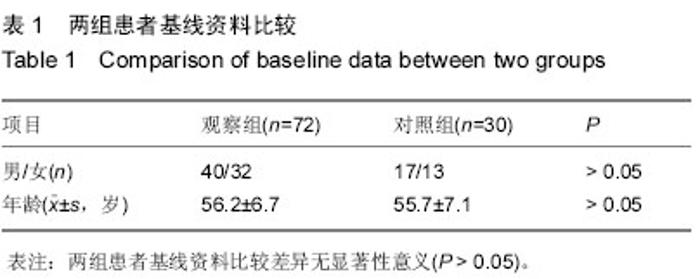
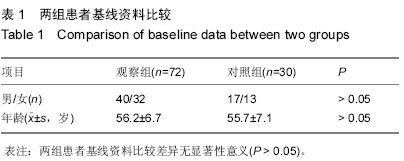
| [1] 王国基,王国军,彭健民,等.腰椎间盘突出症致病因素的流行病学研究[J].现代预防医学,2009, 36(13):2401-2403.
[2] 单治,范顺武,赵凤东.腰椎间盘纤维环的生物力学性能研究进展[J].中华骨科杂志,2014,34(3): 330-335.
[3] 马秀才,沈霖.腰椎间盘退变分子生物学因素研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2011,19(17):1451-1453.
[4] 韩建军,李菊梅,丁文元,等.腰椎间盘突出程度与间盘组织肿瘤坏死因子α水平的关系[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008, 12(33):6462-6465.
[5] 刘旭,车路,王海强,等.椎间盘退变的分子病理机制研究概况[J].中华临床医师杂志(电子版), 2013,7(6):2664-2666.
[6] 李华胜.年龄对腰椎间盘突出症影响的临床进展[J].现代诊断与治疗,2013,24(3):562-564.
[7] 田卫华,赵振营,苏晓路.血管内皮生长因子和表皮生长因子受体在不同年龄组退变椎间盘中的表达[J].实用医技杂志,2012, 19(9):984-985.
[8] 李江平,王金财,梁锦辉,等.腰椎后路镜下椎间盘髓核摘除术标准程序化治疗腰椎间盘突出症[J].中国伤残医学,2014,22(2):39.
[9] 闫志刚,王元利.低温等离子射频消融髓核成形术治疗腰椎间盘突出症60例的临床观察[J].颈腰痛杂志,2014,35(1):73-74.
[10] 杨旸,何晓峰,李彦豪,等.退行性变椎间盘组织中TGF-β1和Bax的表达及意义[J].临床与实验病理学杂志,2012,28(4):399-402.
[11] 江妍霞,王瑞琳,熊光宜,等.退变椎间盘中新生血管与TGF-β1表达的关系及其临床意义[J].临床与实验病理学杂志,2012,28(9): 983-986.
[12] 戴启宇,杨廷桐,王会英,等.以TGF-β1表达诊断人体椎间盘退变的可行性研究[J].实用医药杂志,2013,30(5):388-390.
[13] 董振风,黄秀芳,董永,等.IL-8及TNF在突出椎间盘中的表达意义[J].潍坊医学院学报,2008,30(5):447-448.
[14] 李灏.椎间盘突出症患者退变腰椎间盘组织中IL-6、IL-8、TNF-α的表达变化及意义[J].山东医药,2010,50(30):65-66. |