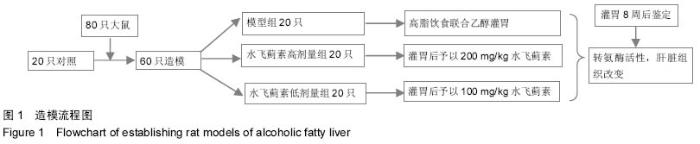
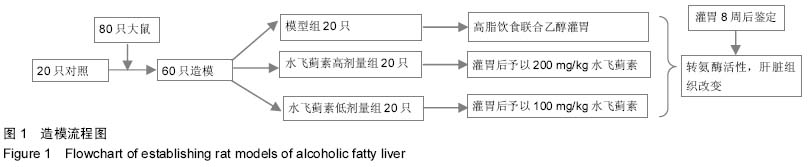
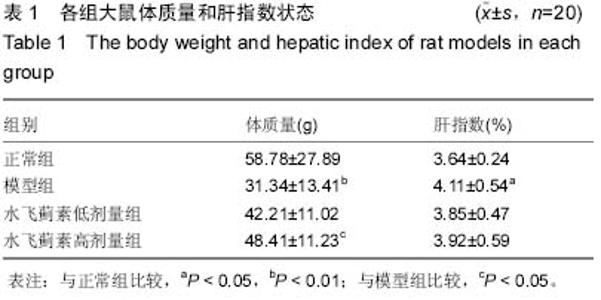
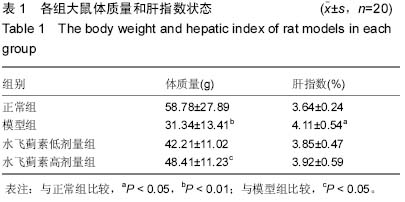
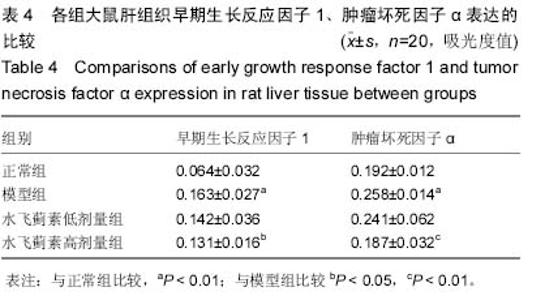
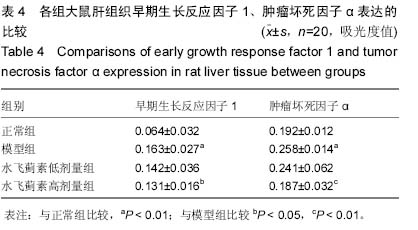
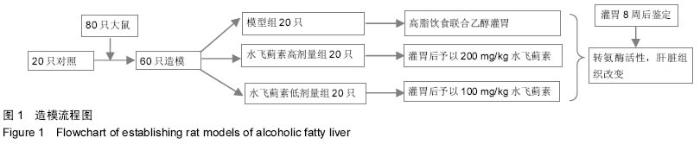
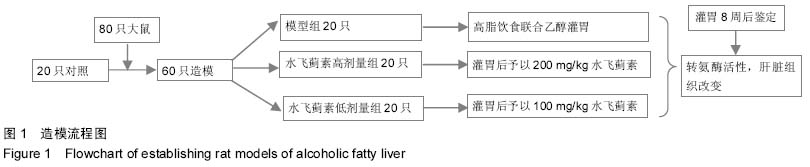
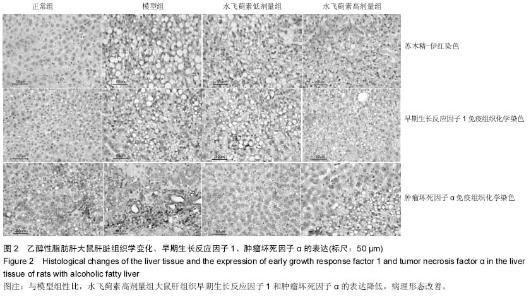
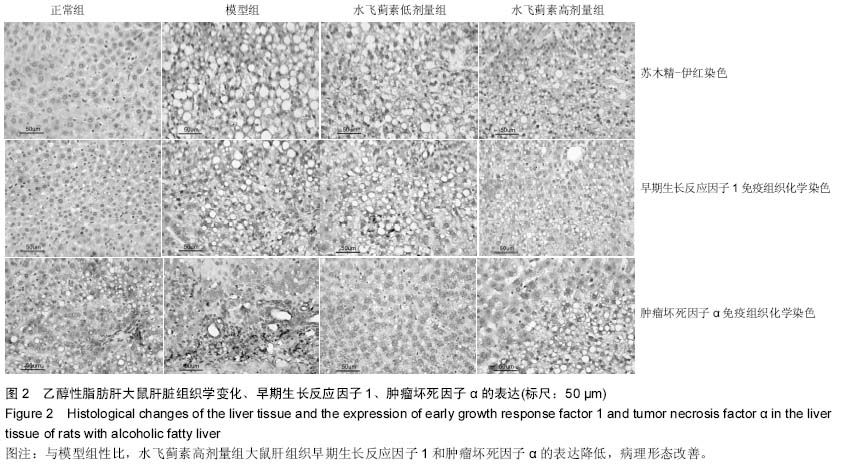
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (27): 4351-4355.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.27.016
Previous Articles Next Articles
Expression of early growth response factor 1 and intervention of silymarin in rat models of alcoholic fatty live
Zhou Hong-xing
- Department of Infectious Diseases, Huangpi District People’s Hospital, Wuhan 430300, Hubei Province, China
-
Online:2015-06-30Published:2015-06-30 -
Contact:Zhou Hong-xing, Department of Infectious Diseases, Huangpi District People’s Hospital, Wuhan 430300, Hubei Province, China -
About author:Zhou Hong-xing, Master, Associate chief physician, Department of Infectious Diseases, Huangpi District People's Hospital, Wuhan 430300, Hubei Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhou Hong-xing. Expression of early growth response factor 1 and intervention of silymarin in rat models of alcoholic fatty live[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(27): 4351-4355.
share this article
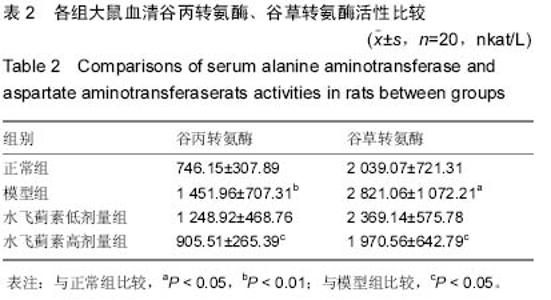
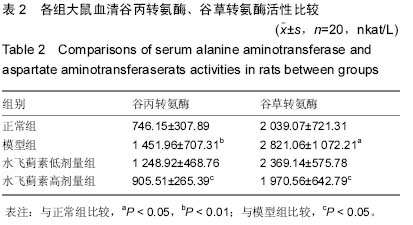
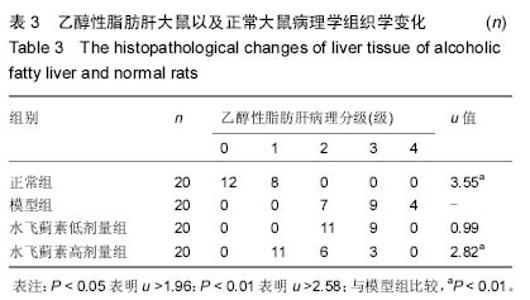
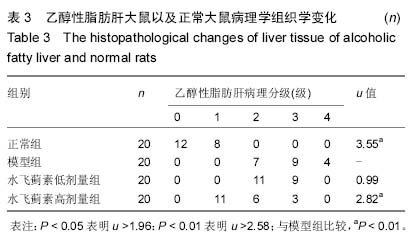
| [1] 孙屹峰,郭李柯,秦咏梅,等.参芪扶正注射液对乙醇性肝纤维化大鼠ROS, SOD, LPO, NF-κB及CTGF mRNA表达的干预作用[J].世界华人消化杂志,2012,20(16):1463-1467. [2] 田图磊.Egr-1在大鼠乙醇性脂肪肝中的表达及水飞蓟素对其干预作用[D].合肥:安徽医科大学,2013. [3] 孙惠,赵彩彦.肿瘤坏死因子α在非乙醇性脂肪性肝病中的作用机制及其综合治疗[J].河北医药,2009,31(15):1978-1978. [4] 田图磊,洪汝涛,徐德祥,等.Egr-1在大鼠乙醇性脂肪肝中的表达及水飞蓟素对其干预作用[J].安徽医药,2013,01(21):23-26. [5] 田德安,洪捷敏,刘南植,等.L-精氨酸对乙醇性肝脂肪变大鼠肝组织NOS表达及氧应激的影响[J].世界华人消化杂志, 2004,12(3): 702-705. [6] 谭海荣,吴谦,潘竞锵,等.水飞蓟宾对抗大鼠乙醇性脂肪肝作用及机制[J].中国临床药理学与治疗学,2004,9(7):803-806. [7] 徐光福,褚月虎,王晓阳,等.中药调肝理脾方对大鼠乙醇性肝病肝纤维化的影响[J].世界华人消化杂志,2006,14(24):2386-2394. [8] 梁基智,林洁茹,谭海荣,等.水飞蓟宾对抗大鼠乙醇性脂肪肝改善肝功能的作用[J].中国临床康复,2006,10(7):183-185. [9] 杨慧莹,林克荣.水飞蓟素治疗脂肪肝的作用机制[J].中华现代内科学杂志,2006,3(8):876-878. [10] 陈世林,洪汝涛,刁磊,等.水飞蓟素对大鼠急性乙醇性肝损伤的保护作用[J].安徽医科大学学报,2010,(2):209-212. [11] 苗羊,金瑞.当飞利肝宁对实验大鼠乙醇性肝损伤防治作用的实验研究[J].中医杂志,2003,44(1):21-22. [12] Woo SM, Min KJ, Kim S, et al. Silibinin induces apoptosis of HT29 colon carcinoma cells through early growth response-1 (EGR-1)-mediated non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug-activated gene-1 (NAG-1) up-regulation. Chem Biol Int. 2014;21(1):32-34. [13] Hahn SS, Tang Q, Zheng F, et al. GW1929 inhibits α7 nAChR expression through PPARγ-independent activation of p38 MAPK and inactivation of PI3-K/mTOR: the role of Egr-1. Cell Signal. 2014;2(64):15-17. [14] Schreiber WB, Asok A, Jablonski SA, et al. Egr-1 mRNA expression patterns in the prefrontal cortex, hippocampus, and amygdala during variants of contextual fear conditioning in adolescent rats. Brain Res. 2014;15(76):23-25. [15] Klenke S, Rump K, Buschkamp K, et al. Characterization of the PLCB1 promoter and regulation by early growth response transcription factor EGR-1. Eur J Pharmacol. 2014;74(2):14-16. [16] Zhang BL, Ni HB, Liu J, et al. Egr-1 participates in abnormally high gdnf gene transcription mediated by histone hyperacetylation in glioma cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014; 18(3911):12-13. [17] 祁慧,薛斌,祁慧,等. EGR-1在肝损伤中的作用[J].世界华人消化杂志,2011,19(18):1914-1921. [18] 宋奎,何群.抗氧化剂An7845对K562白血病细胞的增殖抑制和凋亡诱导活性[J].中南大学学报(医学版),2004,29(3):257-260. [19] 谢正元,文艺,张吉翔.5-脂氧合酶与肝脏疾病[J].世界华人消化杂志,2004,12(8):1905-1908. [20] Hewson AK, Dickson SL. Systemic administration of ghrelin induces Fos and Egr-1 proteins in the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus of fasted and fed rats. J Neuroendocrinol. 2000; 12(11):1047-1049. [21] Fan YY, Ye GH, Lin KZ, et al. Time-dependent expression and distribution of Egr-1 during skeletal muscle wound healing in rats. J Mol Histol. 2013;44(1):75-81. [22] 邹岚,朱波,陈敬,等.pEgr-MIP3α重组质粒的构建及其在Lewis 肺癌细胞中的辐射诱导表达[J].重庆医学,2004,33(7):968-970. [23] 李灏,姜颖,贺福初.乙醇肝毒性及治疗的研究进展[J].中国药理学与毒理学杂志,2008, 22(5):396-400. [24] Asok A, Schreiber WB, Jablonski SA, et al. Egr-1 increases in the prefrontal cortex following training in the context preexposure facilitation effect (CPFE) paradigm. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2013;106:145-153. [25] 于乐成,顾长海.水飞蓟素与乙醇性肝病[J].肝脏,2000,5(3): 182-183. [26] 冷亮,蒋卓勤,纪桂元,等.抗氧化剂防治非乙醇性脂肪肝的研究进展[J].现代预防医学,2012,39(3):564-565. [27] Weaver IC, Hellstrom IC, Brown SE, et al. The methylated-DNA binding protein MBD2 enhances NGFI-A (egr-1)-mediated transcriptional activation of the glucocorticoid receptor. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2014;369(1652). [28] Katche C, Goldin A, Gonzalez C, et al. Maintenance of long-term memory storage is dependent on late posttraining Egr-1 expression. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2012;98(3):220-227. [29] Brown KC, Lau JK, Dom AM, et al. MG624, an α7-nAChR antagonist, inhibits angiogenesis via the Egr-1/FGF2 pathway. Angiogenesis. 2012;15(1):99-114. [30] 古颖娴,吴谦,陈少娟,等.茵陈蒿汤对抗大鼠乙醇性脂肪肝作用[J].中国新医药,2004,3(7):17-19.
|
| [1] | Chen Ziyang, Pu Rui, Deng Shuang, Yuan Lingyan. Regulatory effect of exosomes on exercise-mediated insulin resistance diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4089-4094. |
| [2] | Chen Yang, Huang Denggao, Gao Yuanhui, Wang Shunlan, Cao Hui, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Luo Siqin, Xiao Jingchuan, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes the proliferation and adhesion of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3949-3955. |
| [3] | Yang Junhui, Luo Jinli, Yuan Xiaoping. Effects of human growth hormone on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3956-3961. |
| [4] | Sun Jianwei, Yang Xinming, Zhang Ying. Effect of montelukast combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on spinal cord injury in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3962-3969. |
| [5] | Gao Shan, Huang Dongjing, Hong Haiman, Jia Jingqiao, Meng Fei. Comparison on the curative effect of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells and induced islet-like cells in gestational diabetes mellitus rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3981-3987. |
| [6] | Hao Xiaona, Zhang Yingjie, Li Yuyun, Xu Tao. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing prolyl oligopeptidase on the repair of liver fibrosis in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3988-3993. |
| [7] | Liu Jianyou, Jia Zhongwei, Niu Jiawei, Cao Xinjie, Zhang Dong, Wei Jie. A new method for measuring the anteversion angle of the femoral neck by constructing the three-dimensional digital model of the femur [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3779-3783. |
| [8] | Meng Lingjie, Qian Hui, Sheng Xiaolei, Lu Jianfeng, Huang Jianping, Qi Liangang, Liu Zongbao. Application of three-dimensional printing technology combined with bone cement in minimally invasive treatment of the collapsed Sanders III type of calcaneal fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3784-3789. |
| [9] | Qian Xuankun, Huang Hefei, Wu Chengcong, Liu Keting, Ou Hua, Zhang Jinpeng, Ren Jing, Wan Jianshan. Computer-assisted navigation combined with minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar spondylolisthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3790-3795. |
| [10] | Hu Jing, Xiang Yang, Ye Chuan, Han Ziji. Three-dimensional printing assisted screw placement and freehand pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracolumbar fractures: 1-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3804-3809. |
| [11] | Shu Qihang, Liao Yijia, Xue Jingbo, Yan Yiguo, Wang Cheng. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of a new three-dimensional printed porous fusion cage for cervical vertebra [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3810-3815. |
| [12] | Wang Yihan, Li Yang, Zhang Ling, Zhang Rui, Xu Ruida, Han Xiaofeng, Cheng Guangqi, Wang Weil. Application of three-dimensional visualization technology for digital orthopedics in the reduction and fixation of intertrochanteric fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3816-3820. |
| [13] | Sun Maji, Wang Qiuan, Zhang Xingchen, Guo Chong, Yuan Feng, Guo Kaijin. Development and biomechanical analysis of a new anterior cervical pedicle screw fixation system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3821-3825. |
| [14] | Lin Wang, Wang Yingying, Guo Weizhong, Yuan Cuihua, Xu Shenggui, Zhang Shenshen, Lin Chengshou. Adopting expanded lateral approach to enhance the mechanical stability and knee function for treating posterolateral column fracture of tibial plateau [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3826-3827. |
| [15] | Zhu Yun, Chen Yu, Qiu Hao, Liu Dun, Jin Guorong, Chen Shimou, Weng Zheng. Finite element analysis for treatment of osteoporotic femoral fracture with far cortical locking screw [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3832-3837. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||