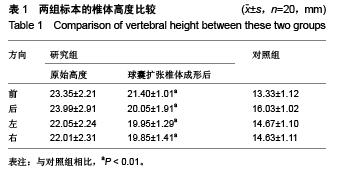
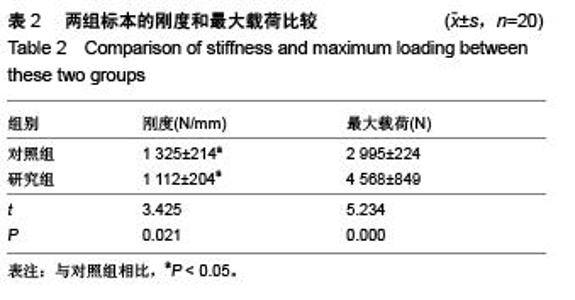
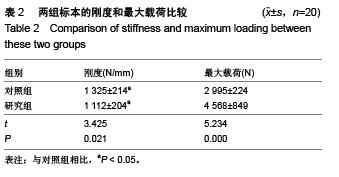
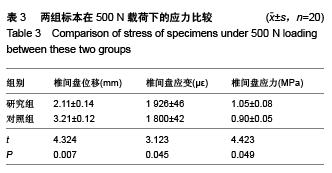
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (53): 8621-8626.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.53.016
Previous Articles Next Articles
Balloon vertebroplasty repairs vertebral compression fractures: biomechanical analysis
Li Song-bai, Zhang Yuan-jin, Sun Fa-rui
- Department of Joint Surgery, Huangshi Central Hospital, Huangshi 435000, Hubei Province, China
-
Received:2015-11-05Online:2015-12-24Published:2015-12-24 -
About author:Li Song-bai, Associate chief physician, Department of Joint Surgery, Huangshi Central Hospital, Huangshi 435000, Hubei Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Song-bai, Zhang Yuan-jin, Sun Fa-rui. Balloon vertebroplasty repairs vertebral compression fractures: biomechanical analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(53): 8621-8626.
share this article
| [1] 秦毅,秦杰,江建明, 等.BCC骨水泥椎体成形术强化骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折的实验研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2013,19(8): 796-799,806.
[2] 熊斌,赵敏,周江军,等.PVP联合PKP结合药物治疗多节段骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2013,19(6):605-607.
[3] 郝定均,谢恩,张子如,等.数字化建模在老年骨质疏松椎体压缩性骨折椎体成形术的应用研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2013,19(4): 319-323.
[4] Zhao H,Shi Q,Sun ZY, et al.The importance of percutaneous vertebroplasty and radiation therapy for pathological vertebral compression fractures secondary to multiple myeloma. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2012;132(11):1669-1670.
[5] 李煜明,孙强,王黎明,等.椎体骨折不愈合微创治疗手术方式的选择[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2013,19(9):973-976,980.
[6] Rho YJ, Choe WJ, Chun YI. Risk factors predicting the new symptomatic vertebral compression fractures after percutaneous vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty. Eur Spine J. 2012; 21(5):905-911.
[7] 刘永强,范金鹏,王朝君,等.经皮椎体后凸成形术联合唑来磷酸治疗骨质疏松椎体压缩性骨折[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2013,19(9): 985-987.
[8] Ma XL,Xing D, Ma JX, et al. Balloonkyphoplasty versus percutaneous vertebroplasty in treating osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture: Grading the evidence through a systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur Spine J. 2012;21(9): 1844-1859.
[9] 赵清平,张艳艳,孙强,等.椎体骨折不愈合微创治疗围手术期管理[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2013,19(3):275-278.
[10] 刘洋,李明辉,梅红军,等.经皮椎体成形术后骨水泥渗漏的回顾性分析及预防策略[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2013,19(4):375-380.
[11] Krüger A,Baroud G,Noriega D,et al.Height restoration and maintenance after treating unstable osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures by cement augmentation is dependent on the cement volume used. Clin Biomech. 2013;28(7):725-730.
[12] Corbiere NC, Lewicki KA, Issen KA, et al. Creating Physiologically Realistic Vertebral Fractures in a Cervine Model. J Biomech Eng. 2014;136(6):064504-1-064504-4.
[13] Noel-Savina E, Descourt R. Osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: A rare complication of radiotherapy in a patient with lung cancer. Clin Imaging. 2013;37(2):390-392.
[14] 黄刚,陈海云,刘卓勋,等.经皮椎体成形术与经皮椎体后凸成形术治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折[J].南方医科大学学报, 2010, 30(12): 2729-2732.
[15] 孙治国,缪晓刚,袁宏,等.椎体成形术与后凸成形术治疗老年陈旧性骨质疏松椎体压缩性骨折的相关问题探讨[J].中国骨伤, 2010, 23(10): 734-738.
[16] Chen YJ, Chen WH, Chen HT, et al. Repeat needle insertion in vertebroplasty to prevent re-collapse of the treated vertebrae. Eur J Radiol. 2012;81(3):558-561.
[17] Yokoyama K,Kawanishi M,Yamada M, et al.Safety and therapeutic efficacy of the second treatment for new fractures developed after initial vertebroplasty performed for painful vertebral compression fractures. Neurol Res. 2013;35(6): 608-613.
[18] 史丽娜,吴春根,李文彬,等.椎体压缩性骨折MRI信号特点与PVP术后疗效相关性分析[J].介入放射学杂志,2011,20(1):32-36.
[19] Li Y, Gu YF, Sun ZK, et al. Comparison of percutaneous vertebroplasty with and without interventional tumour removal for malignant vertebral compression fractures with symptoms of neurological compression. Eur Radiol. 2013;23(10):2754-2763.
[20] Thaler M, Lechner R, Nogler M, et al. Surgical procedure and initial radiographic results of a new augmentation technique for vertebral compression fractures. Eur Spine J. 2013;22(7): 1608-1616.
[21] 申勇,刘法敬,张英泽,等.单、双侧经皮椎体后凸成形术治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的疗效[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2011,21(3):202-206.
[22] 杨益民,任志伟,张智,等.经皮椎体后凸成形术治疗椎体压缩性骨折围手术期并发症分析[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2010,20(3):235-238.
[23] Bednar T,Heyde CE,Bednar G,et al. Kyphoplasty for vertebral augmentation in the elderly with osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: Scenarios and review of recent studies. Clin Ther. 2013;35(11):1721-1727.
[24] Dragan SF, Urbanski W, Zywirski B, et al.Kyphosis correction after vertebroplasty in osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Acta Bioeng Biomech. 2012;14(4):63-69.
[25] 王开化.PKP和PVP治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折效果比较[J].山东医药,2011,51(35):64-65.
[26] Kano S,Tanikawa H,Mogami Y, et al. Comparison between continuous and discontinuous multiple vertebral compression fractures. Eur Spine J. 2012;21(9):1867-1872.
[27] Erdem E, Akdol S, Amole A, et al. Radiofrequency-targeted vertebral augmentation for the treatment of vertebral compression fractures as a result of multiple myeloma.Spine. 2013;38(15):1275-1281.
[28] Nieuwenhuijse MJ,VanRijswijk CSP,VanErkel AR, et al. The intravertebral cleft in painful long-standing osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures treated with percutaneous vertebroplasty: Diagnostic assessment and clinical significance. Spine. 2012;37(11):974-981.
[29] Chu W,Tsuei YC, Liao PH, et al. Decompressed percutaneous vertebroplasty: A secured bone cement delivery procedure for vertebral augmentation in osteoporotic compression fractures. Injury. 2013;44(6):813-818.
[30] Gilula L, Persenaire M. Subsequent fractures post-vertebral augmentation: Analysis of a prospective randomized trial in osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. AJNR. 2013; 34(1):221-227.
[31] Itshayek E,Miller P,Barzilay Y, et al. Vertebral augmentation in the treatment of vertebral compression fractures: Review and new insights from recent studies. J Clin Neur. 2012;19(6): 786-791.
[32] Nieuwenhuijse MJ, Putter H, van Erkel AR, et al. New Vertebral Fractures after Percutaneous Vertebroplasty for Painful Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures: A Clustered Analysis and the Relevance of Intradiskal Cement Leakage. Radiology. 2013;266(3):862-870.
[33] Ruosi C, Liccardo S, Rossi D, et al. Importance of spinal deformity index in risk evaluation of VCF (vertebral compression fractures) in obese subjects: prospective study. Eur Spine J. 2013;22(Suppl6):S945-S949.
[34] 张世民,刘星彰,张兆杰,等.双侧与单侧PKP治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折[J].颈腰痛杂志,2011,32(5):331-334.
[35] Tu PH,Liu ZH.,Lee ST, et al. Treatment of repeated and multiple new-onset osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures with teriparatide. J Clin Neur. 2012;19(4):532-535.
[36] Walter J, Haciyakupoglu E, Waschke A, et al. Cement leakage as a possible complication of balloon kyphoplasty-is there a difference between osteoporotic compression fractures (AO type A1) and incomplete burst fractures (AO type A3.1)? Acta Neurochirurgica. 2012;154(2):313-319.
[37] Ondul S, Durmu M. Minimally invasive stabilization of vertebral compression fractures using balloon kyphoplasty.J Neur Sci. 2012;56(4):357-361.
[38] Yokoyama K, Kawanishi M,Yamada M, et al.Comparative study of percutaneous vertebral body perforation and vertebroplasty for the treatment of painful vertebral compression fractures. AJNR. Am J Neuroradiol. 2012;33(4):685-689.
[39] Knopp-Sihota JA, Newburn-Cook CV, Homik J, et al. Calcitonin for treating acute and chronic pain of recent and remote osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Osteop Int. 2012;23(1):17-38.
[40] Nieuwenhuijse MJ, Bollen L, VanErkel AR, et al. Optimal intravertebral cement volume in percutaneous vertebroplasty for painful osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Spine. 2012;37(20):1747-1755. |
| [1] | Chen Ziyang, Pu Rui, Deng Shuang, Yuan Lingyan. Regulatory effect of exosomes on exercise-mediated insulin resistance diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4089-4094. |
| [2] | Chen Yang, Huang Denggao, Gao Yuanhui, Wang Shunlan, Cao Hui, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Luo Siqin, Xiao Jingchuan, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes the proliferation and adhesion of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3949-3955. |
| [3] | Yang Junhui, Luo Jinli, Yuan Xiaoping. Effects of human growth hormone on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3956-3961. |
| [4] | Sun Jianwei, Yang Xinming, Zhang Ying. Effect of montelukast combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on spinal cord injury in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3962-3969. |
| [5] | Gao Shan, Huang Dongjing, Hong Haiman, Jia Jingqiao, Meng Fei. Comparison on the curative effect of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells and induced islet-like cells in gestational diabetes mellitus rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3981-3987. |
| [6] | Hao Xiaona, Zhang Yingjie, Li Yuyun, Xu Tao. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing prolyl oligopeptidase on the repair of liver fibrosis in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3988-3993. |
| [7] | Liu Jianyou, Jia Zhongwei, Niu Jiawei, Cao Xinjie, Zhang Dong, Wei Jie. A new method for measuring the anteversion angle of the femoral neck by constructing the three-dimensional digital model of the femur [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3779-3783. |
| [8] | Meng Lingjie, Qian Hui, Sheng Xiaolei, Lu Jianfeng, Huang Jianping, Qi Liangang, Liu Zongbao. Application of three-dimensional printing technology combined with bone cement in minimally invasive treatment of the collapsed Sanders III type of calcaneal fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3784-3789. |
| [9] | Qian Xuankun, Huang Hefei, Wu Chengcong, Liu Keting, Ou Hua, Zhang Jinpeng, Ren Jing, Wan Jianshan. Computer-assisted navigation combined with minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar spondylolisthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3790-3795. |
| [10] | Hu Jing, Xiang Yang, Ye Chuan, Han Ziji. Three-dimensional printing assisted screw placement and freehand pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracolumbar fractures: 1-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3804-3809. |
| [11] | Shu Qihang, Liao Yijia, Xue Jingbo, Yan Yiguo, Wang Cheng. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of a new three-dimensional printed porous fusion cage for cervical vertebra [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3810-3815. |
| [12] | Wang Yihan, Li Yang, Zhang Ling, Zhang Rui, Xu Ruida, Han Xiaofeng, Cheng Guangqi, Wang Weil. Application of three-dimensional visualization technology for digital orthopedics in the reduction and fixation of intertrochanteric fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3816-3820. |
| [13] | Sun Maji, Wang Qiuan, Zhang Xingchen, Guo Chong, Yuan Feng, Guo Kaijin. Development and biomechanical analysis of a new anterior cervical pedicle screw fixation system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3821-3825. |
| [14] | Lin Wang, Wang Yingying, Guo Weizhong, Yuan Cuihua, Xu Shenggui, Zhang Shenshen, Lin Chengshou. Adopting expanded lateral approach to enhance the mechanical stability and knee function for treating posterolateral column fracture of tibial plateau [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3826-3827. |
| [15] | Zhu Yun, Chen Yu, Qiu Hao, Liu Dun, Jin Guorong, Chen Shimou, Weng Zheng. Finite element analysis for treatment of osteoporotic femoral fracture with far cortical locking screw [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3832-3837. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||