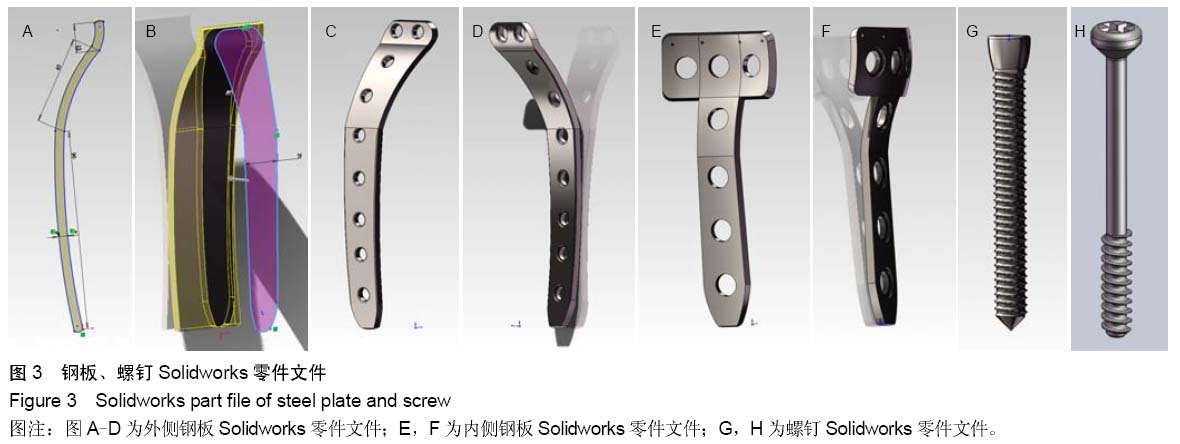
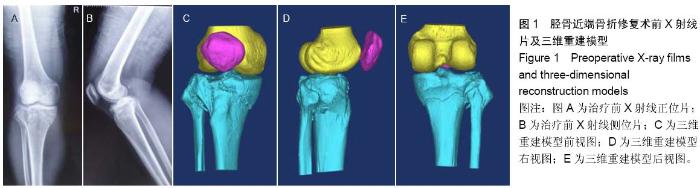
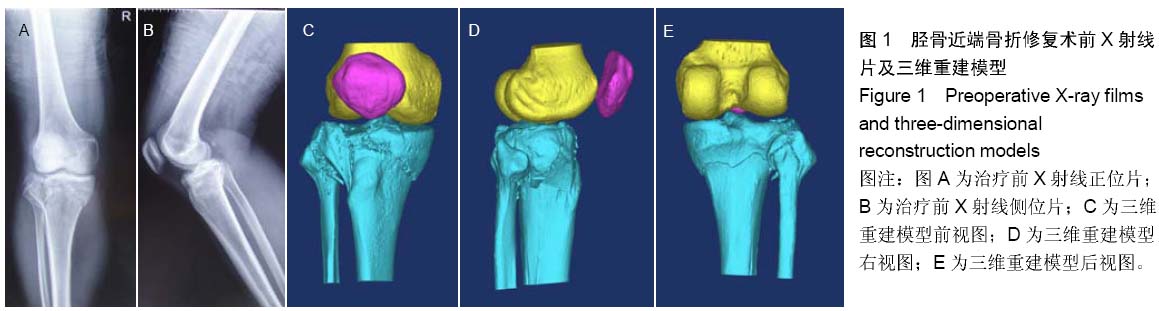
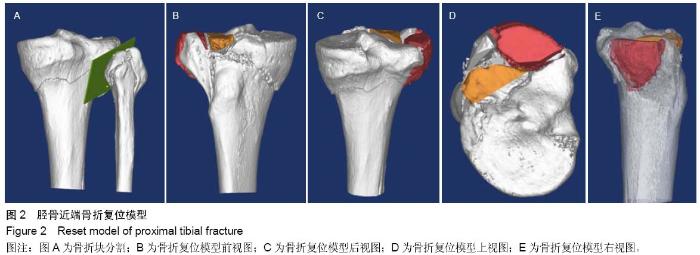
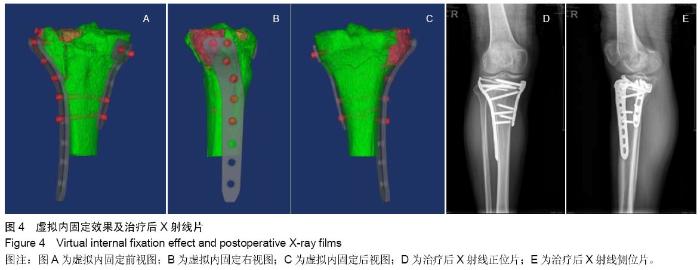
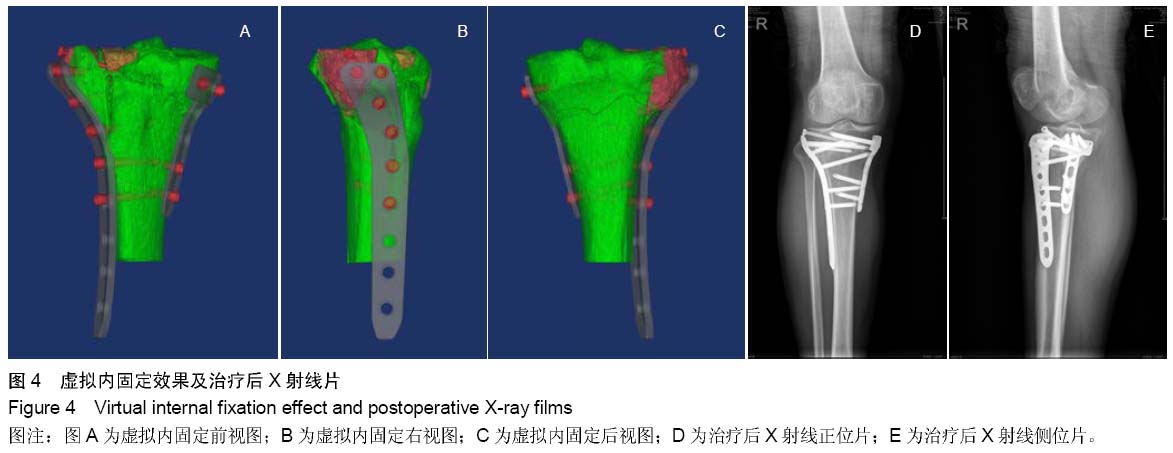
| [1] 蔡伟斌,胡鸿璇,郭新辉,等.锁定加压钢板与解剖钢板置入内固定治疗复杂胫骨平台骨折[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(52): 9750-9755.
[2] 张国栋,陶圣祥,郑和平,等.基于三维重建技术的股骨远端数字钢板设计[J].实用骨科杂志,2010,16(1):35-38.
[3] Mc Broom S, Bruce D.The tibial plateau fracture.The Toronto experience 1968-1975.Clin Orthop. 1979;(138):94-104.
[4] Borrelli J Jr,Prickett W,Song E,et al. Extraosseous blood supply of the tibia and the effects of different plating techniques: a human cadaveric study. J Orthop Trauma. 2002;16(10):691-695.
[5] MacNab I. Negative disc exploration. An analysis of the causes of nerve-root involvement in sixty-eight patients. J Bone Joint Surg(Am). 1971;53(5):891-903.
[6] Gösling T, Klingler K, Geerling J, et al. Improved intra-operative reduction control using a three-dimensional mobile image intensifier--a proximal tibia cadaver study. Knee.2009;16(1):58-63.
[7] Papagelopoulos PJ, Partsinevelos AA, Themistocleous GS, et al. Complications after tibia plateau fracture surgery. Injury.2006;37(6):475-484.
[8] Taylor J, Langenbach A, Marcellin-Little DJ. Risk factors for fibular fracture after TPLO. Vet Surg. 2011;40(6): 687-693.
[9] Yu Z,Zheng L,Zhang Y,et al. Functional and radiological evaluations of high-energy tibial plateau fractures treated with double -buttress plate fixation. Eur J Med Res. 2009;14(5): 200-2005.
[10] Yu B,Han K,Zhan C,et al.Fibular head osteotomy: a new approach for the treatment of lateral or posterolateral tibial plateau fractures. Knee. 2010;17(5):313.
[11] Cimerman M, Kristan A. Preoperative planning in pelvic and acetabular surgery: The value of advanced computerised planning modules. Injury. 2007;38:442-449.
[12] 扈延龄,金丹,苏秀云,等.基于三维CT数据的髋臼骨折计算机辅助虚拟手术设计[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志, 2008, 10(2): 137-137.
[13] Doornberg JN, Rademakers MV, van den Bekerom MP, et al.Two-dimensional and three-dimensional computed tomography for the classification and characterisation of tibial plateau fractures. Injury. 2011;42(12):1416-1425.
[14] Waschke A, Walter J, Duenisch P, et al. CT-navigation versus fluoroscopy-guided placement of pedicle screws at the thoracolumbar spine: single center experience of 4,500 screws. Eur Spine J. 2013;22(3):654-660.
[15] 田伟,郎昭,刘亚军,等.术中即时三维导航辅助下轴性旋转腰椎椎弓根螺钉置入的实验研究[J]. 中华外科杂志,2010,48(11): 838-841.
[16] Villard J, Ryang YM, Demetriades AK, et al. Radiation exposure to the surgeon and the patient during posterior lumbar spinal instrumentation: a prospective randomized comparison of navigated versus non-navigated freehand techniques. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014;39(13): 1004-1009.
[17] Tormenti MJ, Kostov DB, Gardner PA, et al. Intraoperative computed tomography image-guided navigation for posterior thoracolumbar spinal instrumentation in spinal deformity surgery. Neurosurg Focus. 2010;28(3): E11.
[18] Lee MH, Lin MH, Weng HH, et al. Feasibility of Intra-operative Computed Tomography Navigation System for Pedicle Screw Insertion of the Thoraco-lumbar Spine. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2012.
[19] Hodges SD, Eck JC, Newton D. Analysis of CT-based navigation system for pedicle screw placement. Orthopedics. 2012;35(8):1221-1224.
[20] Tabaraee E, Gibson AG, Karahalios DG, et al. Intraoperative cone beam-computed tomography with navigation (O-ARM) versus conventional fluoroscopy (C-ARM): a cadaveric study comparing accuracy, efficiency, and safety for spinal instrumentation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013;38(22): 1953-1958.
[21] Oertel MF, Hobart J, Stein M, et al. Clinical and methodological precision of spinal navigation assisted by 3D intraoperative O-arm radiographic imaging. J Neurosurg Spine. 2011;14(4):532-536.
[22] Silbermann J, Riese F, Allam Y, et al. Computer tomography assessment of pedicle screw placement in lumbar and sacral spine: comparison between free-hand and O-arm based navigation techniques. Eur Spine J. 2011;20(6):875-881.
[23] Kantelhardt SR, Martinez R, Baerwinkel S, et al. Perioperative course and accuracy of screw positioning in conventional, open robotic-guided and percutaneous robotic-guided, pedicle screw placement. Eur Spine J. 2011;20(6):860-868.
[24] Bourgeois AC, Faulkner AR, Bradley YC, et al. Improved Accuracy of Minimally Invasive Transpedicular Screw Placement in the Lumbar Spine with Three-dimensional Stereotactic Image Guidance: A Comparative Meta-analysis. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2014.
[25] Lu S, Xu YQ, Zhang YZ, et al. A novel computer-assisted drill guide template for placement of C2 laminar screws. Eur Spine J. 2009;18(9):1379-1385.
[26] Merc M, Drstvensek I, Vogrin M, et al. A multi-level rapid prototyping drill guide template reduces the perforation risk of pedicle screw placement in the lumbar and sacral spine. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2013;133(7):893-899.
[27] Ma T, Xu YQ, Cheng YB, et al. A novel computer-assisted drill guide template for thoracic pedicle screw placement: a cadaveric study. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2012;132(1):65-72.
[28] Hu YL, Ye FG, Ji AY, et al. Three-dimensional computed tomography imaging increases the reliability of classification systems for tibial plateau fractures. Injury. 2009;40(12): 1282-1285.
[29] Hu Y,Li H,Qiao G,et al.Computer-assisted virtual surgical procedure for acetabular fractures based on real CT data. Injury.2011;42(10):1121-1124.
[30] Messmer P,Brig G,Suhm N,et al.Three-dimensional fracture simulation for preoperative planning and education.Eur J Trauma. 2001;27:171-177.
[31] Osti M,Philipp H,Meusburger B,et al.Analysis of failure following anterior screw fixation of Type II odontoid fractures in geriatric patients. Eur Spine J. 2011;20(11):1915-1920.
[32] Osti M,Philipp H,Meusburger B,et al.Analysis of failure following anterior screw fixation of Type II odontoid fractures in geriatric patients. Eur Spine J. 2011;20(11):1915-1920.
[33] Chen C,Ruan D,Wu C,et al.CT morphometric analysis to determine the anatomical basis for the use of transpedicular screws during reconstruction and fixations of anterior cervical vertebrae. PLoS One. 2013;8(12):e81159.
[34] Khoury A,Liebergall M,Weil Y,et al. Computerized fluoroscopic-based navigation-assisted intramedullary nailing. Am J Orthop. 2007;36(11):582-585.
[35] 张国栋,林海滨,陈宣煌,等.基于多平面三维测量的髋臼骨折数字化内固定置入方案[J].中华临床医师杂志:电子版,2012,6(8): 2010-2015.
[36] 陈宣煌,张国栋,吴长福,等.数字化颈前路螺钉内固定方案设计:Ⅱ型齿状突骨折的临床应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(26): 4926-4933.
[37] 陈宣煌,林海滨,张国栋,等.腰椎后路数字化内固定手术方案及临床应用[J].中华临床医师杂志:电子版,2012,6(17):5249-5251.
[38] 陈宣煌,林海滨,张国栋,等.枕颈融合内固定治疗C1 Jefferson骨折的数字化设计及意义.中华临床医师杂志:电子版,2013,7(9): 4110-4112.
[39] 陈宣煌,张国栋,吴长福.C1侧块骨折Magerl技术内固定的数字化模拟及应用[J].临床骨科杂志,2013,16(6):712-715.
[40] Blemker SS, Asakawa DS,Gold GE,et al.Image-based musculoskeletal modeling:applications, advances, and future opportunities.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2007;25(2):441-451.
[41] Aurouer N, Obeid I, Gille O, et al. Computerized preoperative planning for correction of sagittal deformity of the spine. Surg Radiol Anat. 2009;31:781-792.
[42] Klein S, Whyne CM, Rush R, et al.CT-based patient-specific simulation software for pedicle screw insertion. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2009;22(7):502-506. |