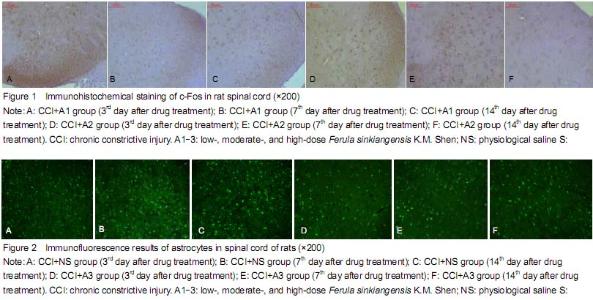
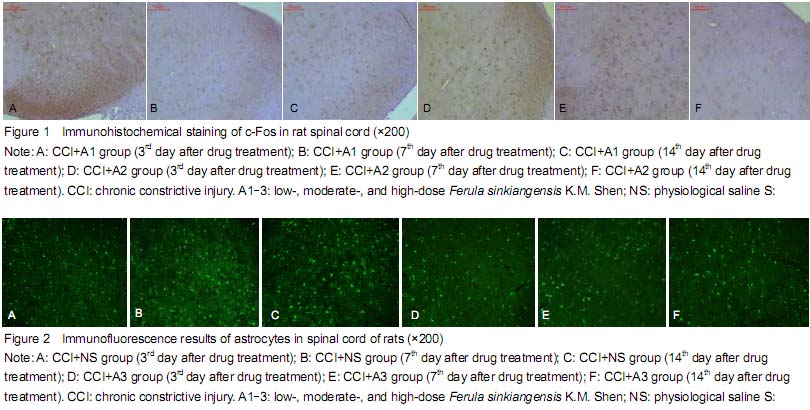
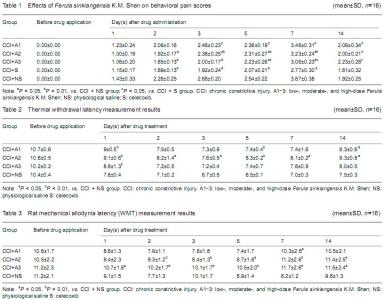
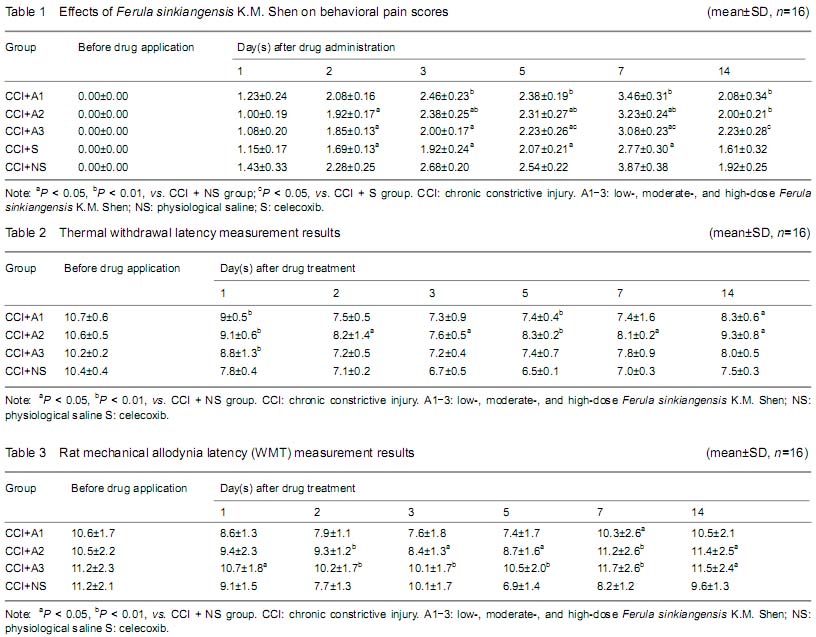
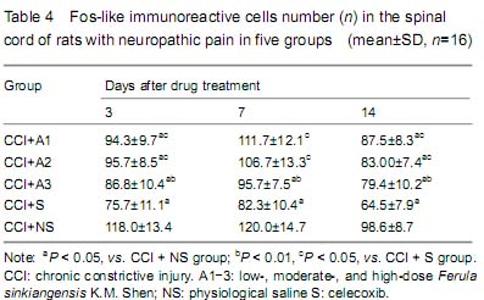
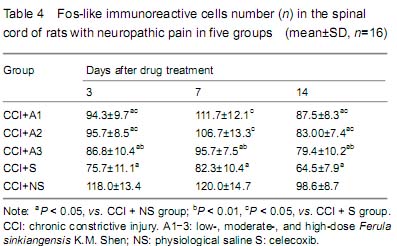
| [1] Bibi Y, Nisa S, Chaudhary FM, et al. Antibacterial activity of some selected medicinal plants of Pakistan. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2011;11:52.
[2] Li XJ, Lin Jiang, Palida. Preparation and Investigation of the pharmacodynamics of effective antiulcerative composition in Ferula sinkiangensis K. M. Shen. Zhongguo Xiandai Zhongyao. 2007;9(10):8.
[3] Sun Y, Liu HQ, Chen FF, et al. Observation of synergistic anti-inflammatory effect of combination of sodium ferulate and oxymatrine. Zhongcaoyao. 2011;42(3):538-541.
[4] Gao TT, Yu FH, Tan Y, et al. Study on antimicrobial activity in vitro of extracts from three species of ferula root. Beifang Yuanyi. 2013;(24):156-158.
[5] Jiang ZL, Wang SS, Wang YD, et al. The effects of Ferula sinkiangensis essential oil on the withdrawal syndrome of Morphine dependent rats and mice. Huaxi Yaoxue Zazhi. 2011;26(6):547-550.
[6] Lv WH, Zhang L, Wu SJ, et al. Analgesic effect of ferulic acid on CCI mice: behavior and neurobiological analysis. Zhongfuo Zhongyao Zazhi. 2013;38(21):3736-3741.
[7] Bennett GJ, Xie YK. A peripheral mononeuropathy in rat that produces disorders of pain sensation like those seen in man. Pain. 1988;33(1):87-107.
[8] Zhang HY, Xue J, Tian F. Experimental study on acute toxicity of awei capsule. Zhongguo Yaoye. 2011;20(11):5-6.
[9] Attal N, Jazat F, Kayser V, et al. Further evidence for ‘pain-related’ behaviours in a model of unilateral peripheral mononeuropathy. Pain. 1990;41(2):235-251.
[10] Hargreaves K, Dubner R, Brown F, et al. A new and sensitive method for measuring thermal nociception in cutaneous hyperalgesia. Pain. 1988;32(1):77-88.
[11] Chaplan SR, Bach FW, Pogrel JW, et al. Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the rat paw. J Neurosci Methods. 1994;53(1):55-63.
[12] Chen ZX, Wen XJ, Zeng YM, et al. The effect of mibefradil administered intrathecally and lateral ventricle to the pain threshold of the rats following chronic constriction injury (CCI) of the sciatic nerve. Zhongguo Yaolixue Tongbao. 2006;22 (5):571-575.
[13] Del-Bel EA, Borges CA, Defino HL, et al. Induction of Fos protein immunoreactivity by spinal cord contusion. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2000;33(5):521-528.
[14] Munglani R, Hunt SP. Molecular biology of pain. Br J Anaesth. 1995;75(2):186-192.
[15] Milligan ED, Twining C, Chacur M, et al. Spinal glia and proinflammatory cytokines mediate mirror-image neuropathic pain in rats. J Neurosci. 2003;23(3):1026-1040.
[16] Raghavendra V, Tanga FY, DeLeo JA. Attenuation of morphine tolerance, withdrawal-induced hyperalgesia, and associated spinal inflammatory immune responses by propentofylline in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2004;29(2):327-334.
[17] Watkins LR, Hutchinson MR, Ledeboer A, et al. Norman Cousins Lecture. Glia as the “bad guys”: implications for improving clinical pain control and the clinical utility of opioids. Brain Behav Immun. 2007;21(2):131-146.
[18] Popovich PG, Wei P, Stokes BT. Cellular inflammatory response after spinal cord injury in Sprague-Dawley and Lewis rats. J Comp Neurol. 1997;377(3):443-464. |