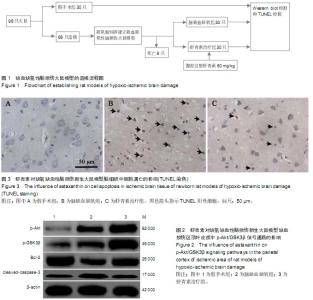
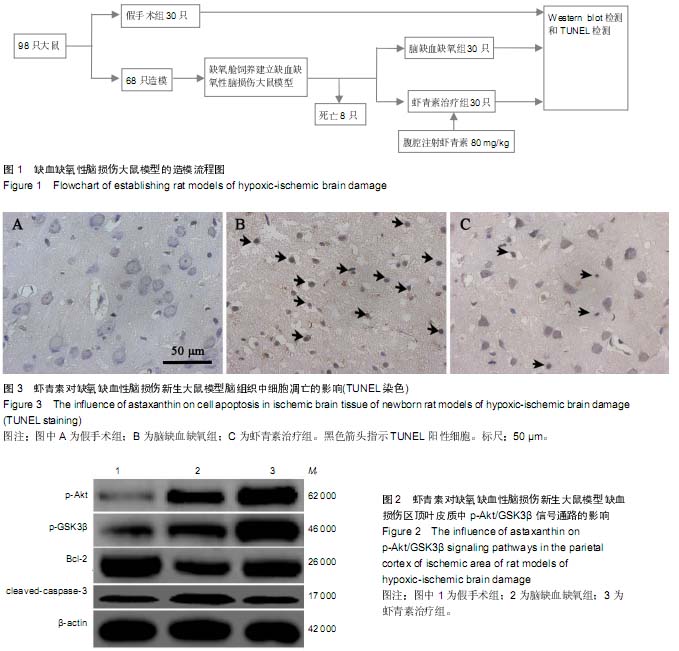
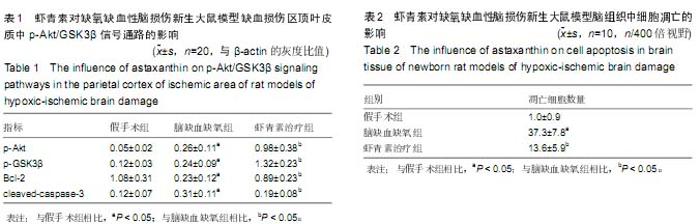
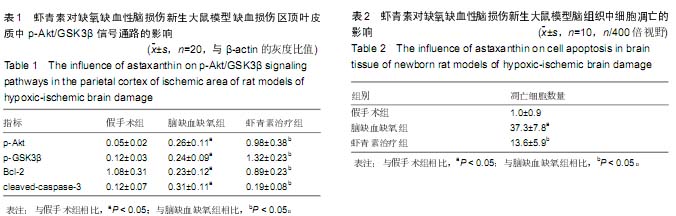
| [1] Wu YW, Gonzalez FF. Erythropoietin: a novel therapy for hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy? Dev Med Child Neurol. 2015;57 Suppl 3:34-39.
[2] Mcintyre S, Badawi N, Blair E, et al. Does aetiology of neonatal encephalopathy and hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy influence the outcome of treatment? Dev Med Child Neurol. 2015;57 Suppl 3:2-7.
[3] Zalewska T, Jaworska J, Ziemka-Nalecz M. Current and experimental pharmacological approaches in neonatal hypoxic- ischemic encephalopathy. Curr Pharm Des. 2015; 21(11):1433-1439.
[4] Rocha-Ferreira E, Hristova M. Antimicrobial peptides and complement in neonatal hypoxia-ischemia induced brain damage. Front Immunol. 2015;6:56.
[5] Juul SE, Ferriero DM. Pharmacologic neuroprotective strategies in neonatal brain injury. Clin Perinatol. 2014; 41(1):119-131.
[6] Hansen G, Al Shafouri N, Narvey M, et al. High blood carbon dioxide variability and adverse outcomes in neonatal hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2015:1-4.
[7] Saliba E, Fakhri N, Debillon T. Establishing a hypothermia service for infants with suspected hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 2015;20(2):80-86.
[8] Shankaran S, Laptook AR, Pappas A, et al. Effect of depth and duration of cooling on deaths in the NICU among neonates with hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2014;312(24):2629-2639.
[9] Chen A, Xiong LJ, Tong Y, et al. The neuroprotective roles of BDNF in hypoxic ischemic brain injury. Biomed Rep. 2013;1(2):167-176.
[10] Greer DM, Rosenthal ES, Wu O. Neuroprognostication of hypoxic-ischaemic coma in the therapeutic hypothermia era. Nat Rev Neurol. 2014;10(4):190-203.
[11] Wassink G, Gunn ER, Drury PP, et al. The mechanisms and treatment of asphyxial encephalopathy. Front Neurosci. 2014;8:40.
[12] Chicha L, Smith T, Guzman R. Stem cells for brain repair in neonatal hypoxia-ischemia. Childs Nerv Syst. 2014;30(1):37-46.
[13] Shioda N, Han F, Fukunaga K. Role of Akt and ERK signaling in the neurogenesis following brain ischemia. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2009;85:375-387.
[14] Guo SX, Zhou HL, Huang CL, et al. Astaxanthin attenuates early acute kidney injury following severe burns in rats by ameliorating oxidative stress and mitochondrial-related apoptosis. Mar Drugs. 2015;13(4):2105-2123.
[15] Wang JY, Lee YJ, Chou MC, et al. Astaxanthin protects steroidogenesis from hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress in mouse Leydig cells. Mar Drugs. 2015;13(3):1375-1388.
[16] Zhou L, Gao M, Xiao Z, et al. Protective effect of astaxanthin against multiple organ injury in a rat model of sepsis. J Surg Res. 2015.in press.
[17] Li J, Xia Y, Liu T, et al. Protective Effects of Astaxanthin on ConA-Induced Autoimmune Hepatitis by the JNK/p-JNK Pathway-Mediated Inhibition of Autophagy and Apoptosis. PLoS One. 2015;10(3):e0120440.
[18] Al-Amin MM, Rahman MM, Khan FR, et al. Astaxanthin improves behavioral disorder and oxidative stress in prenatal valproic acid-induced mice model of autism. Behav Brain Res. 2015;286:112-121.
[19] Sila A, Kamoun Z, Ghlissi Z, et al. Ability of natural astaxanthin from shrimp by-products to attenuate liver oxidative stress in diabetic rats. Pharmacol Rep. 2015;67(2):310-316.
[20] PLOS ONE Staff. Correction: Organization of Astaxanthin within Oil Bodies of Haematococcus pluvialis Studied with Polarization-Dependent Harmonic Generation Microscopy. PLoS One. 2015;10(3):e0121773.
[21] Sun H, Kong Q, Geng Z, et al. Enhancement of cell biomass and cell activity of astaxanthin-rich Haematococcus pluvialis. Bioresour Technol. 2015;186:67-73.
[22] Zhang XS, Zhang X, Wu Q, et al. Astaxanthin offers neuroprotection and reduces neuroinflammation in experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Surg Res. 2014;192(1):206-213.
[23] Zhang XS, Zhang X, Wu Q, et al. Astaxanthin alleviates early brain injury following subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats: possible involvement of Akt/bad signaling. Mar Drugs. 2014;12(8):4291-4310.
[24] Buyukakilli B, Atici A, Balli E, et al. Effects of a tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibitor (etanercept) on the sciatic nerve in a hypoxic ischemia-induced neonatal rat model. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2014;23(5):705-713.
[25] Lu YP, Liu SY, Sun H, et al. Neuroprotective effect of astaxanthin on H(2)O(2)-induced neurotoxicity in vitro and on focal cerebral ischemia in vivo. Brain Res. 2010;1360:40-48.
[26] Charriaut-Marlangue C, Nguyen T, Bonnin P, et al. Sildenafil mediates blood-flow redistribution and neuroprotection after neonatal hypoxia-ischemia. Stroke. 2014;45(3):850-856.
[27] Kitagishi Y, Matsuda S. Diets involved in PPAR and PI3K/AKT/PTEN pathway may contribute to neuroprotection in a traumatic brain injury. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2013;5(5):42.
[28] Phukan S, Babu VS, Kannoji A, et al. GSK3beta: role in therapeutic landscape and development of modulators. Br J Pharmacol. 2010;160(1):1-19.
[29] Kim JY,Jeon BS,Kim HJ,et al.林Nanomolar concentration of alpha-synuclein enhances dopaminergic neuronal survival via Akt pathway.Neural Regen Res. 2013;8 (35): 3269-3274.
[30] Huai YP,Dong YH,Xu J,et al.L-3-n-butylphthalide protects against vascular dementia via activation of the Akt kinase pathway.Neural Regen Res. 2013;8 (19): 1733-1742.
[31] Li X, Zhang J, Chai S, et al. Progesterone alleviates hypoxic-ischemic brain injury via the Akt/GSK-3β signaling pathway. Exp Ther Med. 2014;8(4):1241-1246.
[32] Li L, Klebe D, Doycheva D, et al. G-CSF ameliorates neuronal apoptosis through GSK-3β inhibition in neonatal hypoxia-ischemia in rats. Exp Neurol. 2015;263:141-149.
[33] 熊涛.AKT-GSK3信号通路与缺血缺氧性脑损伤[J].医学综述, 2010,16(23):3521-3524.
[34] Li L, McBride DW, Doycheva D, et al. G-CSF attenuates neuroinflammation and stabilizes the blood-brain barrier via the PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β signaling pathway following neonatal hypoxia-ischemia in rats. Exp Neurol. 2015. in press.
[35] Ambati RR, Phang SM, Ravi S, et al. Astaxanthin: sources, extraction, stability, biological activities and its commercial applications--a review. Mar Drugs. 2014;12(1):128-152.
[36] Fassett RG, Coombes JS. Astaxanthin in cardiovascular health and disease. Molecules. 2012;17(2):2030-2048
[37] Balietti M, Giannubilo SR, Giorgetti B, et al. The effect of astaxanthin on the aging rat brain: gender-related differences in modulating inflammation. J Sci Food Agric. 2015. in press.
[38] Qiu X, Fu K, Zhao X, et al. Protective effects of astaxanthin against ischemia/reperfusion induced renal injury in mice. J Transl Med. 2015;13(1):28.
[39] Huang LJ, Chen WP. Astaxanthin ameliorates cartilage damage in experimental osteoarthritis. Mod Rheumatol. 2015:1-4.
[40] Yamagishi R, Aihara M. Neuroprotective effect of astaxanthin against rat retinal ganglion cell death under various stresses that induce apoptosis and necrosis. Mol Vis. 2014;20:1796-1805.
[41] Wu Q, Zhang XS, Wang HD, et al. Astaxanthin activates nuclear factor erythroid-related factor 2 and the antioxidant responsive element (Nrf2-ARE) pathway in the brain after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats and attenuates early brain injury. Mar Drugs. 2014;12(12):6125-6141.
[42] Zhang XS, Zhang X, Wu Q, et al. Astaxanthin alleviates early brain injury following subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats: possible involvement of Akt/bad signaling. Mar Drugs. 2014; 12(8):4291-4310.
|