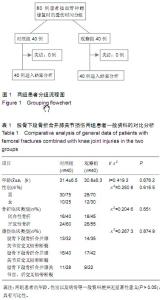
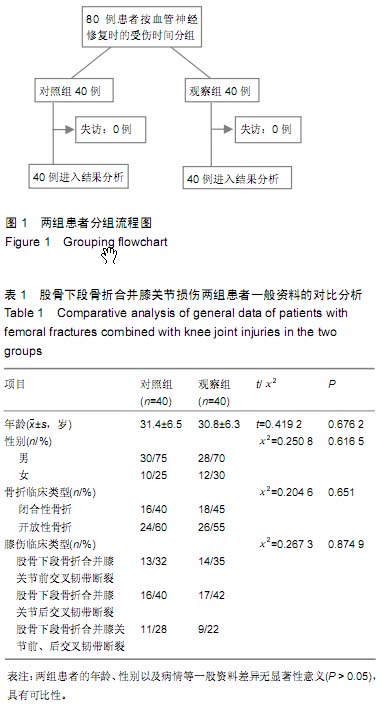
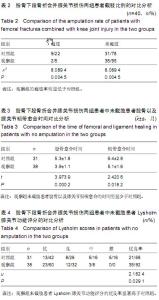
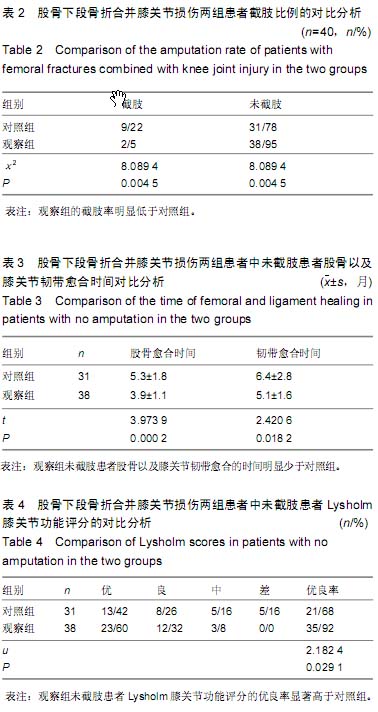
| [1] 马健超,陈皓,赵贺,等.股骨干骨折合并同侧股骨颈骨折35例[J]. 中国老年学杂志,2014,34(15):4378-4379.
[2] 沈佳祚,练克俭.股骨颈骨折早期股骨头缺血性坏死的评估[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2012,16(17):3227-3230.
[3] 罗伟初,李翠芳,林庆培.股骨骨折术后早期的体位对膝关节功能恢复的影响研究[J].中国社区医师:医学专业,2012,14(12): 185-187.
[4] 林岿然.四肢骨折合并血管损伤治疗的临床分析[J].河南外科学杂志,2012,18(4): 57-58.
[5] 李裕林,卢盛斌,蒋建军.膝关节周围骨折合并血管神经损伤临床分析[J].中国实用神经疾病杂志,2014,17(15):84-85.
[6] 茹江英,胡玉华.膝周骨折合并血管神经损伤的早期诊疗进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2007,15(14):1081-1084.
[7] 王郑钢,朱勇,吴攀峰.膝关节周围骨折合并血管神经损伤60例临床分析[J].中国医药导报,2012,9(7):149-150.
[8] 王光林,张晖,刘雷.膝关节周围骨折的治疗建议[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2010,12(12):1150.
[9] 解先宽,李杭,郑强.膝关节周围骨折、脱位伴血管损伤的诊疗分析[J].中华外科杂志,2009,47(23):1794-1795.
[10] 苏庚洵,冯奎伟,李子木.四肢主要动脉损伤的处理32例分析[J].骨与关节损伤杂志,1996,11:294.
[11] 黄耀添,陆裕朴,李稔生.下肢骨折脱位合并动脉损伤[J].中华骨科杂志,1992,12(5):322-324.
[12] 王辉.四肢骨折合并血管损伤治疗的临床探析[J].中国保健营养(下旬刊),2012,22(1):101.
[13] 高忠礼,赵长福,于庆巍.下肢骨折并血管损伤的治疗[J].中国骨伤, 1999,12(3):11-13.
[14] 黄钧荣,陆行,刘伯泉.下肢骨折并血管损伤的治疗[J].实用医学杂志,1995,11(12):84.
[15] 王剑华. 膝关节周围骨折合并血管神经损伤临床分析[J].中国基层医药,2013,20(2):242-243.
[16] 车明学,张颖,侯勇,等. 膝关节周围开放性骨折合并血管神经损伤的治疗[J].中国老年学杂志,2007,27(21):2142-2143.
[17] 胡玉华,茹江英,胡传亮,等. 膝关节周围骨折合并血管神经损伤早期诊断与治疗[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2008,23(07): 533-535.
[18] 刘敏,志勇.腘动脉损伤的早期诊断及显微外科修复[J].中华显微外科杂志,2003,26(2):155 -156.
[19] 陈东旭,孙占胜.急诊手术治疗修复周围神经损伤50例体会[J]. 山东医药,2001,41(10):43- 44.
[20] 张作民.膝关节周围骨折合并神经损伤的处理[J].中国实用神经疾病杂志,2009,12(8):50.
[21] 辛雷,苏佳灿.膝关节功能评分:现状与展望[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(39):7367-7370.
[22] 刘宇鹏,赵德伟,王卫明,等.神经生长因子可促进骨折愈合过程中血管内皮生长因子的表达(英文).中国组织工程研究, 2014, 18(24): 3863-3869.
[23] 陈学明,卢森桂.股骨下段骨折合并的血管神经伤早期修复[J]. 创伤外科杂志,2000,2(3):131-133
[24] Zhou FY, Guo XS, Gao WY, et al. Clinical significance of MESS scoring system in the treatment of fractures of lower limb combined with vascular injuries. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2010;23(6):445-447.
[25] 张成生,孙建光,张金明.边远地区股骨骨折并股动脉断裂12小时救治一例[J].包头医学,2011,35(02):68+86.
[26] 江武,姚建华.急性膝关节脱位合并多发韧带损伤早期评估进展[J].医学综述,2014,20(21):3929-3932.
[27] Boopalan PR, Sait A, Jepegnanam TS, et al.Clin Orthop Relat Res.The efficacy of single-stage open intramedullary nailing of neglected femur fractures. 2014;472(2):759-764.
[28] Sugder WH .Vascular injuries near the knee: An updated series and over view of the problem. Surgery, 1982;91:502-507 .
[29] 许九生,蔡会玲,李同森.四肢骨折合并血管损伤35 例临床分析[J].中国医药指南,2011,9(26):243-244.
[30] 章柏平,吕仁发,徐燕荣,等. 股骨下段骨折合并血管损伤的早期修复[J].中国骨伤,2007,20(8):551-552.
[31] 陈海,黄德征,唐传其.周围主要血管损伤68例诊治分析[J].中华显微外科杂志,1999,22(1):67-68.
[32] 闫德明,李亚伟,刘拥军等.闭合性膝关节周围骨折合并血管神经损伤32例[J].中医正骨,2010,22(09):49-52.
[33] Rodriguez-Merchan EC, Moraleda L, Gomez-Cardero P. Injuries associated with femoral shaft fractures with special emphasis on occult injuries. Arch Bone Jt Surg.2013;1(2): 59-63.
[34] 万世勇,姜民浩,张宏志,等.延误诊治的下肢大血管损伤的临床救治[J].创伤外科杂志,2003, 5(4):264-265.
[35] 马珑,崔宏勋,夏凯,等. 膝关节周围骨折合并血管神经损伤51例临床治疗[J].河南科技大学学报:医学版,2006,24(1):39-40.
[36] 崔宏勋,马珑,冯卫华.膝关节周围骨折合并血管神经损伤96例临床治疗[J].中国现代医生,2009,47(14):133-134. |