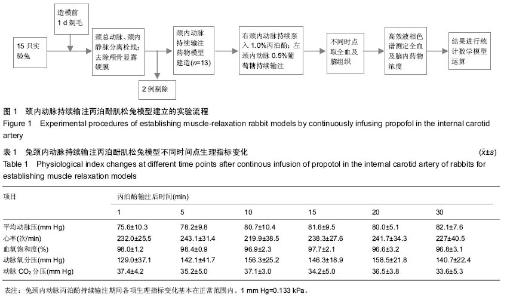
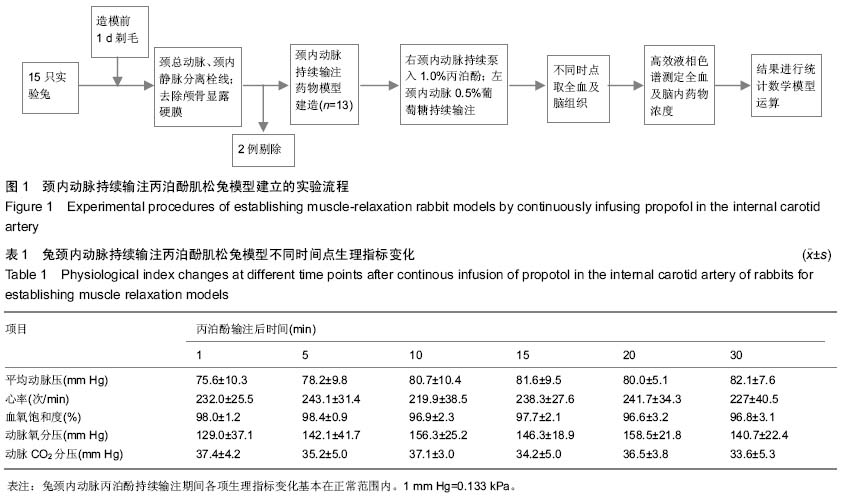
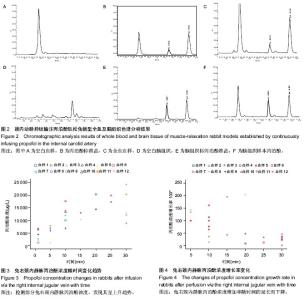
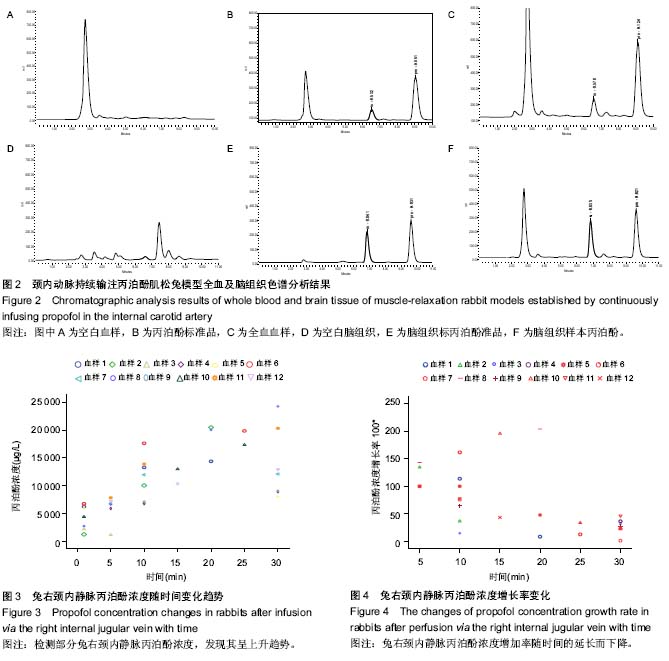
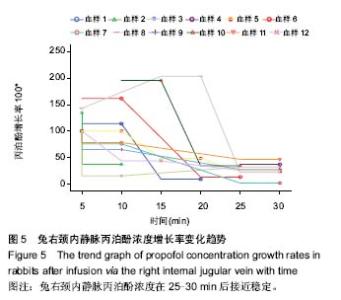
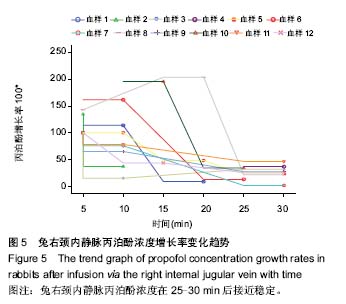
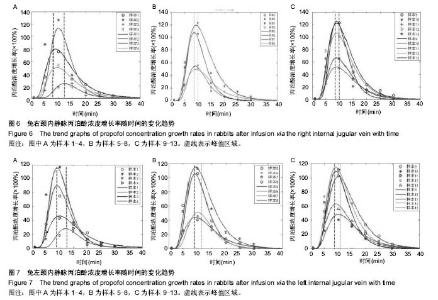
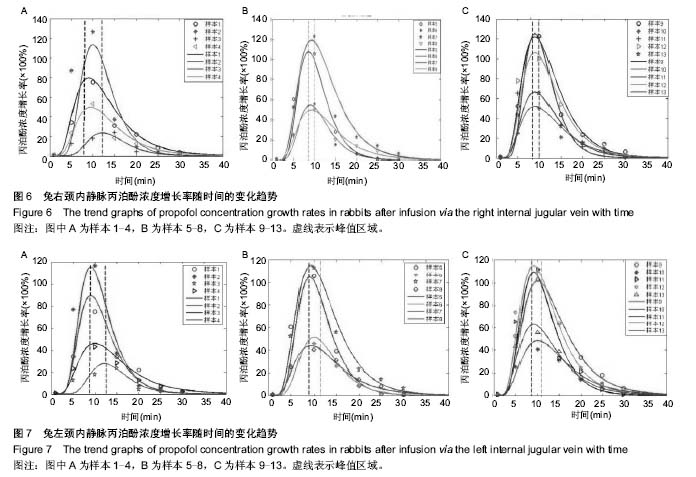
| [1] Joshi S, Emala CW, Pile-Spellman J. Intra-arterial drug delivery: a concise review. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol. 2007;19(2):111-119.
[2] Wada J, Rasmussen T. Intracarotid injection of sodium amytal for the lateralization of cerebral speech dominance. 1960. J Neurosurg. 2007;106(6):1117-1133.
[3] Wang M, Joshi S, Emerson RG. Comparison of intracarotid and intravenous propofol for electrocerebral silence in rabbits. Anesthesiology. 2003;99(4):904-910.
[4] Joshi S, Wang M, Etu JJ, et al. Bolus configuration affects dose requirements of intracarotid propofol for electroencephalographic silence. Anesth Analg. 2006;102(6): 1816-1822.
[5] 盖成林,陈卫民,冉德春,等.颈总动脉输注异丙酚维持全身麻醉的临床观察[J].南方医科大学学报,2008,28(8):1422-1424.
[6] 盖成林,陈卫民,郑晓春,等.犬颈总动脉和股静脉输注异丙酚至脑电静息对循环呼吸的影响[J].南方医科大学学报,2006,26(12): 1799-1802.
[7] Dedrick RL. Arterial drug infusion: pharmacokinetic problems and pitfalls. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1988;80(2):84-89.
[8] Joshi S, Wang M, Nishanian EV, et al. Electrocerebral silence by intracarotid anesthetics does not affect early hyperemia after transient cerebral ischemia in rabbits. Anesth Analg. 2004;98(5):1454-1459, table of contents.
[9] Aeschbacher G, Webb AI. Propofol in rabbits. 1. Determination of an induction dose. Lab Anim Sci. 1993;43(4):324-327.
[10] Aeschbacher G, Webb AI. Propofol in rabbits. 2. Long-term anesthesia. Lab Anim Sci. 1993;43(4):328-335.
[11] Joshi S, Wang M, Hartl R. Retinal discoloration test. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2004;24(3):305-308.
[12] Shyr MH, Tsai TH, Tan PP, et al. Concentration and regional distribution of propofol in brain and spinal cord during propofol anesthesia in the rat. Neurosci Lett. 1995;184(3):212-215.
[13] 薛定宇,陈阳泉.基于MATALAB/Simulink的系统仿真技术与应用[M].2版.北京:清华大学出版社,2011.
[14] 李九龙,周凌柯.基于“3σ法则”的显著误差检测[J].计算机与现代化,2012(1):10-13.
[15] 于广华,裔照国,陈国忠,等.药动学模型的Matlab模拟[J].中国医院药学杂志,2008,28(22):1956-1959.
[16] 杨帆.应用MATLAB求算静脉注射给药的药动学参数[J].抗感染药学,2009,6(3):157-161.
[17] 尹红,陈卫民,朱俊超,等.兔颈内动脉不同浓度丙泊酚输注药效学研究[J].中国医科大学学报,2013,42(6):551-556.
[18] Yin H, Chen WM, Zhao P. Cerebral state index may reflect electrical brain activity during propofol or isoflurane anaesthesia in rabbits. Vet Rec. 2013;172(7):184. |