Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (33): 4971-4978.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.33.015
Previous Articles Next Articles
Research progress in pathogenesis of ossification of ligamentum flavum
Dong Xing-cheng, Jia Lian-shun, Chen Xiong-sheng
- Department of Orthopedics, Changzheng Hospital, Second Military Medical University, Shanghai 200003, China
-
Received:2016-06-06Online:2016-08-12Published:2016-08-12 -
Contact:Jia Lian-shun, Chief physician, Professor, Department of Orthopedics, Changzheng Hospital, Second Military Medical University, Shanghai 200003, China -
About author:Dong Xing-cheng, Department of Orthopedics, Changzheng Hospital, Second Military Medical University, Shanghai 200003, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Dong Xing-cheng, Jia Lian-shun, Chen Xiong-sheng. Research progress in pathogenesis of ossification of ligamentum flavum[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(33): 4971-4978.
share this article
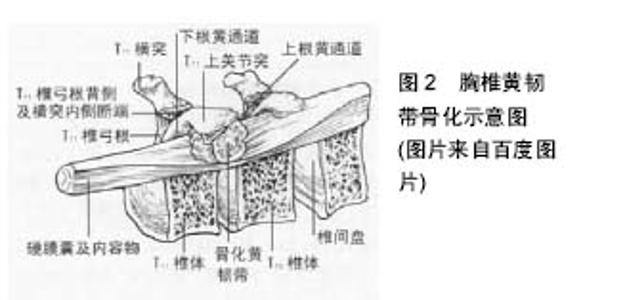
2.1 流行病学分析 流行病学调查显示,黄韧带骨化的发病有家族倾向、种族差异及性别差异[9-10]。黄韧带骨化在黄种人群的发病率较高,主要分布于中日韩等亚洲国家,尤以日本为显著;而欧美及非洲的高加索人、加勒比人以及黑人发病率较低[11-13]。黄韧带骨化的种族差异表明可能与某种遗传因素相关。该病为中老年性疾病,Aizawa等[14]研究发现男性的高发年龄段在60岁左右,而女性其高发年龄段在50-70岁,随年龄增长呈增高趋势,男性发病较女性多,发病率之比为2-3∶1,平均发病年龄约为61岁。在年龄超过65岁的亚洲人中,韧带骨化的发病率可高达20%,而对于欧美人群的发病情况却罕见报道[15]。 2.2 解剖结构退变相关因素 黄韧带骨化的发生与其解剖基础有着密切的联系。一些学者采用尸体做研究,Lirk等[16]研究者行尸体研究发现,下胸段双侧黄韧带的汇合连接,构成了解剖学的体积变小。黄韧带骨化多发于中老年人,以下胸段多见。Kobayashi等[17]认为黄韧带骨化的发生与解剖相关,因骨化常发生于韧带与骨连接处,C6/7节段以上的关节囊部黄韧带未与骨性部位相连,C6/7以下关节囊部与椎板间部分均与骨性部位相连,故颈椎黄韧带骨化少见,而胸椎黄韧带骨化常见。弹性纤维异常是黄韧带骨化的一个表现,颈椎的屈伸活动使动态压力反复作用而有利于弹性纤维的维持;胸椎和脊柱胸腰段由于长期静态张力致弹性纤维丢失,代之以胶原增生、成纤维细胞向软骨样细胞分化及韧带骨化的出现(图2)。Hadley- Miller等[18]国外学者研究发现编码原纤维的单基因在黄韧带骨化患者身上发生突变,该基因位于第15条染色体上,突变后会引起成纤维细胞所合成的原纤维无法结合胶原纤维,进而导致弹性纤维解剖学上的形成异常。但尚缺乏进一步研究证实黄韧带骨化的发生与此基因的相关性。黄韧带骨化的发生常伴有前纵韧带、后纵韧带等骨化,邻近关节突关节的增生肥大以及相应椎体的骨质增生骨赘形成,该病理变化与慢性退行性改变相一致。同样的结论也得到了Jayakumar等[19]学者的研究表明黄韧带骨化患者病理检测结果为黄韧带呈软骨样改变,内部胶原纤维大量增生,而起连接作用的弹性纤维明显减少,向骨化过度,为典型的慢性退行性变。"
| [1] Guo JJ, Luk KD, Karppinen J, et al. Prevalence, distribution, and morphology of ossification of the ligamentum flavum: a population study of one thousand seven hundred thirty-six magnetic resonance imaging scans.Spine.2010;35(1): 51-56. [2] Wang W and Kong L.Ossification of ligamentum. J Neurosurg Spine.2007;6(1):96; author reply 96-97. [3] Kudo S, Ono M,Russell WJ. Ossification of thoracic ligamenta flava. AJR Am J Roentgenol.1983;141(1): 117-121. [4] Okada K, Oka S, Tohge K, et al. Thoracic myelopathy caused by ossification of the ligamentum flavum. Clinicopathologic study and surgical treatment. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).1991;16(3): 280-287. [5] 陈仲强,党耕町,刘晓光,等. 胸椎黄韧带骨化症的治疗方法选择[J].中华骨科杂志,1999,19(4): 3-6. [6] 周方,党耕町.颈椎后纵韧带骨化症合并胸椎黄韧带骨化症的诊断[J].中华骨科杂志,1995,15(9): 575-577. [7] 王全平, 李明全,李新奎,等.胸椎黄韧带骨化[J].中华骨科杂志,1996,16(7): 40-43+68. [8] 倪斌, 贾连顺,戴力扬,等.胸椎黄韧带骨化所致椎管狭窄症的诊断及手术治疗[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 1994,4(2): 56-58. [9] Sakou T, Matsunaga S,Koga H.Recent progress in the study of pathogenesis of ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. J Orthop Sci.2000; 5(3): 310-315. [10] Matsunaga S, Yamaguchi M, Hayashi K, et al. Genetic analysis of ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).1999;24(10): 937-938; discussion 939. [11] Xu R, Sciubba DM, Gokaslan ZL, et al.Ossification of the ligamentum flavum in a Caucasian man. J Neurosurg Spine.2008;9(5): 427-437. [12] Wiseman DB, Stokes JK, Toselli RM. Paraparesis in a black man brought on by ossification of the ligamentum flavum: case report and review of the literature. J Spinal Disord Tech, 2002. 15(6): 542-545. [13] Pascal-Moussellard H, Cabre P, Smadja D,et al.Symptomatic ossification of the ligamentum flavum: a clinical series from the French Antilles. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2005;30(14): E400-405. [14] Aizawa T,Sato T,Tanaka Y,et al.Thoracic myelopathy in Japan: epidemiological retrospective study in Miyagi Prefecture during 15 years. Tohoku J Exp Med.2006. 210(3): 199-208. [15] Kruse JJ, Awasthi D, Harris M, et al.Ossification of the ligamentum flavum as a cause of myelopathy in North America: report of three cases.J Spinal Disord.2000; 13(1): 22-25. [16] Lirk P, Kolbitsch C, Putz G, et al.Cervical and high thoracic ligamentum flavum frequently fails to fuse in the midline. Anesthesiology.2003;99(6): 1387-1390. [17] Kobayashi K, Takahashi N, Jimi E, et al. Tumor necrosis factor α stimulates osteoclast differentiation by a mechanism independent of the ODF/RANKL–RANK interaction. J Exp Med. 2000;191(2):275-286. [18] Hadley-Miller N, Mims B, and Milewicz DM.The potential role of the elastic fiber system in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am.1994; 76(8): 1193-1206. [19] Jayakumar P, Devi BI, Bhat D, et al. Thoracic cord compression due to ossified hypertrophied ligamentum flavum. Neurology India.2002;50(3): 286. [20] Maigne JY, Ayral X,Guerin-Surville H. Frequency and size of ossifications in the caudal attachments of the ligamentum flavum of the thoracic spine. Role of rotatory strains in their development. An anatomic study of 121 spines. Surg Radiol Anat.1992;14(2): 119-124. [21] Nakatani T, Marui T, Hitora T, et al. Mechanical stretching force promotes collagen synthesis by cultured cells from human ligamentum flavum via transforming growth factor-β1. J Orthop Res. 2002; 20(6):1380-1386. [22] Cai H-X, Yayama T, Uchida K, et al.Cyclic tensile strain facilitates the ossification of ligamentum flavum through β-catenin signaling pathway: in vitro analysis. Spine.2012;37(11): E639-E646. [23] Fan D, Chen Z, Wang D, et al. Osterix is a key target for mechanical signals in human thoracic ligament flavum cells. J Cell Physiol. 2007;211(3):577-584. [24] Kang YM,Suk KS,Lee BH,et al.Herniated Intervertebral Disk Induces Hypertrophy and Ossification of Ligamentum Flavum. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2014;27(7): 382- 389. [25] Kim YH,Khuyagbaatar B,Kim K.Biomechanical effects of spinal cord compression due to ossification of posterior longitudinal ligament and ligamentum flavum: a finite element analysis. Med Eng Physics. 2013; 35(9):1266-1271. [26] Otani K,Aihara T,Tanaka A,et al.Ossification of the ligamentum flavum of the thoracic spine in adult kyphosis. Int Orthop.1986;10(2): 135-139. [27] Kaneyama S,Doita M, Nishida K, et al. Thoracic myelopathy due to ossification of the yellow ligament in young baseball pitchers. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2008; 21(1):68-771. [28] Ben Hamouda K,Jemel H,Haouet S,et al.Thoracic myelopathy caused by ossification of the ligamentum flavum: a report of 18 cases.J Neurosurg. 2003;99(2 Suppl): 157-161. [29] Benoist M. Natural history of the aging spine. Eur Spine J.2003;12 Suppl 2: S86-89. [30] Kang YM, Suk KS, Lee BH, et al. Herniated intervertebral disk induces hypertrophy and ossification of ligamentum flavum. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2014;27(7): 382-389. [31] Fan D, Chen Z, Wang D, et al. Osterix is a key target for mechanical signals in human thoracic ligament flavum cells.J Cell Physiol.2007;211(3): 577-584. [32] Carvalho HF, Felisbino SL, Keene DR, et al.Identification, content, and distribution of type VI collagen in bovine tendons. Cell Tissue Res.2006; 325(2): 315-324. [33] Kong Q, Ma X, Li F, et al.COL6A1 polymorphisms associated with ossification of the ligamentum flavum and ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. Spine.2007;32(25): 2834-2838. [34] Liu Y, Zhao Y, Chen Y, et al. RUNX2 polymorphisms associated with OPLL and OLF in the Han population. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010 Dec;468(12):3333-3341. [35] Satake M,Nomura S,Yamaguchi-Iwai Y,et al. Expression of the Runt domain-encoding PEBP2 alpha genes in T cells during thymic development. Mol Cell Biol.1995;15(3): 1662-1670. [36] Kishiya M,Sawada T,Kanemaru K,et al.A functional RNAi screen for Runx2-regulated genes associated with ectopic bone formation in human spinal ligaments. J Pharmacol Sci. 2008;106(3):404-414. [37] Miyamoto S,Yonenobu K, Ono K.Elevated plasma fibronectin concentrations in patients with ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament and ossification of the ligamentum flavum. Spine.1993;18(15): 2267-2270. [38] Miyamoto S,Takaoka K,Yonenobu K,et al.Ossification of the ligamentum flavum induced by bone morphogenetic protein.An experimental study in mice. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1992;74(2):279-283. [39] 陈雄生,贾连顺,倪斌,等. BMP-2 mRNA在实验性黄韧带骨化组织中的表达及其意义[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2001,8(8): 59-62. [40] 陈雄生, 贾连顺,倪斌,等.重组人骨形态发生蛋白-2诱发黄韧带骨化的实验模型[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2002, 12(1): 31-34+85. [41] Hou XF,Fan DW,Sun CG,et al.Recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2–induced ossification of the ligamentum flavum in rats and the associated global modification of histone H3: Laboratory investigation. Journal of Neurosurgery: Spine.2014; 21(3): 334-341. [42] Ikegawa S. [Animal models for bone and joint disease. ttw (tiptoe walking), a model mouse of OPLL (ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament of the spine)]. Clinical calcium.2011;21(2): 294-300. [43] Moon SH, Park SR, Kim H, et al. Biologic modification of ligamentum flavum cells by marker gene transfer and recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004;29(9): 960-965. [44] Yang L,Yongfei Z,Yu C,et al.RUNX2 Polymorphisms Associated with OPLL and OLF in the Han Population. Clin Orthop Related Res. 2010;468(12): 3333-3341 (3339). [45] 赵伟光,刘振武,刘利,等.胸椎黄韧带骨化症与骨形态发生蛋白4基因单核苷酸多态性的关联[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(24): 4376-4380. [46] 张颖哲, 吴东进, and 彭长亮,等. siRNA 抑制转化生长因子-β1 对小鼠黄韧带骨化的影响[J]. 山东大学学报:医学版,2014,52(8): 27-33. [47] Park JO, Lee BH, Kang YM, et al.Inflammatory cytokines induce fibrosis and ossification of human ligamentum flavum cells. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2013; 26(1):E6-E12. [48] Sakou T,Taketomi E,Matsunaga S, et al.Genetic study of ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament in the cervical spine with human leukocyte antigen haplotype. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).1991; 16(11): 1249-1252. [49] 颜廷宾, 张佐伦,于锡欣,等. 胸椎黄韧带骨化与HLA-DQA1等位基因的相关性研究[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2002,10(S2):1402-1404. [50] Shiigi E,Sugiyama T,Tanaka H,et al.Possible involvement of vitamin D receptor gene polymorphism in male patients with ossification of spinal ligaments. J Bone Miner Metab.2001;19(5): 308-311. [51] Schmidt RF, Goldstein IM, Liu JK. Ossified ligamentum flavum causing spinal cord compression in a patient with acromegaly. J Clin Neurosci. 2013;20(11): 1599-1603. [52] Braddock R,Siman CM,Hamilton K,et al. Gamma-linoleic acid and ascorbate improves skeletal ossification in offspring of diabetic rats. Pediatr Res. 2002;51(5): 647-652. [53] Shirakura Y, Sugiyama T, Tanaka H, et al. Hyperleptinemia in female patients with ossification of spinal ligaments. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000;267(3):752-755. [54] Fan D,Chen Z,Chen Y,et al.Mechanistic roles of leptin in osteogenic stimulation in thoracic ligament flavum cells. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(41):29958-29966. [55] Chin S,Furukawa KI,Ono A,et al.Immunohistochemical localization of mesenchymal stem cells in ossified human spinal ligaments. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;436(4):698-704. [56] 王哲, 王全平,张俊华,等. 骨形成蛋白在黄韧带骨化中的表达定位[J]. 第四军医大学学报, 2002,11(4): 341-343. [57] Jacoby BH and Davis WL. The electron microscopic immunolocalization of a copper-zinc superoxide dismutase in association with collagen fibers of periodontal soft tissues. J Periodontol.1991;62(7): 413-420. [58] Muthukumar N. Ossification of the ligamentum flavum as a result of fluorosis causing myelopathy: report of two cases. Neurosurgery.2005;56(3): E622; discussion E622. [59] Imai S,Hukuda S. Cervical radiculomyelopathy due to deposition of calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystals in the ligamentum flavum: historical and histological evaluation of attendant inflammation. J Spinal Disord. 1994; 7(6): 513-517. [60] Hirakawa K,Hanakita J,Suwa H,et al.A post-traumatic ligamentum flavum progressive hematoma: a case report. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2000;25(9): 1182-1184. [61] 秦德安, 张佐伦,李晓东,等. 脊柱黄韧带骨化细胞 COX2, VEGF 的表达及其意义[J]. 中国组织化学与细胞化学杂志, 2006,15(1): 44-48. [62] Furusawa N,Baba H,Maezawa Y,et al.Calcium crystal deposition in the ligamentum flavum of the lumbar spine.Clin Exp Rheumatol.1997;15(6): 641-647. [63] Yayama T, Uchida K, Kobayashi S, et al.Thoracic ossification of the human ligamentum flavum: histopathological and immunohistochemical findings around the ossified lesion. J Neurosurg Spine. 2007; 7(2):184-193. |
| [1] | Hu Wandong, He Jialin, Zhang Longsheng, Liao Wenbo. Differential proteomics study of patients with sternal ossification of the ligamentum flavum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(17): 2625-2629. |
| [2] | Xu Guofeng, Li Xuebin, Tang Yifan, Zhao Yin, Zhou Shengyuan, Chen Xiongsheng, Jia Lianshun. The role of autophagy in ossification of the human ligamentum flavum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(8): 1174-1181. |
| [3] | Zhang Fangxin, Kang Peng, Wang Qiteng, Zhang Xiao, Liu Wei, Yang Hongtao, Aierken•Amudong. Apoptosis and expression of apoptotic factors caspase-3, fas and p53 in lumbar ligamentum flavum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(8): 1195-1199. |
| [4] | Shen Canghai, Feng Yongjian, Song Yancheng, Liu Gang, Liu Zhiwei, Wang Ling, Dai Haiyang. Value of quantitative MRI T2WI parameters in predicting surgical outcome of thoracic ossification of the ligamentum flavum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(18): 2893-2899. |
| [5] | Wang Xuefeng, Shang Xifu . Curative effects of three filling materials in the treatment of osteoporotic thoracolumbar fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(6): 863-869. |
| [6] | Zhu Aiguo, Zhang Feng, Zhu Jianwei, Jin Guohua. Anatomic measurement and clinical significance of the lumbosacral nerve roots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(4): 573-577. |
| [7] | Tang Xianneng, Chen Yueping, Zhang Xiaoyun. Clinical application of bone morphogenetic proteins in bone and cartilage tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(4): 591-596. |
| [8] | Liu Junyin, Feng Wei, Xie Yingchun, Li Yuwan, Zeng Jitao, Liu Ziming, Tu Xiaolin. Bone morphologic protein signaling pathway in bone regeneration and repair: accurate regulation and treatment targets [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(4): 606-612. |
| [9] | Yang Jinfeng, Ma Sanhui. Association between polymorphism of aggregate protein metabolic pathway gene and severity of lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(31): 4939-4944. |
| [10] | Li Shuwen, Yang Zhe, Yin Heping, Wu Yimin, Bai Ming, Du Zhicai, Wang Yupeng, Meng Gedong. Preserving ligamentum flavum for preventing dural adhesions after lumbar surgery in model rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(3): 416-420. |
| [11] | Liu Shuzhong1, Lao Lifeng2. Effects of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 on the proliferation of breast cancer MCF-7 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(3): 458-463. |
| [12] | Lu Yanqin, Yi Fang, Ju Wei, Li Wenjie, Lei Lei. Reparation of femoral defects with a Ca-P coated magnesium alloy scaffold carrying sustained release microspheres [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(2): 232-238. |
| [13] | Li Haoliang, Wang Xibin, Zuo Ruiting. Calcium phosphate cement/fibrin glue composite loaded with recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein 2 promotes osteoporotic fracture healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(14): 2156-2161. |
| [14] | Zhang Xufeng, Fu Qiya, Zheng Genjian, Guo Yusu, Chen Danyu, Fu Fangman, Wu Hui, Wang Lin. Autologous platelet gel-collagen biologically active composite membrane for repair of periodontal bone defect in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(14): 2177-2182. |
| [15] | Gu Jianhua, Shi Zhicai . Placement position of artificial vertebral pedicle screws based on the anatomical structure of lumbar nerve roots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(12): 1829-1833. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||