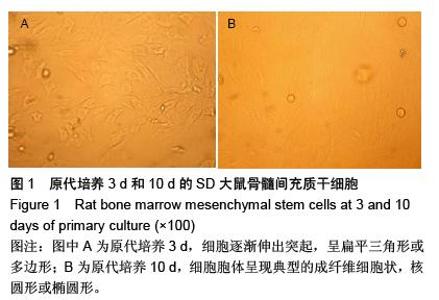
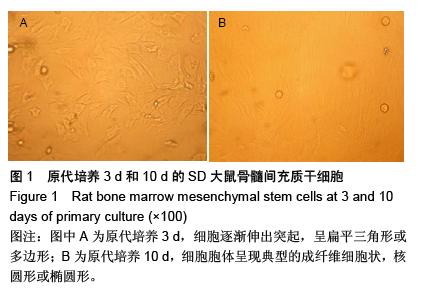
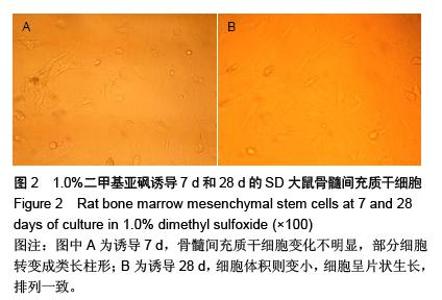
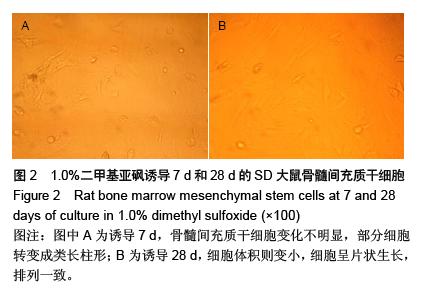
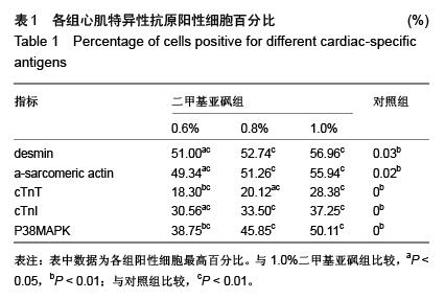
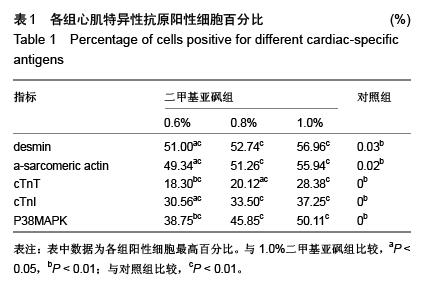
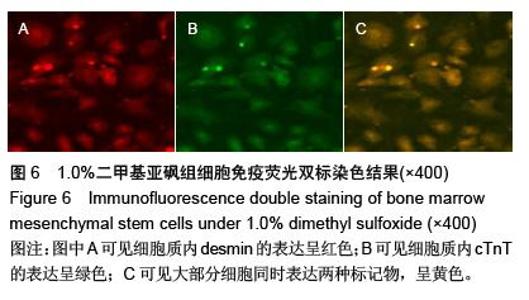
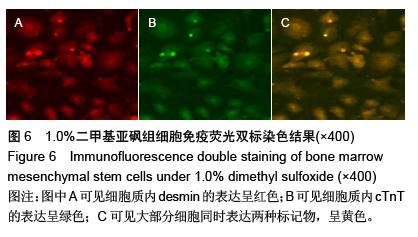
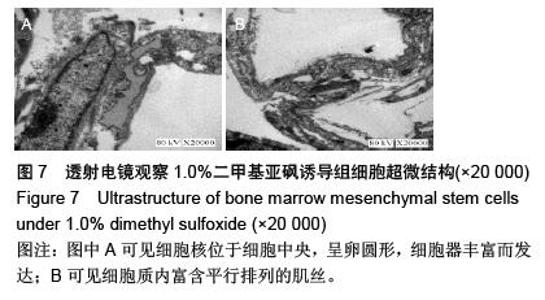
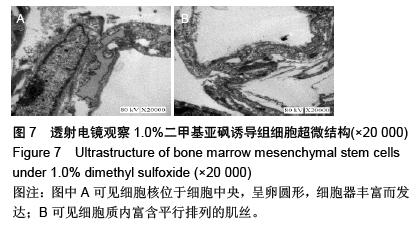
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research
Previous Articles Next Articles
Dimethyl sulfoxide induces differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into myocardial cells
Sun Long-yun
- Zhangjiakou University, Zhangjiakou 075000, Hebei Province, China
-
Online:2016-01-01Published:2016-01-01 -
About author:Sun Long-yun, Master, Lecturer, Zhangjiakou University, Zhangjiakou 075000, Hebei Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Sun Long-yun. Dimethyl sulfoxide induces differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into myocardial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.01.005.
share this article
| [1] Richards M, Huibregtse BA, Caplan AI, et al. Marrow-derived progenitor cell injections enhance new bone formation during distraction. J Orthop Res. 1999;17(6):900-908.
[2] Ouyang JF, Lou J, Yan C, et al. In-vitro promoted differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells towards hepatocytes induced by salidroside. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2010;62(4):530-538.
[3] Lu P, Blesch A, Tuszynski MH. Induction of bone marrow stromal cells to neurons: differentiation, transdifferentiation, or artifact. J Neurosci Res. 2004;77(2):174-191.
[4] Cipriani P, Guiducci S, Miniati I, et al. Impairment of endothelial cell differentiation from bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells: new insight into the pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56(6):1994-2004.
[5] Clabaut A, Delplace S, Chauveau C, et al. Human osteoblasts derived from mesenchymal stem cells express adipogenic markers upon coculture with bone marrow adipocytes. Differentiation. 2010;80(1):40-45.
[6] Fukuda K. Molecular characterization of regenerated cardiomyocytes derived from adult mesenchymal stem cells. Congenit Anom (Kyoto). 2002;42(1):1-9.
[7] Makino S, Fukuda K, Miyoshi S, et al. Cardiomyocytes can be generated from marrow stromal cells in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1999;103(5):697-705.
[8] Woodbury D, Reynolds K, Black IB. Adult bone marrow stromal stem cells express germline, ectodermal, endodermal, and mesodermal genes prior to neurogenesis. J Neurosci Res. 2002;69(6):908-917.
[9] Oh SH, Muzzonigro TM, Bae SH, et al. Adult bone marrow-derived cells trans-differentiating into insulin-producing cells for the treatment of type I diabetes. Lab Invest. 2004;84(5):607-617.
[10] 李秀华,张雷,王海萍,等. P19 细细胞体外DMSO诱导向心肌样细胞分化[J].第四军医大学学报, 2006, 27(2):129-132.
[11] Sotkis HV, Lazarenko PM, Boldyriev OI, et al. Identification of E-4031-sensitive potassium current component in murine P19 embryonic carcinoma cell line differentiated in cardiomyocytes. Fiziol Zh. 2006;52(1):49-61.
[12] Moscoso I, Centeno A, López E, et al. Differentiation "in vitro" of primary and immortalized porcine mesenchymal stem cells into cardiomyocytes for cell transplantation. Transplant Proc. 2005;37(1):481-482.
[13] Fukuda K. Development of regenerative cardiomyocytes from mesenchymal stem cells for cardiovascular tissue engineering. Artif Organs. 2001;25(3):187-193.
[14] Krysko DV, Vanden Berghe T, D'Herde K, et al. Apoptosis and necrosis: detection, discrimination and phagocytosis. Methods. 2008;44(3):205-221.
|
| [1] | Jiang Tao, Ma Lei, Li Zhiqiang, Shou Xi, Duan Mingjun, Wu Shuo, Ma Chuang, Wei Qin. Platelet-derived growth factor BB induces bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to differentiate into vascular endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3937-3942. |
| [2] | Chen Yang, Huang Denggao, Gao Yuanhui, Wang Shunlan, Cao Hui, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Luo Siqin, Xiao Jingchuan, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes the proliferation and adhesion of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3949-3955. |
| [3] | Zhang Lishu, Liu Anqi, He Xiaoning, Jin Yan, Li Bei, Jin Fang. Alpl gene affects the therapeutic effect of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on ulcerative colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3970-3975. |
| [4] | Ruan Guangping, Yao Xiang, Liu-Gao Miyang, Cai Xuemin, Li Zian, Pang Rongqing, Wang Jinxiang, Pan Xinghua. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for traumatic systemic inflammatory response syndrome in tree shrews [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3994-4000. |
| [5] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [6] | Chen Lei, Zheng Rui, Jie Yongsheng, Qi Hui, Sun Lei, Shu Xiong. In vitro evaluation of adipose-derived stromal vascular fraction combined with osteochondral integrated scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3487-3492. |
| [7] | Wei Qin, Zhang Xue, Ma Lei, Li Zhiqiang, Shou Xi, Duan Mingjun, Wu Shuo, Jia Qiyu, Ma Chuang. Platelet-derived growth factor-BB induces the differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into osteoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2953-2957. |
| [8] | Chen Xiao, Guo Zhi, Chen Lina, Liu Xuanyong, Zhang Yihuizhi, Li Xumian, Wang Yueqiao, Wei Liya, Xie Jing, Lin Li. Factors affecting the mobilization and collection of autologous peripheral blood hematopoietic stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2958-2962. |
| [9] | Guo Zhibin, Wu Chunfang, Liu Zihong, Zhang Yuying, Chi Bojing, Wang Bao, Ma Chao, Zhang Guobin, Tian Faming. Simvastatin stimulates osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2963-2968. |
| [10] | Li Congcong, Yao Nan, Huang Dane, Song Min, Peng Sha, Li Anan, Lu Chao, Liu Wengang. Identification and chondrogenic differentiation of human infrapatellar fat pad derived stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2976-2981. |
| [11] | Gao Yuanhui, Xiang Yang, Cao Hui, Wang Shunlan, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang, Huang Denggao. Comparison of biological characteristics of adipose derived mesenchymal stem cells in Wuzhishan inbreed miniature pigs aged two different months [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2988-2993. |
| [12] | Cao Yang, Zhang Junping, Peng Li, Ding Yi, Li Guanghui. Isolation and culture of rabbit aortic endothelial cells and biological characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3000-3003. |
| [13] | Dai Min, Wang Shuai, Zhang Nini, Huang Guilin, Yu Limei, Hu Xiaohua, Yi Jie, Yao Li, Zhang Ligang. Biological characteristics of hypoxic preconditioned human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3004-3008. |
| [14] | Qin Yanchun, Rong Zhen, Jiang Ruiyuan, Fu Bin, Hong Xiaohua, Mo Chunmei. Chinese medicine compound preparation inhibits proliferation of CD133+ liver cancer stem cells and the expression of stemness transcription factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3016-3023. |
| [15] | Dai Yaling, Chen Lewen, He Xiaojun, Lin Huawei, Jia Weiwei, Chen Lidian, Tao Jing, Liu Weilin. Construction of miR-146b overexpression lentiviral vector and the effect on the proliferation of hippocampal neural stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3024-3030. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||