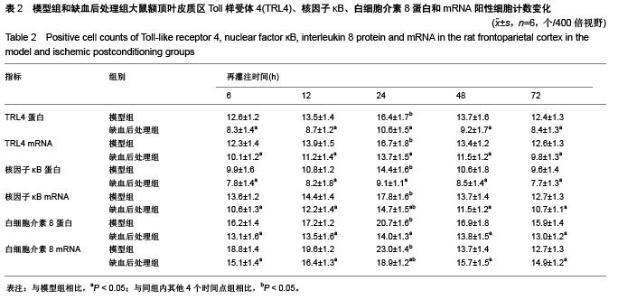
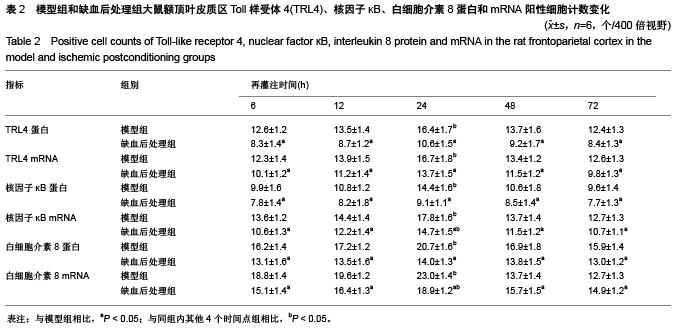
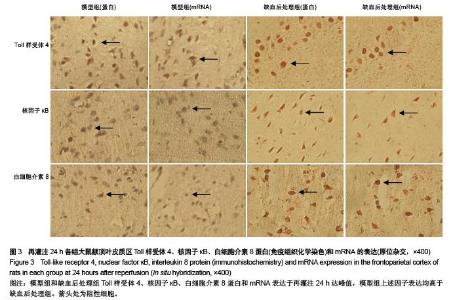
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (49): 7938-7944.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.49.012
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of ischemic postconditioning on related pathways and interleukin 8 expression in rat models of focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion
Li Zhi-xing1, Lv Jing-lei2, Chen Ping1, Zhao Ren-liang2
- 1Qingdao University Medical College, Qingdao 266000, Shandong Province, China; 2Department of Neurology, the Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University, Qingdao 266003, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2015-09-07Online:2015-11-30Published:2015-11-30 -
Contact:Zhao Ren-liang, M.D., Chief physician, Professor, Master's supervisor, Department of Neurology, the Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University, Qingdao 266003, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Li Zhi-xing, Studying for master’s degree, Qingdao University Medical College, Qingdao 266000, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:a grant from Qingdao Municipal Science and Technology Bureau, China, No. 14-2-3-14-nsh
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Zhi-xing, Lv Jing-lei, Chen Ping, Zhao Ren-liang. Effects of ischemic postconditioning on related pathways and interleukin 8 expression in rat models of focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(49): 7938-7944.
share this article
| [1] Zhao ZQ, Corvera JS, Halkos ME, et al. Inhibition of myocardial injury by ischemic postconditioning during reperfusion: comparison with ischemic preconditioning. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2003;285(2):H579-H588.
[2] Zhao H, Sapolsky RM, Steinberg GK. Interrupting reperfusion as a stroke therapy: ischemic postconditioning reduces infarct size after focal ischemia in rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2006;26(9):1114-1121.
[3] 王岭,孙丽,高焕民,等.胡黄连苷II对大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤后炎症反应影响[J].青岛大学医学院学报,2011,47(1):62-64.
[4] Hamanaka J, Hara H. Involvement of Toll-like receptors in ischemia-induced neuronal damage. Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem. 2011;11(2):107-113.
[5] Li XQ, Wang J, Fang B, et al. Intrathecal antagonism of microglial TLR4 reduces inflammatory damage to blood-spinal cord barrier following ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Mol Brain. 2014;7:28.
[6] Pradillo JM, Fernández-López D, García-Yébenes I, et al. Toll-like receptor 4 is Involved in neuroprotection afforded by ischemic preconditioning. Neurochem. 2009;109(1):287-294.
[7] Liang J, Luan Y, Lu B, et al. Protection of ischemic postconditioning against neuronal apoptosis induced by transient focal ischemia is associated with attenuation of NF-κB/p65 activation. PLoS One. 2014;9(5):e96734.
[8] Wang Q, Tang XN, Yenari MA. The inflammatory response in stroke. J Neuroimmunol. 2007;184(1-2):53-68.
[9] Feng R, Li S, Li F. Toll-like receptor 4 is involved in ischemic tolerance of postconditioning in hippocampus of tree shrews to thrombotic cerebral ischemia. Brain Res. 2011;1384: 118-127.
[10] Gao Y, Fang X, Sun H. Toll-like receptor 4-mediated myeloid differentiation factor 88-dependent signaling pathway is activated by cerebral ischemia-reperfusion in hippocampal CA1 region in mice. Biol Pharm Bull. 2009;32(10):1665-1671.
[11] Bhattacharyya S, Gill R, Chen ML, et al. Toll-like receptor 4 mediates induction of the Bcl10-NFkappaB-interleukin-8 inflammatory pathway by carrageenan in human intestinal epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 2008;283(16):10550-10558.
[12] Kostulas N, Kivisäkk P, Huang Y, et al. Ischemic stroke is associated with a systemic increase of blood mononuclear cells expressing interleukin-8 mRNA. Stroke. 1998;29(2): 462-466.
[13] 中华人民共和国科学技术部.关于善待实验动物的指导性意见.2006.
[14] 吕敬雷,王国峰,王鹏,等.缺血后处理下调脑缺血再灌注大鼠白细胞介素-1β和肿瘤坏死因子-α表达[J].国际脑血管病杂志, 2012, 20(2):135-141.
[15] Logga EZ, Weinstein PR, Carson S, et a1. Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 1989;20(1):84-91.
[16] Menzies SA, Hoff JT, Betz A. Middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats: a neurological and pathological evaluation of a reproducible model. Neurosurgery. 1992;31(1):100-106.
[17] 谢惠芳,徐如祥,陈中灿.线栓法制作大鼠局灶性脑缺血再灌注损伤模型的改进[J].中华神经医学杂志,2007,6(4):340-342.
[18] Wang JY, Shen J, Gao Q, et al. Ischemic postconditioning protects against global cerebral ischemia/reperfusion-induced injury in rats. Stroke. 2008;39(3):983-990.
[19] Ren HC, Gao XW, Niu G, et al. Delayed Postconditioning Protects against Focal Ischemic Brain Injury in Rats. PLoS One. 2008;3(12):e3851.
[20] Wang JK, Wu HF, Zhou H, et al. Postconditioning with sevoflurane protects against focal cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury involving mitochondrial ATP-dependent potassium channel and mitochondrial permeability transition pore. Neurol Res. 2015;37(1):77-83.
[21] Yang F, Zhang X, Sun Y, et al. Ischemic postconditioning decreases cerebral edema and brain blood barrier disruption caused by relief of carotid stenosis in a rat model of cerebral hypoperfusion. PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e57869.
[22] 孙静,董海龙,栾琪,等.缺血后处理减轻大鼠局灶性脑缺血再灌注损伤最佳方案[J].第四军医大学学报,2007,28(24):2214-2216.
[23] He Y, ZHou AL, Jiang W.Toll-like receptor 4-mediated signaling participates in apoptosis of hippocampal neurons. Neural Regen Res. 2013;8 (29): 2744-2753
[24] Li XQ, Wang J, Fang B, et al. Intrathecal antagonism of microglial TLR4 reduces inflammatory damage to blood-spinal cord barrier following ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Mol Brain. 2014;7:28.
[25] Hu YE,Mao JH,Zhang Y,et al.Role of Toll-like receptor 4 in inflammatory reactions of hippocampal neurons.Neural Regen Res. 2013;8 (16): 1465-1472.
[26] Cao CX, Yang QW, Lv FL. Reduced cerebralischemia- reperfusion injury in Toll-like receptor 4 deficient mice. Biochem Biophys Res. 2007;353(2):509-514.
[27] Hyakkoku K, Hamanaka J, Tsuruma K, et al. Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), but not TLR3 or TLR9, knock-out mice have neuroprotective effects against focal cerebral ischemia. Neuroscience. 2010;171(1):258-267.
[28] 冯蕊,李树清.缺血后适应对脑缺血树鼩海马TLR4表达的影响[J].中国病理生理杂志,2011,27(6):1048-1052.
[29] Wasserman JK, Yang H, Schlichter LC. Glial responses,neuron death and lesion resolution after intracerebral hemorrhage in young vs aged rats. Eur J Neurosci. 2008;28(7):1316-1328.
[30] Zwagerman N, Plumlee C, Guthikonda M, et al. Toll-like receptor-4 and cytokine cascade in stroke after exercise. Neurol Res. 2010;32(2):123-126.
[31] Ding Y, Clark JC. Cerebrovascular injury in stroke. Neurol Res. 2006;28(1):3-10.
[32] Frangogiannis NG. Chemokines in ischemia and reperfusion. Thromb Haemost. 2007;97(5):738-747.
[33] Owens T, Babcock AA, Millward JM, et al. Cytokine and chemokine inter-regulation in the inflamed or injured CNS. Brain Res Rev. 2005;48(2):178-184.
[34] Masdumoto T, Yokoi K, Mukaida N, et al. Pivotal role of interleukin-8 in the acute respiratory distress syndrome and cerebral reperfusion injury. J Leukoc Boil. 1997;62(11): 581-587.
[35] Zeng L, Wang Y, Liu J, et al. Pro-inflammatory cytokine network in peripheral inflammation response to cerebral ischemia. Neurosci Lett. 2013;548:4-9.
[36] Huber AR, Kunkel SL, Todd RF, et al. Regulation of transendothelial neutrophil migration by endogenous interleukin-8. Science. 1991;254(5028):99-102. |
| [1] | Chen Ziyang, Pu Rui, Deng Shuang, Yuan Lingyan. Regulatory effect of exosomes on exercise-mediated insulin resistance diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4089-4094. |
| [2] | Chen Yang, Huang Denggao, Gao Yuanhui, Wang Shunlan, Cao Hui, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Luo Siqin, Xiao Jingchuan, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes the proliferation and adhesion of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3949-3955. |
| [3] | Yang Junhui, Luo Jinli, Yuan Xiaoping. Effects of human growth hormone on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3956-3961. |
| [4] | Sun Jianwei, Yang Xinming, Zhang Ying. Effect of montelukast combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on spinal cord injury in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3962-3969. |
| [5] | Gao Shan, Huang Dongjing, Hong Haiman, Jia Jingqiao, Meng Fei. Comparison on the curative effect of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells and induced islet-like cells in gestational diabetes mellitus rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3981-3987. |
| [6] | Hao Xiaona, Zhang Yingjie, Li Yuyun, Xu Tao. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing prolyl oligopeptidase on the repair of liver fibrosis in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3988-3993. |
| [7] | Liu Jianyou, Jia Zhongwei, Niu Jiawei, Cao Xinjie, Zhang Dong, Wei Jie. A new method for measuring the anteversion angle of the femoral neck by constructing the three-dimensional digital model of the femur [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3779-3783. |
| [8] | Meng Lingjie, Qian Hui, Sheng Xiaolei, Lu Jianfeng, Huang Jianping, Qi Liangang, Liu Zongbao. Application of three-dimensional printing technology combined with bone cement in minimally invasive treatment of the collapsed Sanders III type of calcaneal fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3784-3789. |
| [9] | Qian Xuankun, Huang Hefei, Wu Chengcong, Liu Keting, Ou Hua, Zhang Jinpeng, Ren Jing, Wan Jianshan. Computer-assisted navigation combined with minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar spondylolisthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3790-3795. |
| [10] | Hu Jing, Xiang Yang, Ye Chuan, Han Ziji. Three-dimensional printing assisted screw placement and freehand pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracolumbar fractures: 1-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3804-3809. |
| [11] | Shu Qihang, Liao Yijia, Xue Jingbo, Yan Yiguo, Wang Cheng. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of a new three-dimensional printed porous fusion cage for cervical vertebra [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3810-3815. |
| [12] | Wang Yihan, Li Yang, Zhang Ling, Zhang Rui, Xu Ruida, Han Xiaofeng, Cheng Guangqi, Wang Weil. Application of three-dimensional visualization technology for digital orthopedics in the reduction and fixation of intertrochanteric fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3816-3820. |
| [13] | Sun Maji, Wang Qiuan, Zhang Xingchen, Guo Chong, Yuan Feng, Guo Kaijin. Development and biomechanical analysis of a new anterior cervical pedicle screw fixation system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3821-3825. |
| [14] | Lin Wang, Wang Yingying, Guo Weizhong, Yuan Cuihua, Xu Shenggui, Zhang Shenshen, Lin Chengshou. Adopting expanded lateral approach to enhance the mechanical stability and knee function for treating posterolateral column fracture of tibial plateau [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3826-3827. |
| [15] | Zhu Yun, Chen Yu, Qiu Hao, Liu Dun, Jin Guorong, Chen Shimou, Weng Zheng. Finite element analysis for treatment of osteoporotic femoral fracture with far cortical locking screw [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3832-3837. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||