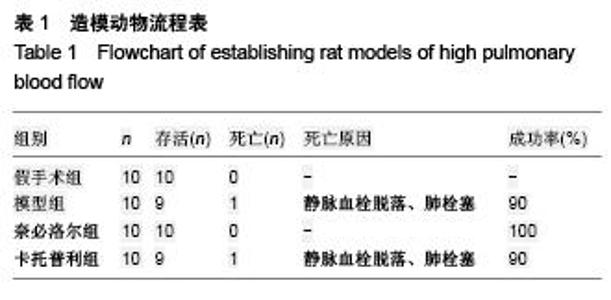
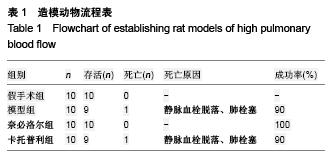
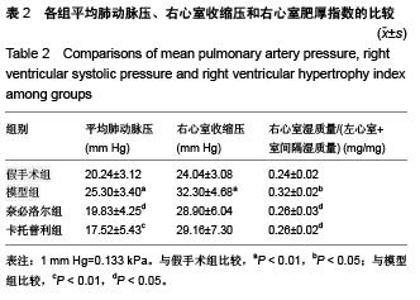
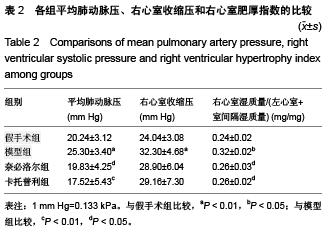
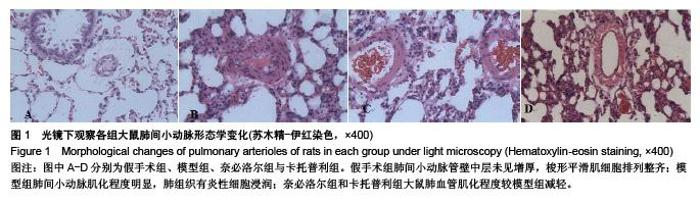
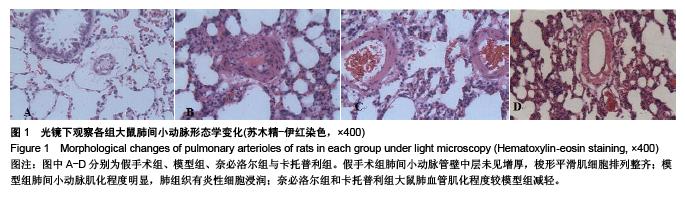
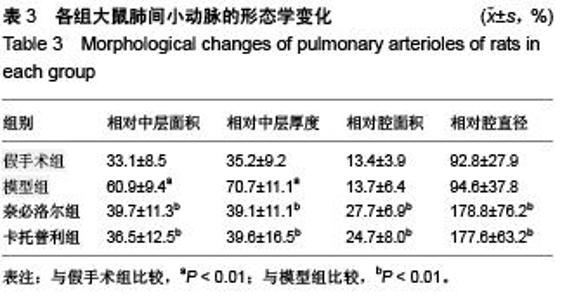
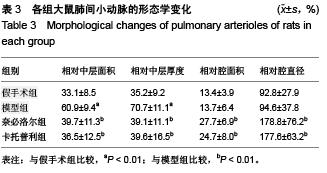
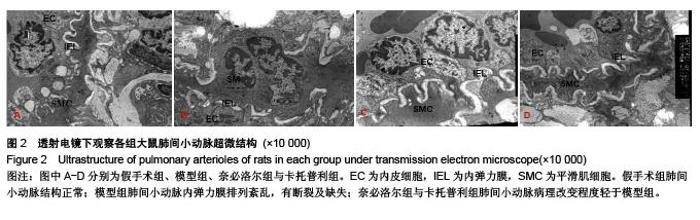
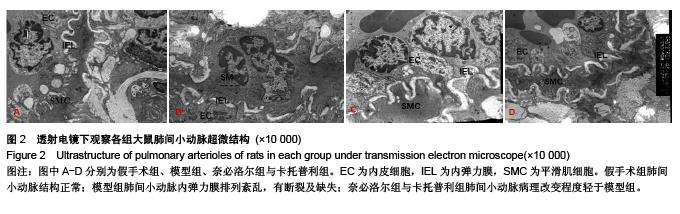
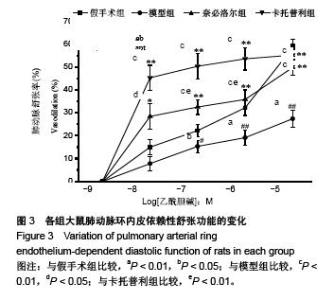
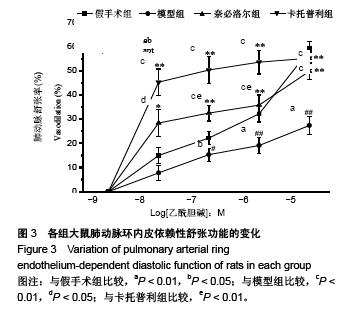
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of nebivolol on pulmonary artery remodeling in rats with high pulmonary blood flow
Chen Peng1, Jiang Ping1, Zhu Can-yang1,Yang Mei1, Ma Hong-jun2, Li Yan-feng1
- 1Department of Pharmacology, Basic Medical College of Hebei Medical University; 2Electron Microscopy Room, Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050017, Hebei Province, China
-
Online:2015-11-30Published:2015-11-30 -
Contact:Li Yan-feng, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Department of Pharmacology, Basic Medical College of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050017, Hebei Province, China -
About author:Chen Peng, Master, Nurse-in-charge, Department of Pharmacology, Basic Medical College of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050017, Hebei Province, China -
Supported by:The Science and Technology Research and Development Plan Project of Hebei Province of China, No. 10276105D-11
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Peng, Jiang Ping, Zhu Can-yang,Yang Mei, Ma Hong-jun, Li Yan-feng . Effect of nebivolol on pulmonary artery remodeling in rats with high pulmonary blood flow[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.49.013.
share this article
| [1] Neutel JM,Giles TD,Punzi H,et al.Long-term safety of nebivolol and valsartan combination therapy in patients with hypertension: an open-label, single-arm, multicenter study.J Am Soc Hypertens. 2014;8(12):915-920.
[2] Kamp O,Metra M,Bugatti S,et al.Nebivolol: haemodynamic effects and clinical significance of combined beta-blockade and nitric oxide release.Drugs. 2010;70(1):41-56.
[3] Ignarro LJ,Byrns RE,Trinh K,et al.Nebivolol: a selective beta(1)-adrenergic receptor antagonist that relaxes vascular smooth muscle by nitric oxide- and cyclic GMP-dependent mechanisms.Nitric Oxide.2002;7(2): 75-82.
[4] D'Agostino B,Gallellia L,Falciania M,et al.Nebivolol and airway responsiveness in the rabbit.Life Sci.2001; 68(18):2159-2168.
[5] Ocampo C,Ingram P,Ilbawi M,et al.Revisiting the surgical creation of volume load by aorto-caval shunt in rats.Mol Cell Biochem.2003;251(1-2):139-143.
[6] Pinar Yildiz.Molecular mechanisms of pulmonary hypertension. Clinica Chimica Acta 2009, 403: 9-16.
[7] KlingerJR.The nitric oxide/cGMP signaling pathway in pulmonary hypertension.Clin Chest Med. 2007;28(1): 143-167,ix.
[8] Mandegar M,Fung YC,Huang W,et al.Cellular and molecular mechanisms of pulmonary vascular remodeling:role in the development of pulmonary hypertension. Microvasc Res. 2004;68(2):75-103.
[9] Perros F,Ranchoux B,Izikki M,et al.Nebivolol for improving endothelial dysfunction, pulmonary vascular remodeling, and right heart function in pulmonary hypertension.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015;65(7):668-680.
[10] Vermeersch P,Buys E,Pokreisz P,et al.Soluble guanylate cyclase-alpha1 deficiency selectively inhibits the pulmonary vasodilator response to nitric oxide and increases the pulmonary vascular remodeling response to chronic hypoxia. Circulation. 2007;116(8):936-943.
[11] Napoli C,Paolisso G,Casamassimi A,et al.Effects of nitric oxide on cell proliferation: novel insights. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;62(2):89-95.
[12] Sato J,Nair K,Hiddinga J,et al. eNOS gene transfer to vascular smooth muscle cells inhibits cell proliferation via upregulation of p27 and p21 and not apoptosis. Cardiovasc Res.2000;47(4):697-706.
[13] Bakris GL,Basile JN,Giles TD,et al.The role of nitric oxide in improving endothelial function and cardiovascular health: focus on nebivolol.Am J Med. 2010;123(7 Suppl 1):S2-8.
[14] Maffei A,Vecchione C,Aretini A,et al. Characterization of nitric oxide release by nebivolol and its metabolites.BAm J Hypertens.2006;19(6):579-586.
[15] Bayar E,Ilhan G,Furat C,et al.The effect of different β-blockers on vascular graft nitric oxide levels: comparison of nebivolol versus metoprolol.Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg.2014;47(2): 204-218.
[16] Price A,Raheja P,Wang Z,et al.Differential effects of nebivolol versus metoprolol on functional sympatholysis in hypertensive humans.Hypertension.2013;61:1263-1269.
[17] Valentini M,Revera M,Bilo G,et al.Effects of beta-blockade on exercise performance at high altitude: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial comparing the efficacy of nebivolol versus carvedilol in healthy subjects.Cardiovasc Ther.2012; 30:240-248.
[18] de Nigris F,Rienzo M,Schiano C,et al. Prominent cardioprotective effects of third generation beta blocker nebivolol against anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity using the model of isolated perfused rat heart.Eur J Cancer.2008; 44(3):334-340.
[19] Wolf SC,Sauter G,Jobst J,et al.Major differences in gene expression in human coronary smooth muscle cells after nebivolol or metoprolol treatment.Int J Cardiol. 2008;125(1): 4-10.
[20] Katragadda S,Arora RR.Role of angiotensin-converting engyme inhibitors in vascular modulation:beyond the hypertensive effects.Am J Ther.2010;17(1):11.
[21] Caglar N,Dincer I.Comparison between nebivolol and ramipril in patients with hypertension and left ventricular hypertrophy: a randomized open blinded end-point (PROBE) trial.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.2011;15:1359-1368.
[22] Frishman WH.b-Adrenergic blockade in cardiovascular disease.Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther.2013;18:310-319.
[23] Fares H,Lavie CJ,Ventura HO. Vasodilating versus first -generation b-blockers for cardiovascular protection.Postgrad Med.2012;124:7-15.
[24] Waeber B,Feihl F.Nebivolol and valsartan: useful treatment for hypertension? Lancet.2014;383(6):1864-1866.
[25] Baker JG.The selectivity of β-adrenoceptor agonists at human β1-,β2- and β3-adrenoceptors. Br J Pharmacol. 2010;160: 1048-1061.
[26] Bundkirchen A,Brixius K,Bölck B,et al.Beta 1-adrenoceptor selectivity of nebivolol and bisoprolol. A comparison of [3H]CGP 12.177 and [125I]iodocyanopindolol binding studies.Eur J Pharmacol.2003;460(1):19-26.
[27] Rubin LJ. The Beta-Adrenergic Receptor in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension:A Novel Therapeutic Target?J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015;65(7):681-683.
[28] Nodari S,Metra M,Dei Cas L.Beta-blocker treatment of patients with diastolic heart failure and arterial hypertension. A prospective, randomized, comparison of the long-term effects of atenolol vs. nebivolol.Eur J Heart Fail.2003;5:621-627.
[29] Conraads VM,Metra M,Kamp O,et al.Effects of the long-term administration of nebivolol on the clinical symptoms, exercise capacity,and left ventricular function of patients with diastolic dysfunction: results of the ELANDD study. Eur J Heart Fail. 2012;14:219-225.
|
| [1] | Chen Ziyang, Pu Rui, Deng Shuang, Yuan Lingyan. Regulatory effect of exosomes on exercise-mediated insulin resistance diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4089-4094. |
| [2] | Chen Yang, Huang Denggao, Gao Yuanhui, Wang Shunlan, Cao Hui, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Luo Siqin, Xiao Jingchuan, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes the proliferation and adhesion of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3949-3955. |
| [3] | Yang Junhui, Luo Jinli, Yuan Xiaoping. Effects of human growth hormone on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3956-3961. |
| [4] | Sun Jianwei, Yang Xinming, Zhang Ying. Effect of montelukast combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on spinal cord injury in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3962-3969. |
| [5] | Gao Shan, Huang Dongjing, Hong Haiman, Jia Jingqiao, Meng Fei. Comparison on the curative effect of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells and induced islet-like cells in gestational diabetes mellitus rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3981-3987. |
| [6] | Hao Xiaona, Zhang Yingjie, Li Yuyun, Xu Tao. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing prolyl oligopeptidase on the repair of liver fibrosis in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3988-3993. |
| [7] | Liu Jianyou, Jia Zhongwei, Niu Jiawei, Cao Xinjie, Zhang Dong, Wei Jie. A new method for measuring the anteversion angle of the femoral neck by constructing the three-dimensional digital model of the femur [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3779-3783. |
| [8] | Meng Lingjie, Qian Hui, Sheng Xiaolei, Lu Jianfeng, Huang Jianping, Qi Liangang, Liu Zongbao. Application of three-dimensional printing technology combined with bone cement in minimally invasive treatment of the collapsed Sanders III type of calcaneal fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3784-3789. |
| [9] | Qian Xuankun, Huang Hefei, Wu Chengcong, Liu Keting, Ou Hua, Zhang Jinpeng, Ren Jing, Wan Jianshan. Computer-assisted navigation combined with minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar spondylolisthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3790-3795. |
| [10] | Hu Jing, Xiang Yang, Ye Chuan, Han Ziji. Three-dimensional printing assisted screw placement and freehand pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracolumbar fractures: 1-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3804-3809. |
| [11] | Shu Qihang, Liao Yijia, Xue Jingbo, Yan Yiguo, Wang Cheng. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of a new three-dimensional printed porous fusion cage for cervical vertebra [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3810-3815. |
| [12] | Wang Yihan, Li Yang, Zhang Ling, Zhang Rui, Xu Ruida, Han Xiaofeng, Cheng Guangqi, Wang Weil. Application of three-dimensional visualization technology for digital orthopedics in the reduction and fixation of intertrochanteric fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3816-3820. |
| [13] | Sun Maji, Wang Qiuan, Zhang Xingchen, Guo Chong, Yuan Feng, Guo Kaijin. Development and biomechanical analysis of a new anterior cervical pedicle screw fixation system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3821-3825. |
| [14] | Lin Wang, Wang Yingying, Guo Weizhong, Yuan Cuihua, Xu Shenggui, Zhang Shenshen, Lin Chengshou. Adopting expanded lateral approach to enhance the mechanical stability and knee function for treating posterolateral column fracture of tibial plateau [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3826-3827. |
| [15] | Zhu Yun, Chen Yu, Qiu Hao, Liu Dun, Jin Guorong, Chen Shimou, Weng Zheng. Finite element analysis for treatment of osteoporotic femoral fracture with far cortical locking screw [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3832-3837. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||