Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (53): 8615-8620.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.53.015
Previous Articles Next Articles
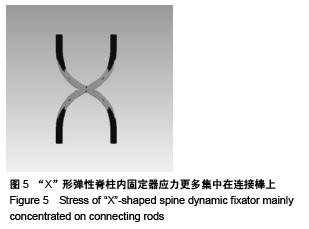
Stress analysis between “X”-shaped spine dynamic fixation and traditional pedicle screw fixation
Wang Yu, Mei Ji-wen, Mu Shang-qiang, Gao Feng, Huang Rui
- Department of Orthopedics, the Affiliated Hospital of Jilin Medical University, Jilin 132013, Jilin Province, China
-
Received:2015-10-13Online:2015-12-24Published:2015-12-24 -
About author:Wang Yu, Master, Associate chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, the Affiliated Hospital of Jilin Medical University, Jilin 132013, Jilin Province, China -
Supported by:the Science and Technology Project of Jilin City, No. 201133104; the Young Physician Research Project of Affiliated Hospital of Jilin Medical University, No. Yuanzi 2014-3
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Yu, Mei Ji-wen, Mu Shang-qiang, Gao Feng, Huang Rui. Stress analysis between “X”-shaped spine dynamic fixation and traditional pedicle screw fixation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(53): 8615-8620.
share this article
| [1] Seoudi H,Laporta M,Griffen M,et al.Experience with 161 cases of anterior exposure of the thoracic and lumbar spine in an acute care surgery model: impact of exposure level and underlying pathology on morbidity.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013;38(18):1602-1606.[2] Landi A,Marotta N,Morselli C,et al.Pannus regression after posterior decompression and occipito-cervical fixation in occipito-atlanto-axial instability due to rheumatoid arthritis: case report and literature review.Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2013;115(2):111-116. [3] Landi A.Interspinous posteriordevices: What is the real surgical indication? World J Clin Cases.2014;2(9):402-408.[4] Kim KT,Lee SH,Son ES,et al.Surgical treatment of "chin-on-pubis" deformity in a patient with ankylosing spondylitis: a case report of consecutive cervical,thoracic,and lumbar corrective osteotomies.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2012; 37(16):E1017-1021.[5] Manchikanti L,Kaye AD,Manchikanti K,et al.Efficacy of epidural injections in the treatment of lumbar central spinal stenosis: a systematic review. Anesth Pain Med. 2015;5(1): e23139. [6] Kalff R,Ewald C,Waschke A,et al.Degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis in older people:current treatment options.Dtsch Arztebl Int.2013;110(37):613-623;quiz 624.[7] Rihn JA, Gandhi SD.Disc space preparation in transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: a comparison of minimally invasive and open approaches.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;472(6): 1800-1805.[8] Perez-Cruet MJ,Hussain NS.Quality-of-life outcomes with minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion based on long-term analysis of 304 consecutive patients. Spine (Phila Pa 1976)2014;39(3):191-198.[9] Liang J,Dong Y,Zhao H.Risk factors for predicting symptomatic adjacent segment degeneration requiring surgery in patients after posterior lumbar fusion.J Orthop Surg Res.2014;9:97. [10] Saavedra-Pozo FM,Deusdara RA,Benzel EC.Adjacent segment disease perspective and review of the literature. Ochsner J.2014;14(1):78-83.[11] Liu HY,Zhou J,Wang B,et al.Comparison of topping-off and posterior lumbar interbody fusion surgery in lumbar degenerative disease: a retrospective study.Chin Med J (Engl).2012;125(22):3942-3946.[12] Zhu Z,Liu C,Wang K,et al.Topping-off technique prevents aggravation of degeneration of adjacent segment fusion revealed by retrospective and finite element biomechanical analysis.J Orthop Surg Res.2015;10(1):10. [13] Yang M,Li C,Chen Z,et al.Short term outcome of posterior dynamic stabilization system in degenerative lumbar diseases. Indian J Orthop.2014;48(6):574-581.[14] Erbulut DU,Zafarparandeh I,Ozer AF,et al.Biomechanics of posterior dynamic stabilization systems.Adv Orthop.2013; 2013:451956.[15] 叶葆青,梁伟国,叶伟雄,等.Bioflex弹性椎弓根钉内固定系统对全椎板切除术与椎间植骨融合术后腰椎活动范围的影响[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2012,20(24):96-99.[16] 肖振平.腰椎动态非动态椎弓根钉内固定系统的有限元分析及初步临床应用[D].南华大学,2012.[17] Chao S,Malloy JP,Bono CM.Complications specific to mo tion-sparing devices in the lumbar spine.Semin Spine Surg. 2011;23(2):123-134.[18] Lee YS,Kim YB,Park SW.Survival rates and risk factors for cephalad and L5-s1 adjacent segment degeneration after L5 floating lumbar fusion : a minimum 2-year follow-up.J Korean Neurosurg Soc.2015;57(2):108-113. [19] Soh J,Lee JC,Shin BJ.Analysis of risk factors for adjacent segment degeneration occurring more than 5 years after fusion with pedicle screw fixation for degenerative lumbar spine.Asian Spine J.2013;7(4):273-281.[20] Gurban CV,Mederle O.The OPG/RANKL system and zinc ions are promoters of bone remodeling by osteoblast prolifer ation in postmenopausal osteoporosis.Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2011;52(3 Suppl): 1113-1119.[21] 车武,姜允琦,马易群,等.单节段椎弓根螺钉固定联合上方棘突间Coflex置入的生物力学评价[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2015,25(1): 62-66.[22] 张文志,段丽群,尚希福,等.Wallis棘突间动态稳定系统治疗腰椎间盘突出症的初步临床应用[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2011,19(3): 203-205.[23] Barbagallo GM,Olindo G,Corbino L,et al.Analysis of complications in patients treated with the X-Stop Interspinous Process Decompression System:Proposal for a novel anatomic scoring system for patient selection and review of the literature. Neurosurgery.2009;65(1):111-120.[24] 闫广辉,张庆胜,靳宪辉,等.经腰椎椎弓根动态内固定研究进展[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2012,9(6):31-34.[25] 王启,贺志荣,王芳等.Ti-Ni形状记忆合金超弹性的研究进展[J].材料导报,2010,24(13):85-88.[26] Canavese F,Dimeglio A,Stebel M,et al. Thoracic cage plasticity in prepubertal New Zealand white rabbits submitted to T1-T12 dorsal arthrodesis: computed tomography evaluation, echocardiographic assessment and cardio-pulmonary measurements. Eur Spine J.2013;22(5): 1101-1112.[27] 霍莉峰,倪衡建.数字骨科应用与展望:更精确、个性、直观的未来前景[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(9):1457-1462.[28] 侯波,王毅,沈宇辉.膝关节动态有限元模型的力学分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(22):3998-4004.[29] 金哲峰,刘爱峰,王平,等.膝关节骨性关节炎生物力学模型及其软骨表面应力分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(29):4629- 4633.[30] Grabowski AM,D'Andrea S.Effects of a powered ankle-foot prosthesis on kinetic loading of the unaffected leg during level-ground walking.J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2013;10:49.[31] 刘延东,毛景松,石先明,等.不同载荷下腰1椎体内应力分布规律的有限元分析[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志.2014,24(9):822-827.[32] 宋富立,靳安民,王瑞,等.短节段椎弓根内固定系统术后断裂临床分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2005,20(6):376-378. |
| [1] | Chen Ziyang, Pu Rui, Deng Shuang, Yuan Lingyan. Regulatory effect of exosomes on exercise-mediated insulin resistance diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4089-4094. |
| [2] | Chen Yang, Huang Denggao, Gao Yuanhui, Wang Shunlan, Cao Hui, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Luo Siqin, Xiao Jingchuan, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes the proliferation and adhesion of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3949-3955. |
| [3] | Yang Junhui, Luo Jinli, Yuan Xiaoping. Effects of human growth hormone on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3956-3961. |
| [4] | Sun Jianwei, Yang Xinming, Zhang Ying. Effect of montelukast combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on spinal cord injury in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3962-3969. |
| [5] | Gao Shan, Huang Dongjing, Hong Haiman, Jia Jingqiao, Meng Fei. Comparison on the curative effect of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells and induced islet-like cells in gestational diabetes mellitus rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3981-3987. |
| [6] | Hao Xiaona, Zhang Yingjie, Li Yuyun, Xu Tao. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing prolyl oligopeptidase on the repair of liver fibrosis in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3988-3993. |
| [7] | Liu Jianyou, Jia Zhongwei, Niu Jiawei, Cao Xinjie, Zhang Dong, Wei Jie. A new method for measuring the anteversion angle of the femoral neck by constructing the three-dimensional digital model of the femur [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3779-3783. |
| [8] | Meng Lingjie, Qian Hui, Sheng Xiaolei, Lu Jianfeng, Huang Jianping, Qi Liangang, Liu Zongbao. Application of three-dimensional printing technology combined with bone cement in minimally invasive treatment of the collapsed Sanders III type of calcaneal fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3784-3789. |
| [9] | Qian Xuankun, Huang Hefei, Wu Chengcong, Liu Keting, Ou Hua, Zhang Jinpeng, Ren Jing, Wan Jianshan. Computer-assisted navigation combined with minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar spondylolisthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3790-3795. |
| [10] | Hu Jing, Xiang Yang, Ye Chuan, Han Ziji. Three-dimensional printing assisted screw placement and freehand pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracolumbar fractures: 1-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3804-3809. |
| [11] | Shu Qihang, Liao Yijia, Xue Jingbo, Yan Yiguo, Wang Cheng. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of a new three-dimensional printed porous fusion cage for cervical vertebra [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3810-3815. |
| [12] | Wang Yihan, Li Yang, Zhang Ling, Zhang Rui, Xu Ruida, Han Xiaofeng, Cheng Guangqi, Wang Weil. Application of three-dimensional visualization technology for digital orthopedics in the reduction and fixation of intertrochanteric fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3816-3820. |
| [13] | Sun Maji, Wang Qiuan, Zhang Xingchen, Guo Chong, Yuan Feng, Guo Kaijin. Development and biomechanical analysis of a new anterior cervical pedicle screw fixation system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3821-3825. |
| [14] | Lin Wang, Wang Yingying, Guo Weizhong, Yuan Cuihua, Xu Shenggui, Zhang Shenshen, Lin Chengshou. Adopting expanded lateral approach to enhance the mechanical stability and knee function for treating posterolateral column fracture of tibial plateau [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3826-3827. |
| [15] | Zhu Yun, Chen Yu, Qiu Hao, Liu Dun, Jin Guorong, Chen Shimou, Weng Zheng. Finite element analysis for treatment of osteoporotic femoral fracture with far cortical locking screw [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3832-3837. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||