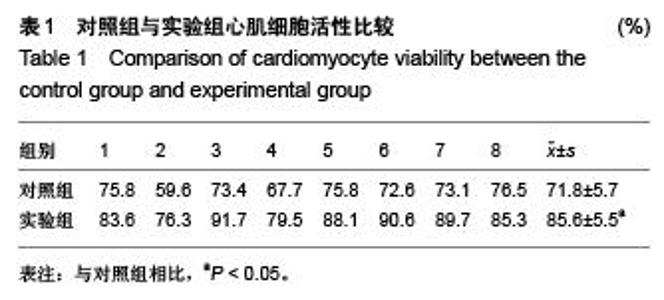
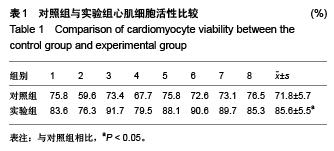
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (51): 8300-8304.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.51.018
Previous Articles Next Articles
Modified cell perfusion appliance for improving the separation efficacy of cardiomyocytes
Zhang Lin1, Zong Jing2, Zhang Qing-tao3
- 1Clinical School of Xuzhou Medical College, Xuzhou 221002, Jiangsu Province, China; 2the Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical College, Xuzhou 221002, Jiangsu Province, China; 3the Third Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical College, Xuzhou 221003, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2015-11-05Online:2015-12-10Published:2015-12-10 -
Contact:Zhang Qing-tao, Master, Associate chief physician, the Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical College, Xuzhou 221002, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Zhang Lin, Master, Associate professor, Clinical School of Xuzhou Medical College, Xuzhou 221002, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81400178; the Scientific Plan Project of Xuzhou City, No. XM13B062
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Lin, Zong Jing, Zhang Qing-tao. Modified cell perfusion appliance for improving the separation efficacy of cardiomyocytes[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(51): 8300-8304.
share this article
| [1] Mitcheson JS,Hancox JC,Levi AJ.Cultured adult cardiacmyocytes:future applications,culture methods, morphological and electrophysiological properties.Cardiovasc Res. 1998;39(2):280-300.
[2] Schluter KD,Schreiber D.Adult ventricular cardiomyocytes: isolation and culture.Methods Mol Biol.2005;290:305-314.
[3] Sun GB, Sun H, Meng XB, et al.Aconitine-induced Ca2+ overload causes arrhythmia and triggers apoptosis through p38 MAPK signaling pathway in rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2014;279(1):8-22.
[4] 王亭忠,席雨涛,吴格如,等.大鼠成体心肌细胞的分离和培养[J].医学争鸣,2005,26(17):1544-1546.
[5] Valarmathi MT,Goodwin RL, Fuseler JW,et al.A3-D cardiac muscle construct for exploring adult marrow stem cell based myocardial regeneration. Biomaterials. 2010;31(12): 3185-3200.
[6] Borchert GH, Yang C, Kolár F. Mitochondrial BKCa channels contribute to protection of cardiomyocytes isolated from chronically hypoxic rats.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011;300(2):H507-513.
[7] Kono T. Roles of collagenases and other proteolytic enzymes in the dispersal of animal tissues. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969; 178(2): 397-400.
[8] Powell T,Twist VW.A rapid technique for the isolation and purification of adult cardiac muscle cells having respiratory control and a tolerance to calcium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976;72(1):327-333.
[9] Al-Rubaiee M, Gangula PR, Millis RM, et al. Inotropic and lusitropic effects of calcitonin gene-related peptide in the heart. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2013;304(11):H1525-1537.
[10] Brennan S, Jackson R, Patel M, et al. Early opening of sarcolemmal ATP-sensitive potassium channels is not a key step in PKC-mediated cardioprotection. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2015;79:42-53.
[11] 李超彦,肖剑锋,沈建新,等.成年SD大鼠心肌细胞分离及其胞内钙离子动态变化测定[J].汕头大学医学院学报,2007,20(3): 138-140.
[12] 高分飞,黄展勤,周燕琼,等.心肌细胞分离方法的改进及其钾电流的观察[J].广西医科大学学报,2008,25(3):338-340.
[13] 熊寿贵,余更生.成年大鼠心肌细胞的急性分离方法探讨[J].重庆医科大学学报,2008,33(7):864-867.
[14] Wolska BM, Solaro RJ. Method for isolation of contraction and micro fluorimetry. Am J Physiol. 1996;271:1250.
[15] Zhang MX, Zhang YM, Esther J, et al. Effects of yiqi huoxue recipe and Coxsackie virus B type 3 on the expression of ribosomal protein S20 in rat cardiac myocytes. Chin J Integr Med. 2011;17(5):376-380.
[16] Bkaily G,Sperelakis N,Doane J.A new method for preparation of isolated single adult myocytes. Am J Physiol. 1984;247 (6 Pt 2): H1018-H1026.
[17] Tytgat J. How to isolate cardiac myocytes. Cardiovasc Res. 1994;28(2):280-283.
[18] 廖华,糜涛,涂志业,等.成年大鼠心肌细胞分离方法的改良[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(33):6536-6539.
[19] Loughrey CM, Seidler T, Miller SL, et al. Over-expression of FK506-binding protein FKBP12.6 alters excitation–contraction coupling in adult rabbit cardiomyocytes. Physiology. 2004;556(3):919-934.
[20] Gorelik J, Yang LQ, Zhang Y, et al. A novel Z groove index characterizing myocardial surface structure. Cardiovasc Res. 2006;72 (3) : 422-429.
[21] Guo Z,Iku S,Zheng X,et al.Three-Dimensional Geometry of Honeycomb Collagen Promotes Higher Beating Rate of Myocardial Cells in Culture. Artif Organs. 2012;36(9):816-819.
[22] 黄泽炳,肖剑锋,沈建新.胞外镁离子对SD成年大鼠心肌细胞胞内钙信号的影响[J].激光生物学报,2010,19(3): 307-313.
[23] 李德,唐兵,杨大春,等.Ⅱ型胶原酶加压灌流提高成年大鼠心肌细胞分离效率[J].中国实验动物学报,2011,19(2): 150-152.
[24] 韦丽兰,莫书荣.成年大鼠心肌细胞的急性分离方法[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(11): 1969-1972.
[25] Zhou YY,Wang SQ, Zhu WZ,et al.Culture and adenoviral infection of adult mouse cardiac myocytes:methods for cellulargenetic physiology.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2000;279:429-436.
[26] Poper HM,Gerrit I.Isolated adult cardiomyocytes. Raton:CRC Press Inc N.W.Boca,1989:44-80.
[27] 宋智钢,刘维永.成熟心肌细胞培养技术及其应用进展[J].临床心血管病杂志,2001,17(8):383-384.
[28] Takemura G, Maruyama R, Goto K, et al. Fate of isolated adult cardiomyocytes undergoing starvation-induced autophagic degeneration.Autophagy. 2009;5(1):90-92.
[29] Krijnen PA, Sipkens JA, Molling JW, et al. Inhibition of Rho-ROCK signaling induces apoptotic and non-apoptotic PS exposure incardiomyocytes via inhibition of flippase.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2010;49(5):781-790.
[30] 李淑娟,娄建石.成年大鼠心肌细胞分离方法[J].河北北方学院学报(医学版),2007;24(1):6-9.
[31] Guinamard R, Hof T, Sallé L. Current recordings at the single channel level in adult mammalian isolated cardiomyocytes.Methods Mol Biol. 2014;1183:291-307.
[32] Mezzavilla M, Iorio A. Insight into genetic determinants of resting heart rate. Gene. 2014;545(1):170-174 .
[33] Maxeiner H, Mufti S, Krehbiehl N, et al. Interleukin-6 contributes to the paracrine effects of cardiospheres cultured from human, murine andrat hearts.J Cell Physiol. 2014; 229(11):1681-1689.
[34] Xu X, Colecraft HM.Primary culture of adult rat heart myocytes. Vis Exp. 2009;(28): pii: 1308.
[35] Egorova MV,Afanaspev SA,Popov SV.A simple method for isolation of cardiomyocytes from adult rat heart. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2005;140(3):370-373.
[36] Galvis-Pareja D, Zapata-Torres G, Hidalgo J, et al. A novel dihydropyridine with 3-aryl meta-hydroxyl substitution blocks L-type calcium channels in ratcardiomyocytes.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2014;279(1):53-62.
[37] Egorova MV,Afanas'ev SA,Popov SV.A simple method for isolation of cardiomyocytes from adult rat heart. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2005;140(3): 370-373. |
| [1] | Chen Ziyang, Pu Rui, Deng Shuang, Yuan Lingyan. Regulatory effect of exosomes on exercise-mediated insulin resistance diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4089-4094. |
| [2] | Chen Yang, Huang Denggao, Gao Yuanhui, Wang Shunlan, Cao Hui, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Luo Siqin, Xiao Jingchuan, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes the proliferation and adhesion of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3949-3955. |
| [3] | Yang Junhui, Luo Jinli, Yuan Xiaoping. Effects of human growth hormone on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3956-3961. |
| [4] | Sun Jianwei, Yang Xinming, Zhang Ying. Effect of montelukast combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on spinal cord injury in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3962-3969. |
| [5] | Gao Shan, Huang Dongjing, Hong Haiman, Jia Jingqiao, Meng Fei. Comparison on the curative effect of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells and induced islet-like cells in gestational diabetes mellitus rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3981-3987. |
| [6] | Hao Xiaona, Zhang Yingjie, Li Yuyun, Xu Tao. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing prolyl oligopeptidase on the repair of liver fibrosis in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3988-3993. |
| [7] | Liu Jianyou, Jia Zhongwei, Niu Jiawei, Cao Xinjie, Zhang Dong, Wei Jie. A new method for measuring the anteversion angle of the femoral neck by constructing the three-dimensional digital model of the femur [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3779-3783. |
| [8] | Meng Lingjie, Qian Hui, Sheng Xiaolei, Lu Jianfeng, Huang Jianping, Qi Liangang, Liu Zongbao. Application of three-dimensional printing technology combined with bone cement in minimally invasive treatment of the collapsed Sanders III type of calcaneal fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3784-3789. |
| [9] | Qian Xuankun, Huang Hefei, Wu Chengcong, Liu Keting, Ou Hua, Zhang Jinpeng, Ren Jing, Wan Jianshan. Computer-assisted navigation combined with minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar spondylolisthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3790-3795. |
| [10] | Hu Jing, Xiang Yang, Ye Chuan, Han Ziji. Three-dimensional printing assisted screw placement and freehand pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracolumbar fractures: 1-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3804-3809. |
| [11] | Shu Qihang, Liao Yijia, Xue Jingbo, Yan Yiguo, Wang Cheng. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of a new three-dimensional printed porous fusion cage for cervical vertebra [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3810-3815. |
| [12] | Wang Yihan, Li Yang, Zhang Ling, Zhang Rui, Xu Ruida, Han Xiaofeng, Cheng Guangqi, Wang Weil. Application of three-dimensional visualization technology for digital orthopedics in the reduction and fixation of intertrochanteric fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3816-3820. |
| [13] | Sun Maji, Wang Qiuan, Zhang Xingchen, Guo Chong, Yuan Feng, Guo Kaijin. Development and biomechanical analysis of a new anterior cervical pedicle screw fixation system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3821-3825. |
| [14] | Lin Wang, Wang Yingying, Guo Weizhong, Yuan Cuihua, Xu Shenggui, Zhang Shenshen, Lin Chengshou. Adopting expanded lateral approach to enhance the mechanical stability and knee function for treating posterolateral column fracture of tibial plateau [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3826-3827. |
| [15] | Zhu Yun, Chen Yu, Qiu Hao, Liu Dun, Jin Guorong, Chen Shimou, Weng Zheng. Finite element analysis for treatment of osteoporotic femoral fracture with far cortical locking screw [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3832-3837. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||