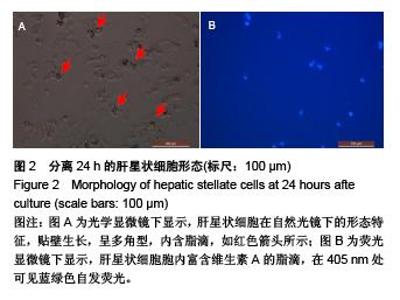
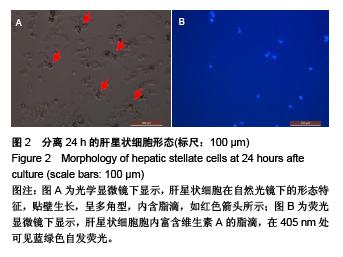
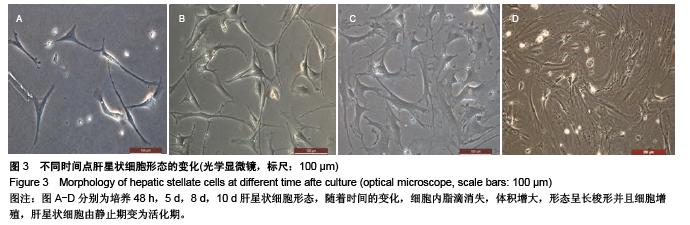
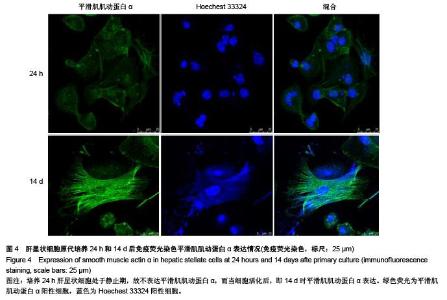
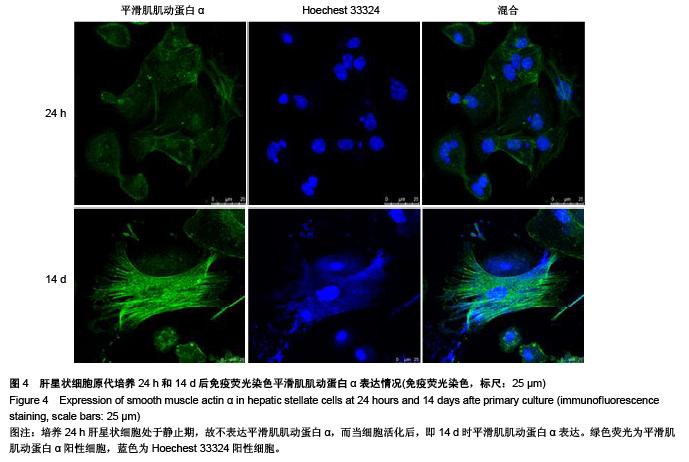
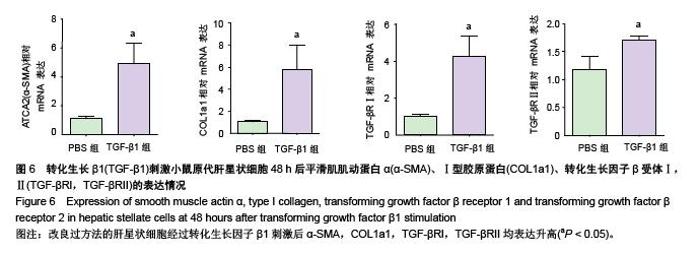
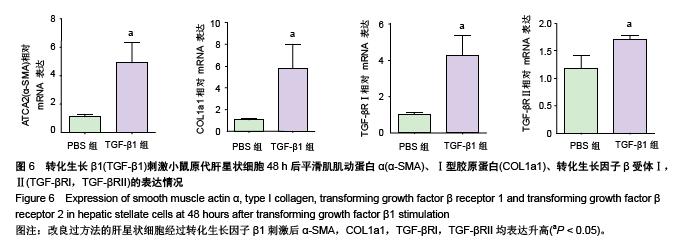
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (51): 8234-8240.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.51.007
Previous Articles Next Articles
Transforming growth factor β1 stimulation improves activation of mouse primary hepatic stellate cells obtained using the improved culture method
Bi Xiao-juan1, 2, Zhang Chuan-shan1, Li Liang1, Lv Guo-dong1, Lin Ren-yong1, 2
- 1Clinical Medicine Research Institute, State Key Laboratory Incubation Base of Xinjiang Major Diseases Research, Xinjiang Key Laboratory of Echinococcosis, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 2Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Preclinical Medicine College, Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830011, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2015-11-02Online:2015-12-10Published:2015-12-10 -
Contact:Lin Ren-yong, M.D., Researcher, Clinical Medicine Research Institute, State Key Laboratory Incubation Base of Xinjiang Major Diseases Research, Xinjiang Key Laboratory of Echinococcosis, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Preclinical Medicine College, Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830011, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Bi Xiao-juan, Assistant researcher, Clinical Medicine Research Institute, State Key Laboratory Incubation Base of Xinjiang Major Diseases Research, Xinjiang Key Laboratory of Echinococcosis, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Preclinical Medicine College, Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830011, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81371838; the Natural Science Foundation of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, No. 2015211C084
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Bi Xiao-juan, Zhang Chuan-shan, Li Liang, Lv Guo-dong, Lin Ren-yong . Transforming growth factor β1 stimulation improves activation of mouse primary hepatic stellate cells obtained using the improved culture method[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(51): 8234-8240.
share this article
| [1] Mehal WZ, Iredale J, Friedman SL. Scraping fibrosis: expressway to the core of fibrosis. Nat Med. 2011;17(5): 552-553.[2] Hellerbrand C. Hepatic stellate cells-the pericytes in the liver. Pflugers Arch. 2013;465(6):775-778.[3] Blouin A, Bolender RP, Weibel ER. Distribution of organelles and membranes between hepatocytes and nonhepatocytes in the rat liver parenchyma: a stereological study. J Cell Biol. 1977;72(2):441-455.[4] Puche JE, Saiman Y, Friedman SL, Hepatic stellate cells and liver fibrosis. Compr Physiol. 2013;3(4):1473-1492.[5] Pellicoro A, Ramachandran P, Iredale JP, et al. Liver fibrosis and repair: immune regulation of wound healing in a solid organ. Nat Rev Immunol. 2014;14(3):181-194.[6] Knook D, Seffelaar A, De Leeuw A. Fat-storing cells of the rat liver: their isolation and purification. Exp Cell Res. 1982; 139(2): 468-471.[7] Galambos JT, Hollingsworth MA, Falek A, et al. The rate of synthesis of glycosaminoglycans and collagen by fibroblasts cultured from adult human liver biopsies. J Clin Invest. 1977; 60(1):107-114.[8] Radaeva S, Sun R, Jaruga B, et al., Natural killer cells ameliorate liver fibrosis by killing activated stellate cells in NKG2D-dependent and tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-dependent manners. Gastroenterology. 2006;130(2):435-452.[9] He X, Bao J. Chen J, et al. Adenovirus-mediated over-expression of Septin4 ameliorates hepatic fibrosis in mouse livers infected with Schistosoma japonicum. Parasitol Int. 2015.[10] Friedman SL, Roll FJ. Isolation and culture of hepatic lipocytes, Kupffer cells, and sinusoidal endothelial cells by density gradient centrifugation with Stractan. Anal Biochem. 1987;161(1):207-218.[11] Mederacke I, Dapito D, Affo H, et al. High-yield and high-purity isolation of hepatic stellate cells from normal and fibrotic mouse livers. Nat Protoc. 2015;10(2):305-315.[12] Bartneck M, Warzecha KT, Tag CG, et al. Isolation and time lapse microscopy of highly pure hepatic stellate cells. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2015;2015:417023.[13] Chang W, Yang M, Song L, et al. Isolation and culture of hepatic stellate cells from mouse liver. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2014;46(4):291-298.[14] Lee SM, Schelcher C, Demmel M, et al. Isolation of human hepatocytes by a two-step collagenase perfusion procedure. J Vis Exp. 2013.[15] Hendriks HF, Verhoofstad WA, Brouwer A, et al. Perisinusoidal fat-storing cells are the main vitamin A storage sites in rat liver. Exp Cell Res. 1985;160(1):138-149.[16] Troeger JS, Mederacke I, Gwak GY, et al. Deactivation of hepatic stellate cells during liver fibrosis resolution in mice. Gastroenterology. 2012;143(4):1073-1083.[17] Roderburg C, Luedde M, Vargas Cardenas D, et al. miR-133a mediates TGF-beta-dependent derepression of collagen synthesis in hepatic stellate cells during liver fibrosis. J Hepatol. 2013;58(4):736-742.[18] D'Ambrosio DN, Walewski JL, Clugston RD, et al. Distinct populations of hepatic stellate cells in the mouse liver have different capacities for retinoid and lipid storage. PLoS One. 2011;6(9):e24993.[19] Lee SM, Schelcher C, Demmel M, et al. Isolation of human hepatocytes by a two-step collagenase perfusion procedure. J Vis Exp, 2013;(79):50615.[20] Yokoi Y, Namihisa T, Kuroda H, et al. Immunocytochemical detection of desmin in fat-storing cells (Ito cells). Hepatology, 1984;4(4):709-714.[21] Ballardini G, Groff P, Badiali L, et al. Ito cell heterogeneity: desmin-negative Ito cells in normal rat liver. Hepatology, 1994;19(2):440-446.[22] Skalli O, Schurch W, Seemayer T, et al. Myofibroblasts from diverse pathologic settings are heterogeneous in their content of actin isoforms and intermediate filament proteins. Lab Invest. 1989;60(2):275-285. [23] Li YH, Woo SH, Choi DH, et al. Succinate causes alpha-SMA production through GPR91 activation in hepatic stellate cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;463(4):853-858.[24] Takeji M, Moriyama T, Oseto S, et al. Smooth muscle alpha-actin deficiency in myofibroblasts leads to enhanced renal tissue fibrosis. J Biol Chem. 2006;281(52): 40193- 40200.[25] Hu GX, Wan ZY, Shao JL, et al. Effects of hydroxycamptothecin on TGFβ1, a-SMA and collagen I expression in rat hepatic satellite cells. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2012;20(6):453-457.[26] Miao CG, Yang YY, He X, et al. Wnt signaling in liver fibrosis: progress, challenges and potential directions. Biochimie. 2013; 95(12):2326-2335.[27] Liu X, Hu H, Yin JQ. Therapeutic strategies against TGF-beta signaling pathway in hepatic fibrosis. Liver Int. 2006;26(1): 8-22.[28] Li HY, Ju D, Zhang DW, et al. Activation of TGF-beta1-CD147 positive feedback loop in hepatic stellate cells promotes liver fibrosis. Sci Rep. 2015;5:16552.[29] Ni MM, Xu T, Wang YR, et al. Inhibition of IRF3 expression reduces TGF-beta1-induced proliferation of hepatic stellate cells. J Physiol Biochem. 2015.[30] Chen N, Geng Q, Zheng J, et al. Suppression of the TGF-beta/Smad signaling pathway and inhibition of hepatic stellate cell proliferation play a role in the hepatoprotective effects of curcumin against alcohol-induced hepatic fibrosis. Int J Mol Med. 2014;34(4):1110-1116. |
| [1] | Chen Ziyang, Pu Rui, Deng Shuang, Yuan Lingyan. Regulatory effect of exosomes on exercise-mediated insulin resistance diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4089-4094. |
| [2] | Chen Yang, Huang Denggao, Gao Yuanhui, Wang Shunlan, Cao Hui, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Luo Siqin, Xiao Jingchuan, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes the proliferation and adhesion of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3949-3955. |
| [3] | Yang Junhui, Luo Jinli, Yuan Xiaoping. Effects of human growth hormone on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3956-3961. |
| [4] | Sun Jianwei, Yang Xinming, Zhang Ying. Effect of montelukast combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on spinal cord injury in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3962-3969. |
| [5] | Gao Shan, Huang Dongjing, Hong Haiman, Jia Jingqiao, Meng Fei. Comparison on the curative effect of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells and induced islet-like cells in gestational diabetes mellitus rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3981-3987. |
| [6] | Hao Xiaona, Zhang Yingjie, Li Yuyun, Xu Tao. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing prolyl oligopeptidase on the repair of liver fibrosis in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3988-3993. |
| [7] | Liu Jianyou, Jia Zhongwei, Niu Jiawei, Cao Xinjie, Zhang Dong, Wei Jie. A new method for measuring the anteversion angle of the femoral neck by constructing the three-dimensional digital model of the femur [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3779-3783. |
| [8] | Meng Lingjie, Qian Hui, Sheng Xiaolei, Lu Jianfeng, Huang Jianping, Qi Liangang, Liu Zongbao. Application of three-dimensional printing technology combined with bone cement in minimally invasive treatment of the collapsed Sanders III type of calcaneal fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3784-3789. |
| [9] | Qian Xuankun, Huang Hefei, Wu Chengcong, Liu Keting, Ou Hua, Zhang Jinpeng, Ren Jing, Wan Jianshan. Computer-assisted navigation combined with minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar spondylolisthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3790-3795. |
| [10] | Hu Jing, Xiang Yang, Ye Chuan, Han Ziji. Three-dimensional printing assisted screw placement and freehand pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracolumbar fractures: 1-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3804-3809. |
| [11] | Shu Qihang, Liao Yijia, Xue Jingbo, Yan Yiguo, Wang Cheng. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of a new three-dimensional printed porous fusion cage for cervical vertebra [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3810-3815. |
| [12] | Wang Yihan, Li Yang, Zhang Ling, Zhang Rui, Xu Ruida, Han Xiaofeng, Cheng Guangqi, Wang Weil. Application of three-dimensional visualization technology for digital orthopedics in the reduction and fixation of intertrochanteric fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3816-3820. |
| [13] | Sun Maji, Wang Qiuan, Zhang Xingchen, Guo Chong, Yuan Feng, Guo Kaijin. Development and biomechanical analysis of a new anterior cervical pedicle screw fixation system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3821-3825. |
| [14] | Lin Wang, Wang Yingying, Guo Weizhong, Yuan Cuihua, Xu Shenggui, Zhang Shenshen, Lin Chengshou. Adopting expanded lateral approach to enhance the mechanical stability and knee function for treating posterolateral column fracture of tibial plateau [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3826-3827. |
| [15] | Zhu Yun, Chen Yu, Qiu Hao, Liu Dun, Jin Guorong, Chen Shimou, Weng Zheng. Finite element analysis for treatment of osteoporotic femoral fracture with far cortical locking screw [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3832-3837. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||