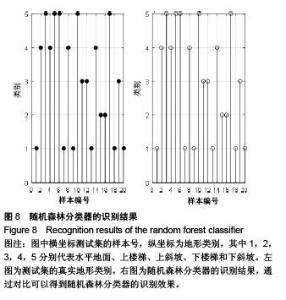
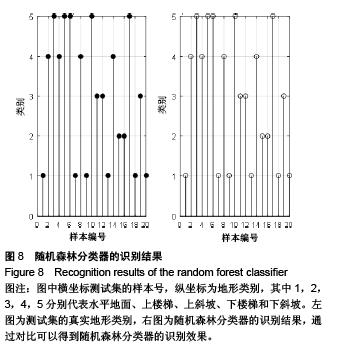
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (53): 8609-8614.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.53.014
Previous Articles Next Articles
Application of random forest algorithm in terrain recognition to control active above-knee prosthesis
Zhang Yan, Gao Xin, Chen Ling-ling, Zhang Hao-miao
- School of Science and Engineering, Hebei University of Technology, Tianjin 300130, China
-
Received:2015-11-16Online:2015-12-24Published:2015-12-24 -
Contact:Gao Xin, Studying for master’s degree, School of Science and Engineering, Hebei University of Technology, Tianjin 300130, China -
About author:Zhang Yan, M.D., Professor, School of Science and Engineering, Hebei University of Technology, Tianjin 300130, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 61203323, 61174009; the Science and Technology Research Project of Hebei Colleges and Universities, No. Q2012079; the Tianjin Application Foundation and Advanced Technology Research Plan, No. 13JCQNJC03400
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Yan, Gao Xin, Chen Ling-ling, Zhang Hao-miao. Application of random forest algorithm in terrain recognition to control active above-knee prosthesis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(53): 8609-8614.
share this article
| [1] 第六次人口普查委员会.2010年第六次全国人口普查主要数据公报(第1号)[R].北京:第六次人口普查委员会,2010.
[2] 中华人民共和国国家统计局.2006年第二次全国残疾人抽样调查主要数据公报(第二号)[R],2007.
[3] 谭冠政,吴立明.国内外人工腿(假肢)研究的进展及发展趋势[J].机器人,2001,23(1):91-96.
[4] 王人成,沈强,金德闻.假肢智能膝关节研究进展[J].中国康复医学杂志,2007,22(12):1093-1094.
[5] 王人成,金德闻.仿生智能假肢的研究与进展[J].中国医疗器械信息,2009,15(1):3-5.
[6] 金德闻,王人成.人工智能假肢[J].中国临床康复,2002,6(20): 2994-2995.
[7] 龚思远,杨鹏,刘启栋,等.智能下肢假肢传感器的应用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(17):3109-3112.
[8] 杨鹏,刘作军,耿艳利,等.智能下肢假肢关键技术研究进展[J].河北工业大学学报,2013,42(1):76-80.
[9] Sup F, Bohara A, Goldfarb M. Design and Control of a Powered Transfemoral Prosthesis. Int J Rob Res. 2008; 27(2):263-273.
[10] Au S, Berniker M, Herr H. Powered ankle-foot prosthesis to assist level-ground and stair-descent gaits. Neural Networks. 2008;21(4):654-666.
[11] Djuric, M. Automatic recognition of gait phases from accelerations of leg segments. 9th Symposium on Neural Network Applications in Electrical Engineering, 25-27 Sept. 2008:121-124.
[12] Sakagami Y, Watanabe R, Aoyama C, et al. The intelligent ASIMO: System overview and integration//Intelligent Robots and Systems, 2002. IEEE/RSJ International Conference on. IEEE. 2002;3:2478-2483.
[13] Chestnutt J, Lau M, Cheung G, et al. Footstep planning for the honda asimo humanoid.Robotics and Automation, 2005. ICRA 2005. Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Conference on. IEEE. 2005:629-634.
[14] Chestnutt J, Michel P, Kuffner J, et al. Locomotion among dynamic obstacles for the honda ASIMO. Intelligent Robots and Systems. 2007. IROS 2007. IEEE/RSJ International Conference on. IEEE. 2007:2572-2573.
[15] 宗光华,唐伯雁.日本拟人型两足步行机器人研发状况及我见[J].机器人,2002,24(6):564-570.
[16] 王岚,张今瑜,王劲松.人体步态相位检测实验研究[J].传感器与微系统,2006,25(5):42-44.
[17] 闫炳雷,谭冠军,曾庆冬,等.智能仿生人工腿CIP-ILeg性能仿真评估研究[J].计算机仿真,2006,(9):231-235.
[18] 谭冠政,何胜军,曾庆冬,等.CIP-Ⅰ智能仿生人工腿步速测量系统研究与设计[J].计算机测量与控制,2005,(11):1164-1166.
[19] 谭冠政,王越超.具有不完全微分的最优模糊PID控制器及其在智能人工腿中应用的仿真研究[J].控制理论与应用,2002,19(3): 462-466.
[20] 贺光辉,谭冠政,曾庆冬,等.智能仿生人工腿位置伺服控制系统的设计[J].计算机测量与控制,2007,(1):52-55.
[21] 王喜太,王强,张晓玉,等. 基于肌电传感器的下肢残肢康复训练模式识别的研究[J]. 中国康复理论与实践,2009,(1):90-92.
[22] 高云园,孟明,罗志增,等.利用多源运动信息的下肢假肢多模式多步态识别研究[J]. 传感技术学报,2011,(11):1574-1578.
[23] 高云园,佘青山,孟明,等.基于多源信息融合的膝上假肢步态识别方法[J].仪器仪表学报,2010,(12):2682-2688.
[24] 刘磊,杨鹏,刘作军.基于多源信息和粒子群优化算法的下肢运动模式识别[J].浙江大学学报(工学版),2015,(3):439-447.
[25] 刘磊,杨鹏,刘作军.基于多源信息和广义回归神经网络的下肢运动模式识别[J].机器人,2015,(3):310-317.
[26] Zhang F, Fang Z, Liu M, et al. Preliminary design of a terrain recognition system// Conference proceedings : annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society. IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society. Annual Conference. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2011:5452-5455.
[27] Ho TK. Random Decision Forests. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition. Montreal Canada. 1995;8:278-282.
[28] Breiman L. Random Forests. Machine Learning. 2001;45(1): 5-32.
[29] John Durkin,蔡竞峰.决策树技术及其当前研究方向[J].控制工程,2005,(1):15-21.
[30] Quinlan JR. Decision trees and decision-making. Syst Man Cybe IEEE Trans. 1990;20(2):339-346. |
| [1] | Chen Ziyang, Pu Rui, Deng Shuang, Yuan Lingyan. Regulatory effect of exosomes on exercise-mediated insulin resistance diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4089-4094. |
| [2] | Chen Yang, Huang Denggao, Gao Yuanhui, Wang Shunlan, Cao Hui, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Luo Siqin, Xiao Jingchuan, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes the proliferation and adhesion of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3949-3955. |
| [3] | Yang Junhui, Luo Jinli, Yuan Xiaoping. Effects of human growth hormone on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3956-3961. |
| [4] | Sun Jianwei, Yang Xinming, Zhang Ying. Effect of montelukast combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on spinal cord injury in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3962-3969. |
| [5] | Gao Shan, Huang Dongjing, Hong Haiman, Jia Jingqiao, Meng Fei. Comparison on the curative effect of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells and induced islet-like cells in gestational diabetes mellitus rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3981-3987. |
| [6] | Hao Xiaona, Zhang Yingjie, Li Yuyun, Xu Tao. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing prolyl oligopeptidase on the repair of liver fibrosis in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3988-3993. |
| [7] | Liu Jianyou, Jia Zhongwei, Niu Jiawei, Cao Xinjie, Zhang Dong, Wei Jie. A new method for measuring the anteversion angle of the femoral neck by constructing the three-dimensional digital model of the femur [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3779-3783. |
| [8] | Meng Lingjie, Qian Hui, Sheng Xiaolei, Lu Jianfeng, Huang Jianping, Qi Liangang, Liu Zongbao. Application of three-dimensional printing technology combined with bone cement in minimally invasive treatment of the collapsed Sanders III type of calcaneal fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3784-3789. |
| [9] | Qian Xuankun, Huang Hefei, Wu Chengcong, Liu Keting, Ou Hua, Zhang Jinpeng, Ren Jing, Wan Jianshan. Computer-assisted navigation combined with minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar spondylolisthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3790-3795. |
| [10] | Hu Jing, Xiang Yang, Ye Chuan, Han Ziji. Three-dimensional printing assisted screw placement and freehand pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracolumbar fractures: 1-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3804-3809. |
| [11] | Shu Qihang, Liao Yijia, Xue Jingbo, Yan Yiguo, Wang Cheng. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of a new three-dimensional printed porous fusion cage for cervical vertebra [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3810-3815. |
| [12] | Wang Yihan, Li Yang, Zhang Ling, Zhang Rui, Xu Ruida, Han Xiaofeng, Cheng Guangqi, Wang Weil. Application of three-dimensional visualization technology for digital orthopedics in the reduction and fixation of intertrochanteric fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3816-3820. |
| [13] | Sun Maji, Wang Qiuan, Zhang Xingchen, Guo Chong, Yuan Feng, Guo Kaijin. Development and biomechanical analysis of a new anterior cervical pedicle screw fixation system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3821-3825. |
| [14] | Lin Wang, Wang Yingying, Guo Weizhong, Yuan Cuihua, Xu Shenggui, Zhang Shenshen, Lin Chengshou. Adopting expanded lateral approach to enhance the mechanical stability and knee function for treating posterolateral column fracture of tibial plateau [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3826-3827. |
| [15] | Zhu Yun, Chen Yu, Qiu Hao, Liu Dun, Jin Guorong, Chen Shimou, Weng Zheng. Finite element analysis for treatment of osteoporotic femoral fracture with far cortical locking screw [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3832-3837. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||