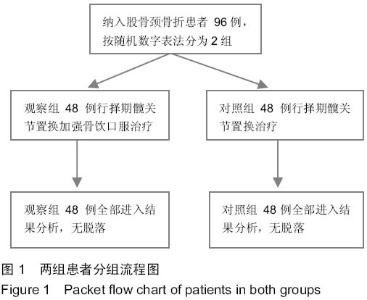
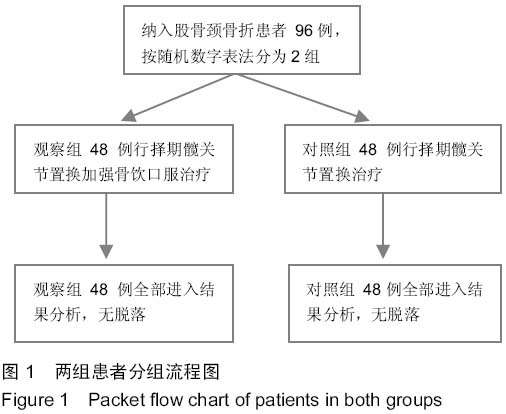
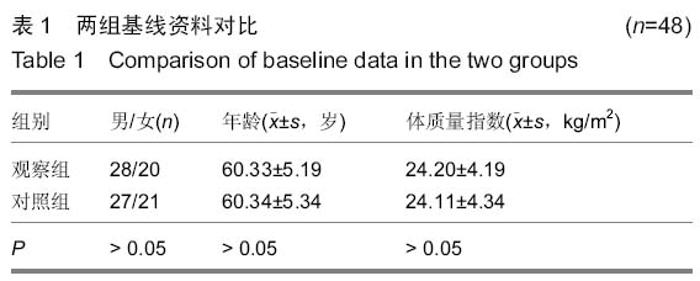
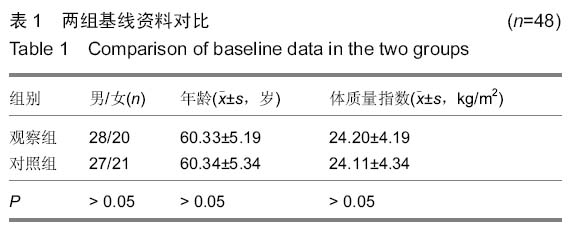
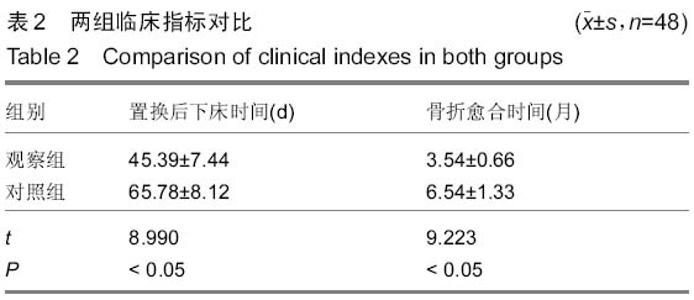
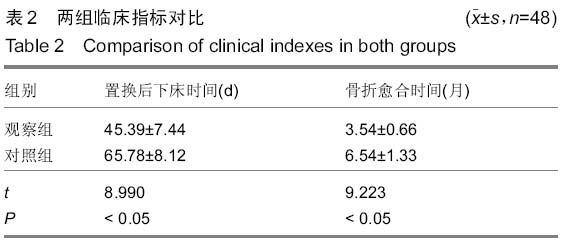
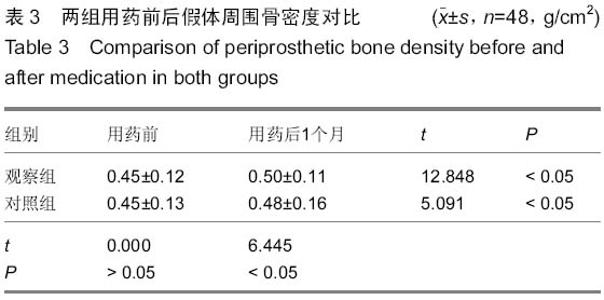
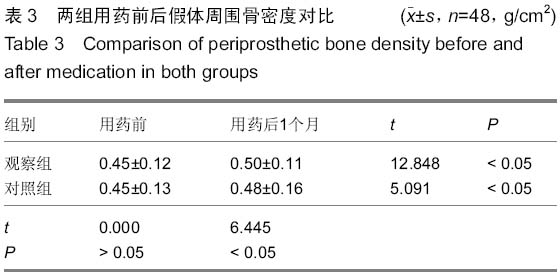
| [1] 中华医学会骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病分会.原发性骨质疏松症诊治指南(2011年)[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志, 2011,4(1): 2-17.
[2] 吴连国,刘康,黄俊俊,等.强骨饮对股骨颈骨折患者人工股骨头置换术后假体周围骨密度的影响[J].中医正骨,2014,4(22):15-18.
[3] Zanotti B, Zingaretti N, Almesberger D, et al. Enhancing dermal and bone regeneration in calvarial defect surgery.Indian J Plast Surg. 2014;47(3):325-332.
[4] 王利,哈巴西•卡肯,殷剑,等.唑来膦酸钠治疗全髋关节置换术后早期假体周围骨密度变化[J].中华临床医师杂志(电子版),2014, 15(7):2898-2900.
[5] 张林林,姜习凤,艾红珍,等.绝经后髋部脆性骨折中铁过载指标与骨密度骨转换指标关系的研究[J].中华外科杂志,2013,51(6): 221-223.
[6] Mechlenburg I, Klebe TM, Døssing KV, et al. Resurfacing implants: two-year results of a randomized controlled clinical trial. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2014;23(10):1427-1436.
[7] 纪泉,赵立连,石磊,等.唑来膦酸对骨质疏松性股骨转子间骨折作用效果分析[J].中华骨科杂志,2014,34(1):99-101.
[8] 李旭云,孙峰,李静伟,等.益气温经方强骨饮治疗原发性骨质疏松症的研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2014,8(12):67-69.
[9] Matsumoto T, Nakamura I, Miura A, et al. Partial transmalleolar approach for lateral impingement after total ankle arthroplasty: a case report. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2015; 54(2):233-236.
[10] 赵稜,汪煌,魏杰,等.自拟强骨饮对绝经后骨质疏松患者血清雌激素水平及骨密度影响的临床观察[J].浙江中医药大学学报, 2011, 35(4):134-136.
[11] 屈瑾,雷新玮,展影,等.髋关节表面置换术假体柄固定方式对股骨近端骨密度及应力影响[J].中华医学杂志,2014,94(35): 2769-2771.
[12] Jakob F, Oertel H, Langdahl B, et al. Effects of Teriparatide in PostmenopausalWomen with OsteoporosisPretreated with Bisphosphonates: 36-month Results from the European Forsteo Observational Study (EFOS). Eur J Endocrinol. 2011; 166(1): 87-97.
[13] 袁宏,陆琳松,钟惠琴,等.唑来膦酸对骨质疏松患者全髋关节置换术后假体周围骨密度的影响[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2014,3(12):278-285.
[14] 臧学慧,孙辉,高立华,等.全膝关节置换后假体周围应力与骨密度的相关性[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,44(12):7071-7076.
[15] Paola P, Maria DR, Francesco C, et al. Screening and early diagnosis of osteoporosis through X-ray and ultrasound based techniques. World J Radiol. 2011;5(11):398-410.
[16] 高广凌,黄相杰,姜红江,等.接骨药丸防治人工股骨头置换术后假体周围骨质疏松的疗效观察[J].中医正骨,2013,25(9):19-21.
[17] 李三华,何志全,陈全利,等.杜仲总黄酮对成骨细胞增殖及Ⅰ型胶原蛋白表达的影响[J].西北药学杂志,2011,26(4):272-274.
[18] Lix LM, Acan Osman B, Adachi JD, et al. Measurement equivalence of the SF-36 in the Canadian multicentre osteoporosis study. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2012;10(1): 29. |