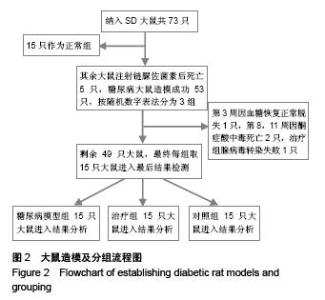
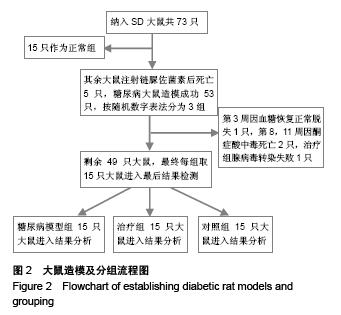
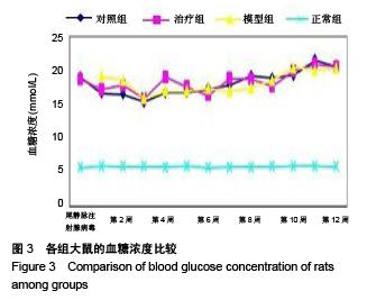
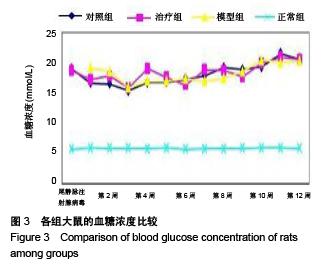
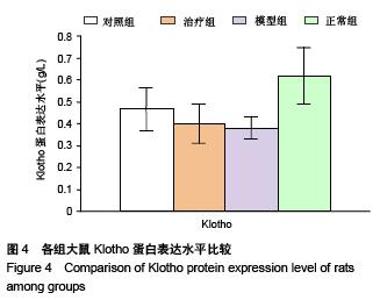
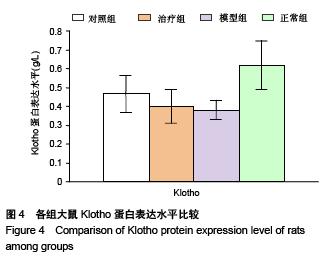
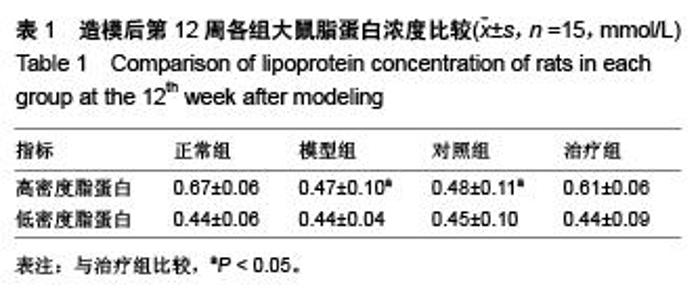
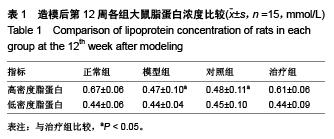
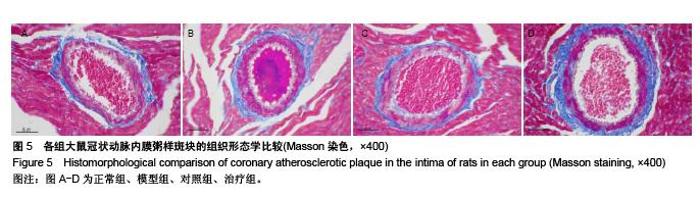
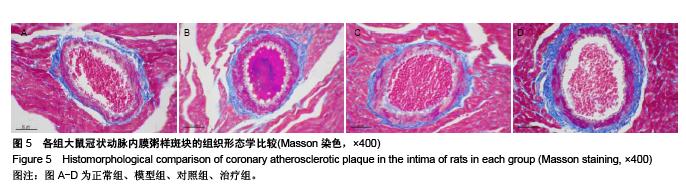
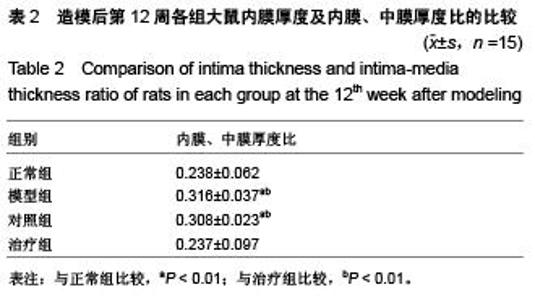
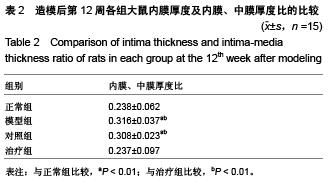
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (49): 7958-7963.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.49.015
Previous Articles Next Articles
Construction of diabetic rat models: protective effect of Klotho gene transfer on coronary artery
Shu Li-liang, Chen Mao-lin, Su Gang, Xu Jing
- First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2015-09-10Online:2015-11-30Published:2015-11-30 -
Contact:Shu Li-liang, M.D., Lecturer, Attending physician, First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China -
About author:Shu Li-liang, M.D., Lecturer, Attending physician, First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Shu Li-liang, Chen Mao-lin, Su Gang, Xu Jing. Construction of diabetic rat models: protective effect of Klotho gene transfer on coronary artery[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(49): 7958-7963.
share this article
| [1] Ginsberg HN,Elam MB,Lovato LC,et al.Effects of combination lipid therapy in type 2 diabetes mellitus.N Engl J Med. 2010; 362(17):1563-1574. [2] Kuro-o M,Matsumura Y,Ailawa H,et al.Mutation of the mouse klotho gene leads to a syndrome resembling ageing. Nature. 1997;390(6655):45-51. [3] Kumsu H, Yamamoto M, Clark JD, et al. Suppression of aging in mice by the hormone Klotho. Science. 2005;309(5742):1829-1833. [4] Aizawa H,Saito Y,Nakamura T,et al.Downregulation of the klotho gene in the kidney under sustained circulatory stress in rats.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1998;249(3):865-871. [5] Arking DE,Becker DM,Yanek LR,et al.KLOTHO allele status and risk of early-onset occult coronary artery disease. Am J Hum Genet. 2003;72(5):1154-1161. [6] Matsumura Y, Aizawa H, Shiraki-Iida T, et al. Identification of the human klotho gene and its two transcripts encoding membrane and secreted klotho protein.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1998;242(3): 626-630. [7] Raekleum N, Rackietan ML, Nadkami MR. Studies on Diabetogenic action of astreptozotocin (NSC-37917). Cancer Chemother Rep. 1993;29:91. [8] 王虎林,司良毅,孙兰英,等.Klotho基因G-395A多态性与动脉硬化的相关性研究[J].中华老年心脑血管病杂志,2008,10(2): 96-98. [9] Takeshita K,Yamamoto K,Ito M,et al. Increased expression of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 wirh fibrin deposition in a murine model of aging,”Klotho” mouse. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2002;28(6):545-554. [10] Biddinger SB,Hernandez-Ono A,Rask-Maden C,et al. Hepatic insulin resistance is sufficient to produce dyslipidemia and susceptibility to atherosclerosis. Cell Metab. 2008;7(2):125-134. [11] Price MJ, Shah PK. New strategies in managing and preventing atherosclerosis: focus on HDL. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2002;3(3):129-137. [12] 房晨鹏,刘怡欣,田鹏,等.Klotho基因多态性与低密度脂蛋白水平的关系[J].现代预防医学, 2011,38(14):2818-2820. [13] Arking DE, Becker DM, Yanek LR, et al. KLOTHO allele status and the risk of early-onset occult coronary artery disease. Am H Hum Genet. 2003;72:1154-1161. [14] Arking DE,Atzmon G,Arking A,et al.Association between a funcitional variant of the KLOTHO gene and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol,blood pressure,stroke,and longevity. Circ Res. 2005;96:412-418. [15] Wang HL, Xu Q, Wu Z, et al. A potential regulatory single nucleotide polymorphism in the promoter of the Klotho gene may be associated with essential hypertension in the Chinese Han population. Clinica Chimica Acta. 2010;411: 386-390. [16] Shu L, Chen M, Wen M, et al. Study of klotho gene transfer for the protective effect of the coronary of diabetic rats. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2014;27(6 Suppl):2095-2099. [17] Navarro-González JF, Donate-Correa J, de Fuentes M, et al. Reduced Klotho is associated with the presence and severity of coronary artery disease. Heart. 2014;100(1):34-40. [18] Ko GJ, Lee YM, Lee EA, et al. The association of Klotho gene polymorphism with the mortality of patients on maintenance dialysis. Clin Nephrol. 2013;80(4):263-269. [19] Tangri N, Alam A, Wooten EC, et al. Lack of association of Klotho gene variants with valvular and vascular calcification in Caucasians: a candidate gene study of the Framingham Offspring Cohort. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2011;26(12): 3998-4002. [20] Jo SH, Kim SG, Choi YJ, et al. KLOTHO gene polymorphism is associated with coronary artery stenosis but not with coronarycalcification in a Korean population. Int Heart J. 2009; 50(1):23-32. [21] Rhee EJ, Oh KW, Lee WY, et al. The differential effects of age on the association of KLOTHO gene polymorphisms with coronary artery disease. Metabolism. 2006;55(10): 1344-1351. |
| [1] | Chen Ziyang, Pu Rui, Deng Shuang, Yuan Lingyan. Regulatory effect of exosomes on exercise-mediated insulin resistance diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4089-4094. |
| [2] | Chen Yang, Huang Denggao, Gao Yuanhui, Wang Shunlan, Cao Hui, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Luo Siqin, Xiao Jingchuan, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes the proliferation and adhesion of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3949-3955. |
| [3] | Yang Junhui, Luo Jinli, Yuan Xiaoping. Effects of human growth hormone on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3956-3961. |
| [4] | Sun Jianwei, Yang Xinming, Zhang Ying. Effect of montelukast combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on spinal cord injury in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3962-3969. |
| [5] | Gao Shan, Huang Dongjing, Hong Haiman, Jia Jingqiao, Meng Fei. Comparison on the curative effect of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells and induced islet-like cells in gestational diabetes mellitus rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3981-3987. |
| [6] | Hao Xiaona, Zhang Yingjie, Li Yuyun, Xu Tao. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing prolyl oligopeptidase on the repair of liver fibrosis in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3988-3993. |
| [7] | Liu Jianyou, Jia Zhongwei, Niu Jiawei, Cao Xinjie, Zhang Dong, Wei Jie. A new method for measuring the anteversion angle of the femoral neck by constructing the three-dimensional digital model of the femur [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3779-3783. |
| [8] | Meng Lingjie, Qian Hui, Sheng Xiaolei, Lu Jianfeng, Huang Jianping, Qi Liangang, Liu Zongbao. Application of three-dimensional printing technology combined with bone cement in minimally invasive treatment of the collapsed Sanders III type of calcaneal fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3784-3789. |
| [9] | Qian Xuankun, Huang Hefei, Wu Chengcong, Liu Keting, Ou Hua, Zhang Jinpeng, Ren Jing, Wan Jianshan. Computer-assisted navigation combined with minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar spondylolisthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3790-3795. |
| [10] | Hu Jing, Xiang Yang, Ye Chuan, Han Ziji. Three-dimensional printing assisted screw placement and freehand pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracolumbar fractures: 1-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3804-3809. |
| [11] | Shu Qihang, Liao Yijia, Xue Jingbo, Yan Yiguo, Wang Cheng. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of a new three-dimensional printed porous fusion cage for cervical vertebra [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3810-3815. |
| [12] | Wang Yihan, Li Yang, Zhang Ling, Zhang Rui, Xu Ruida, Han Xiaofeng, Cheng Guangqi, Wang Weil. Application of three-dimensional visualization technology for digital orthopedics in the reduction and fixation of intertrochanteric fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3816-3820. |
| [13] | Sun Maji, Wang Qiuan, Zhang Xingchen, Guo Chong, Yuan Feng, Guo Kaijin. Development and biomechanical analysis of a new anterior cervical pedicle screw fixation system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3821-3825. |
| [14] | Lin Wang, Wang Yingying, Guo Weizhong, Yuan Cuihua, Xu Shenggui, Zhang Shenshen, Lin Chengshou. Adopting expanded lateral approach to enhance the mechanical stability and knee function for treating posterolateral column fracture of tibial plateau [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3826-3827. |
| [15] | Zhu Yun, Chen Yu, Qiu Hao, Liu Dun, Jin Guorong, Chen Shimou, Weng Zheng. Finite element analysis for treatment of osteoporotic femoral fracture with far cortical locking screw [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3832-3837. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||