Reaults of closed treatment. Clin Orthop. 1993;290:47.
[19] 梁军.跟骨Gissane's角的测量及其临床意义[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2001,19(1):52-53.
[20] 陈雁西.跟骨外侧壁的三维形态学特征及跟骨解剖型钢板的匹配性研究[J].中国创伤骨科杂志,2012,14(8):654-658.
[21] 潘科,张坚,陈欣杰,等.CT反角度扫描在腰椎峡部裂诊治中的价值[J]. 中国卫生产业,2013,11(33):73-75.
[22] 刘秀民,刘晓梅,左自军. 螺旋CT在食管癌中的应用价值[J]. 河南外科学杂志, 2012,18(2):116-117.
[23] 师莉芳,白芝兰,秦瑞峰,等.多层螺旋CT后处理技术在颌面部骨折的临床应用[J].创伤外科杂志,2013,15(6):567-568.
[24] 杨星,马彪,苏勤.螺旋CT三维重建的方法及技巧[J].中华放射学杂志,1999,33(7):492-493.
[25] 何建斌,卢建文.多层螺旋CT矢状位重建技术在跟骨骨折中的应用[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2008,23(1):61.
[26] 潘骏.螺旋CT三维和多层面重建在跟骨关节内骨折中的应用[J]. 中国骨伤,2003,16(3):173-175.
[27] 金吕祥,许春宇.多层螺旋CT重建技术在跟骨骨折检查中的应用价值[J]. 中外医学研究, 2012,10(9):52-53.
[28] 吕冬亮,陆雪华,祝莹,等.多层螺旋CT跟骨骨折中的应用价值[J]. 中国辐射卫生,2010,19(2):244-246.
[29] 赵德伟.共同推进人工关节植入物与数字化骨科领域科研与临床的发展[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011,15(17): 3041-3042.
[30] 任银祥,王德贵.数字化技术在人体解剖学教学中的应用[J].当代医学,2012,18(31):162-163. |