Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (11): 1659-1664.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.11.004
Previous Articles Next Articles
Protective effects of low-concentration hydrogen sulfide on rheumatoid joint disease
Zhou Zhi1, Liu Kai-xiang1, Xie Yue1, Wang Li-ming2
- 1Department of Orthopedics, Huai’an First People’s Hospital Affiliated to Nanjing Medical University, Huaian 223300, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Nanjing Hospital Affiliated to Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210000, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Revised:2014-01-10Online:2014-03-12Published:2014-03-12 -
Contact:Zhou Zhi, Department of Orthopedics, Huai’an First People’s Hospital Affiliated to Nanjing Medical University, Huaian 223300, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Zhou Zhi, Studying for doctorate, Attending physician, Department of Orthopedics, Huai’an First People’s Hospital Affiliated to Nanjing Medical University, Huaian 223300, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:he National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81171745
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhou Zhi, Liu Kai-xiang, Xie Yue, Wang Li-ming. Protective effects of low-concentration hydrogen sulfide on rheumatoid joint disease[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(11): 1659-1664.
share this article
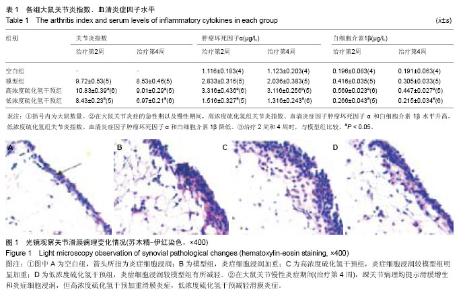
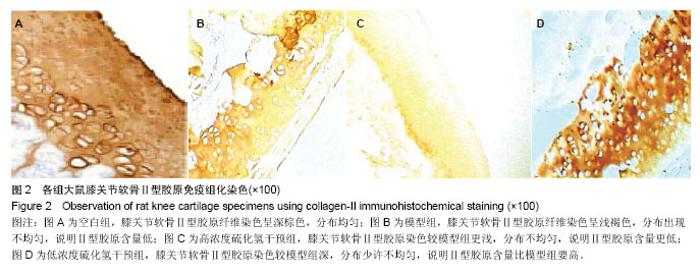
2.1 实验动物数量分析 48只SD雌性大鼠中44只参加实验,中途有4只脱落,出现2只严重免疫反应死亡以及2只造模后足跖无任何反应。模型组和高浓度硫化氢干预组各有1只在第3周死亡,模型组和低浓度硫化氢干预组各有1只造模后足跖无任何反应,于2周时去除,未随机补充。 2.2 各组大鼠关节炎指数 结果可见在大鼠关节炎症的急性期(第2周)以及慢性期间(第4周),高浓度硫化氢干预组关节炎指数升高,低浓度硫化氢干预组关节炎指数降低(表1)。 2.3 各组大鼠血清炎症因子水平比较 结果可见在大鼠关节炎症的急性期(第2周)以及慢性期间(第4周),高浓度硫化氢干预组血清炎症因子肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素1β水平升高,低浓度硫化氢干预组血清炎症因子肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素1β水平降低(表1)。 2.4 各组大鼠踝关节滑膜组织苏木精-伊红染色病理检测 治疗第4周时(关节慢性炎症期间),踝关节病理均提示滑膜增生和炎症细胞浸润,但高浓度硫化氢干预加重滑膜炎症,低浓度硫化氢干预减轻滑膜炎症(图1)。"

| [1] 陆再英,钟南山.内科学[M].7版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2008:848.[2] 杜军保,金红芳,唐朝枢.昔日的废气,今天的气体明星——硫化氢从基础研究走向临床实践[J].中华医学杂志,2011,91(43): 3028-3029.[3] Sowmya S, Swathi Y, Yeo AL,et al. Hydrogen sulfide: regulatory role on blood pressure in hyperhomocysteinemia.Vascul Pharmacol. 2010;53(3-4):138-143.[4] Tamizhselvi R, Moore PK, Bhatia M.Inhibition of hydrogen sulfide synthesis attenuates chemokine production and protects mice against acute pancreatitis and associated lung injury.Pancreas. 2008;36(4):e24-31.[5] Simões SI, Delgado TC, Lopes RM,et al.Developments in the rat adjuvant arthritis model and its use in therapeutic evaluation of novel non-invasive treatment by SOD in Transfersomes.J Control Release. 2005;103(2):419-434.[6] 顾强荣,王黎明,徐燕,等.胶体磷酸铬32P关节腔内注射改善佐剂型关节炎大鼠的相关指标[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2007,11(9):1654-1658.[7] Abd El-Rahman RS, Suddek GM, Gameil NM,et al.Protective potential of MMR vaccine against complete Freund's adjuvant-induced inflammation in rats.Inflammopharmacology. 2011;19(6):343-348. [8] 宋珊珊,张玲玲,魏伟.实验性关节炎动物模型建立及病理机制研究进展[J].中国药理学通报,2011,27(12):1648-1652.[9] Bevaart L, Vervoordeldonk MJ, Tak PP.Evaluation of therapeutic targets in animal models of arthritis: how does it relate to rheumatoid arthritis?Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62(8): 2192-2205.[10] Esser RE, Hildebrand AR, Angelo RA,et al.Measurement of radiographic changes in adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats by quantitative image analysis.Arthritis Rheum.1995;38(1): 129-138.[11] Philippe L, Gegout-Pottie P, Guingamp C,et al. Relations between functional, inflammatory, and degenerative parameters during adjuvant arthritis in rats.Am J Physiol. 1997;273(4 Pt 2):R1550-1556.[12] 杨军平,邱丽瑛,肖亮,等.自拟通痹汤对Ⅱ型胶原性关节炎关节软骨的作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(42):7843-7848.[13] 刘曦,邵福灵,刘爱京.沙利度胺与胶原诱导型关节炎大鼠炎症因子的表达[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(20): 3666-3668.[14] 陈疆,熊新贵,梁清华,等.类风湿性关节炎患者关节滑膜组织蛋白质组学[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(28):5206-5211.[15] Ma Y, Pope RM.The role of macrophages in rheumatoid arthritis.Curr Pharm Des. 2005;11(5):569-580.[16] Mishra R, Singh A, Chandra V,et al.A comparative analysis of serological parameters and oxidative stress in osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.Rheumatol Int. 2012;32(8):2377- 2382.[17] Warenycia MW, Goodwin LR, Benishin CG,et al.Acute hydrogen sulfide poisoning. Demonstration of selective uptake of sulfide by the brainstem by measurement of brain sulfide levels.Biochem Pharmacol. 1989;38(6):973-981.[18] Martelli A, Testai L, Breschi MC,et al.Hydrogen sulphide: novel opportunity for drug discovery.Med Res Rev. 2010. [Epub ahead of print][19] Li L, Bhatia M, Zhu YZ,et al.Hydrogen sulfide is a novel mediator of lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in the mouse.FASEB J. 2005;19(9):1196-1198. [20] Rinaldi L, Gobbi G, Pambianco M,et al.Hydrogen sulfide prevents apoptosis of human PMN via inhibition of p38 and caspase 3.Lab Invest. 2006;86(4):391-397.[21] Bhatia M, Sidhapuriwala J, Moochhala SM,et al.Hydrogen sulphide is a mediator of carrageenan-induced hindpaw oedema in the rat.Br J Pharmacol. 2005;145(2): 141-144.[22] Alvira CM, Abate A, Yang G,et al.Nuclear factor-kappaB activation in neonatal mouse lung protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007;175(8):805-815. [23] Cheng DS, Han W, Chen SM,et al.Airway epithelium controls lung inflammation and injury through the NF-kappa B pathway.J Immunol. 2007;178(10):6504-6513.[24] Tamizhselvi R, Koh YH, Sun J,et al.Hydrogen sulfide induces ICAM-1 expression and neutrophil adhesion to caerulein-treated pancreatic acinar cells through NF-kappaB and Src-family kinases pathway.Exp Cell Res. 2010;316(9): 1625-1636. [25] Sivarajah A, Collino M, Yasin M,et al.Anti-apoptotic and anti-inflammatory effects of hydrogen sulfide in a rat model of regional myocardial I/R.Shock. 2009;31(3):267-274.[26] Hirata I, Naito Y, Takagi T, et al. Endogenous hydrogen sulfide is an anti-inflammatory molecule in dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis in mice.Dig Dis Sci. 2011;56(5): 1379-1386.[27] Tamizhselvi R, Sun J, Koh YH,et al.Effect of hydrogen sulfide on the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-protein kinase B pathway and on caerulein-induced cytokine production in isolated mouse pancreatic acinar cells.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2009; 329(3):1166-1177. [28] Whiteman M, Haigh R, Tarr JM,et al.Detection of hydrogen sulfide in plasma and knee-joint synovial fluid from rheumatoid arthritis patients: relation to clinical and laboratory measures of inflammation.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010;1203: 146-150.[29] Chen WP, Tang JL, Bao JP,et al.Effects of diallyl sulphide in chondrocyte and cartilage in experimental osteoarthritis in rabbit.Phytother Res. 2011;25(3):351-356.[30] Kloesch B, Liszt M, Krehan D,et al.High concentrations of hydrogen sulphide elevate the expression of a series of pro-inflammatory genes in fibroblast-like synoviocytes derived from rheumatoid and osteoarthritis patients.Immunol Lett. 2012;141(2):197-203. [31] Kloesch B, Liszt M, Steiner G,et al.Inhibitors of p38 and ERK1/2 MAPkinase and hydrogen sulphide block constitutive and IL-1β-induced IL-6 and IL-8 expression in the human chondrocyte cell line C-28/I2.Rheumatol Int. 2012;32(3): 729-736.[32] Williams FM, Skinner J, Spector TD,et al.Dietary garlic and hip osteoarthritis: evidence of a protective effect and putative mechanism of action.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2010;11: 280.[33] Lee HS, Lee CH, Tsai HC,et al.Inhibition of cyclooxygenase 2 expression by diallyl sulfide on joint inflammation induced by urate crystal and IL-1beta.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2009; 17(1):91-99.[34] Ekundi-Valentim E, Santos KT, Camargo EA, et al.Differing effects of exogenous and endogenous hydrogen sulphide in carrageenan-induced knee joint synovitis in the rat.Br J Pharmacol. 2010;159(7):1463-1474. [35] Szekanecz Z, Koch AE.Angiogenesis and its targeting in rheumatoid arthritis.Vascul Pharmacol. 2009;51(1):1-7.[36] Komorowski J, Jerczyńska H, Siejka A, et al.Effect of thalidomide affecting VEGF secretion, cell migration, adhesion and capillary tube formation of human endothelial EA.hy 926 cells.Life Sci. 2006;78(22):2558-2563. [37] Lainer DT, Brahn E.New antiangiogenic strategies for the treatment of proliferative synovitis.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2005;14(1):1-17.[38] Esposito E, Cuzzocrea S.TNF-alpha as a therapeutic target in inflammatory diseases, ischemia-reperfusion injury and trauma.Curr Med Chem. 2009;16(24):3152-3167.[39] Tweedie D, Sambamurti K, Greig NH.TNF-alpha inhibition as a treatment strategy for neurodegenerative disorders: new drug candidates and targets.Curr Alzheimer Res. 2007;4(4): 378-385.[40] Deng A, Harvey V, Sina B,et al.Interstitial granulomatous dermatitis associated with the use of tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibitors.Arch Dermatol. 2006;142(2):198-202.[41] Greig NH, Giordano T, Zhu X,et al.Thalidomide-based TNF-alpha inhibitors for neurodegenerative diseases.Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars). 2004;64(1):1-9.[42] Davis JC Jr.Understanding the role of tumor necrosis factor inhibition in ankylosing spondylitis.Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2005;34(4):668-677.[43] Kapoor M, Martel-Pelletier J, Lajeunesse D,et al.Role of proinflammatory cytokines in the pathophysiology of osteoarthritis.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011;7(1):33-42.[44] Egeblad M, Werb Z.New functions for the matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression.Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2(3):161-174.[45] Hunziker EB.Articular cartilage repair: basic science and clinical progress. A review of the current status and prospects.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2002;10(6):432-463.[46] Ishiguro N.Cartilage degradation in rheumatoid arthritis.Clin Calcium. 2009;19(3):347-354.[47] Skoumal M, Haberhauer G, Kolarz G,et al.Serum cathepsin K levels of patients with longstanding rheumatoid arthritis: correlation with radiological destruction.Arthritis Res Ther. 2005;7(1):R65-70.[48] Leong DJ, Gu XI, Li Y,et al.Matrix metalloproteinase-3 in articular cartilage is upregulated by joint immobilization and suppressed by passive joint motion.Matrix Biol. 2010;29(5): 420-426. [49] Cho TJ, Lehmann W, Edgar C,et al.Tumor necrosis factor alpha activation of the apoptotic cascade in murine articular chondrocytes is associated with the induction of metalloproteinases and specific pro-resorptive factors.Arthritis Rheum. 2003;48(10):2845-2854.[50] Glasson SS, Askew R, Sheppard B,et al.Characterization of and osteoarthritis susceptibility in ADAMTS-4-knockout mice.Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50(8):2547-2558.[51] Lohmander LS, Brandt KD, Mazzuca SA,et al.Use of the plasma stromelysin (matrix metalloproteinase 3) concentration to predict joint space narrowing in knee osteoarthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52(10):3160-3167. |
| [1] | Lin Han-wen, Wen Jun-mao, Huang Chao-yuan, Zhou Chi, Tang Hong-yu. Correlation between the changes in lower limb power line and pain area in the knee osteoarthritis patients: imaging evaluation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1110-1114. |
| [2] |
Gao Wei-lu, Li Hong, Liu Bi-quan, Hu Yong, Liu Jing-jun, Yin Li, Liu Hu, Mei Bin, Yin Zong-sheng.
Analgesic effect of femoral and sciatic nerve block under multimodal analgesia in total knee arthroplasty
|
| [3] | Yin Chun-ming, Pan Xiao-hua. Expression of miR-140-3p in synovial fluid of knee osteoarthritis patients reflects the progression of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(35): 5277-5283. |
| [4] | Lu Ning, Yang Yang. Unicompartmental knee replacement for medial compartmental knee osteoarthritis: a four to six-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(31): 4575-4581. |
| [5] | Gao Ji-hai, Wang Jiang-quan, Lv Dong-wei . Influencing factors of knee function in osteoarthritis patients after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(31): 4582-4588. |
| [6] | Qi Wei-zhong, Lin Li-jun, Li Qi. Humeral head replacement in a hemophilia B omarthritis patient [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(31): 4596-4602. |
| [7] | Liu Peng, Liu Ping-ping. A comparison of computer-assisted total knee arthroplasty through vastus medialis approach and conventional arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(22): 3205-3211. |
| [8] | Ren Zhi-shuai, Cheng Zhao-jun, Sun He-jun, Sun Zhen-hui, Cui Zi-jian, Zhang Li-long, Lin Yong-zhi, Zhang Ren-zan, Peng Bing, Zhang Xue-li. Osteoporosis-related factors in patients with knee osteoarthritis before total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(22): 3212-3218. |
| [9] | Chen Rong-bo, Hou Na, Wang Ren, He Ming, Wang Er-feng, Zhang Wei-tao, Li Xiao-jian, Li Xian-zhi . Total knee arthroplasty for the treatment of bilateral knee rheumatoid arthritis in the same period [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(4): 493-498. |
| [10] | Zhang Sheng-hai, Fu Li-ming, Ma Zhao-ji, Jiang Guo-wang. Evaluation and influencing factors of knee function in aged patients with osteoarthritis before and after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(4): 499-503. |
| [11] | Xu Peng-fei, Yin Zong-sheng, Gao Wei-lu, Ma Zhi-xiang. Epidemiology of total knee arthroplasty: a retrospective analysis among 1 146 cases in Hefei City from 2008 to 2013 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(4): 504-509. |
| [12] | Li Hong-shi, Chen Xin, Feng Yan, Yin Yin, Cao Jun-kai. Changes of cartilage matrix components, related growth factors and inflammatory factors in the temporomandibular joint under high acceleration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(11): 1663-1667. |
| [13] | Yu Yang, Cui Lei. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha and granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor in knee osteoarthritis cartilage [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(11): 1683-1687. |
| [14] | Ouyang Hai-chun, Wu Wo-dong, Zhong Dong-mei, Wu Yan-xian, Li Wen-jie, Chen Xi-ming. Effects of Xingnaojing on recombinant human tumor necrosis factor-mediated tissue-type plasminogen activator and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 expression in human umbilical cord vein endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(11): 1717-1721. |
| [15] | Zhang Shi-song, Zhang Zhi-feng, Huang Jian. Connective tissue growth factor and articular cartilage repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(11): 1755-1760. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||