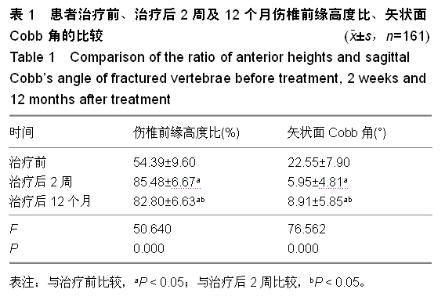
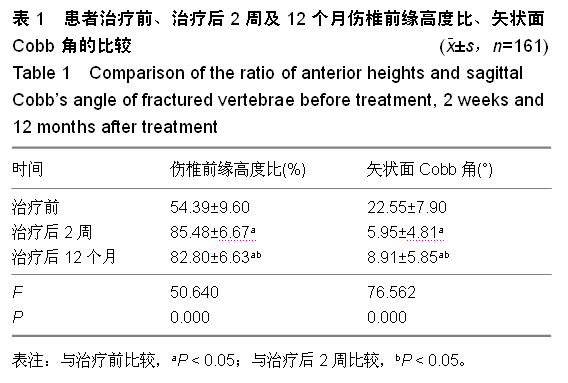
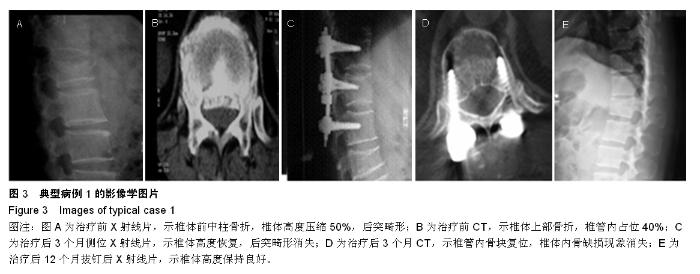
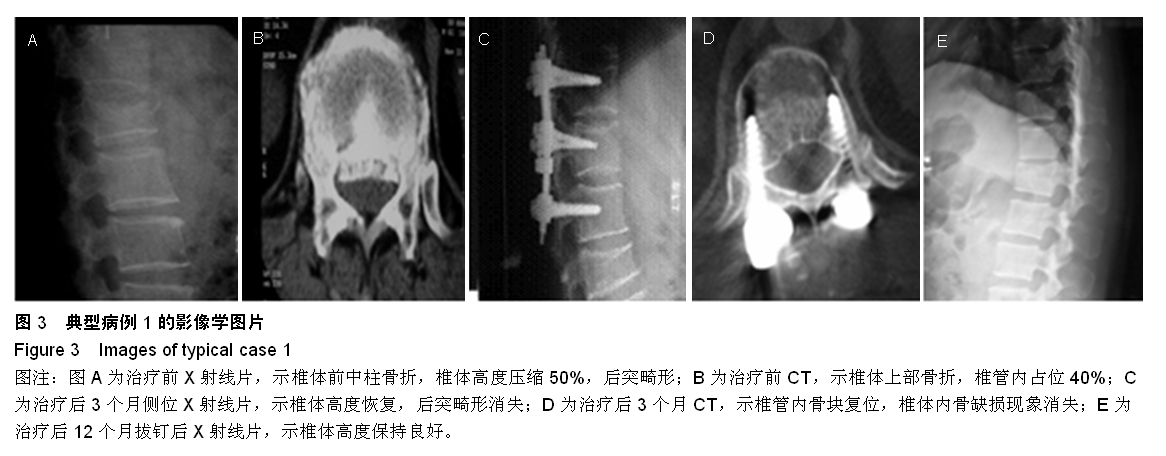
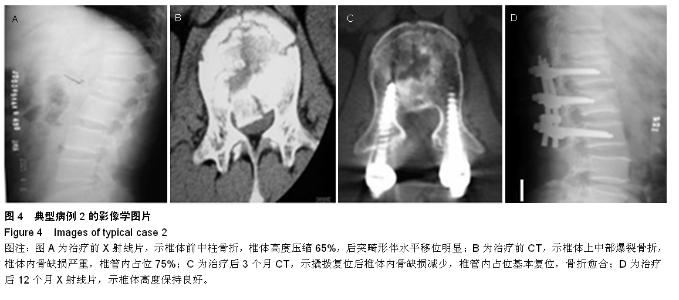
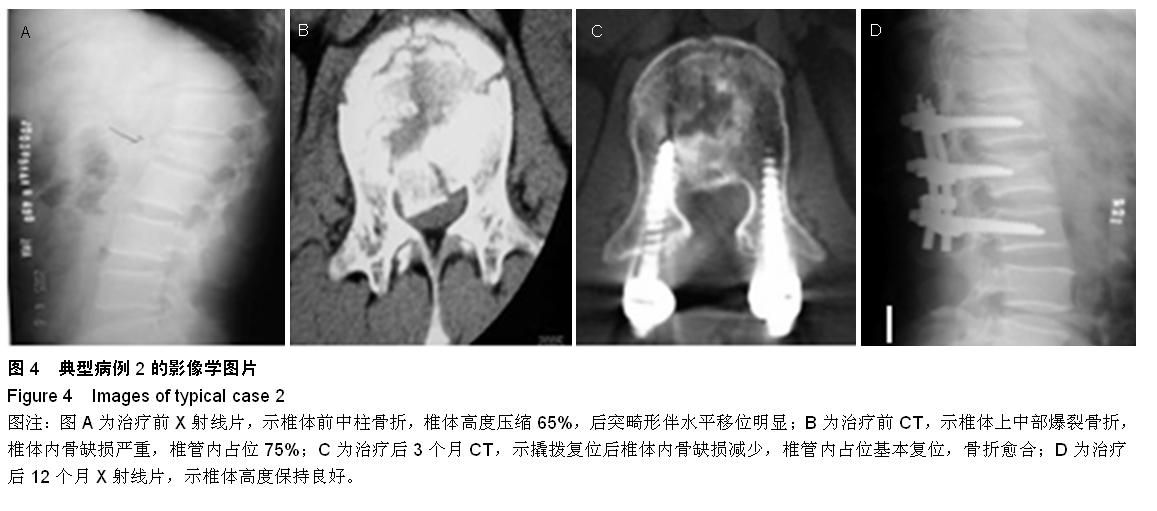
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (35): 5636-5640.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.35.012
Previous Articles Next Articles
Design and application of screw-assisted reduction of fractured vertebrae
Li Guo-hua1, Wu Wei-ping2, He Shi-sheng2, Li Shan-zhu1, Zeng Zhi-li3, Yu Yan3, Cai Xiao-bing2, Yilihamu•Tuoheti1
- 1Department of Orthopeadic Surgery, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830063, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Tenth People’s Hospital of Tongji University, Shanghai 200072, China; 3Department of Orthopedics, Tongji Hospital Affiliated to Tongji University, Shanghai 200065, China