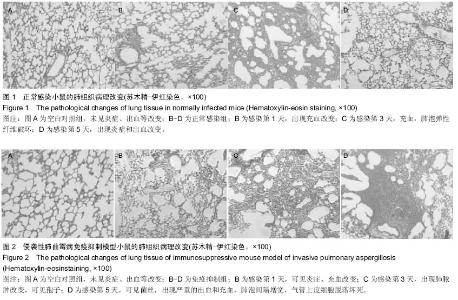
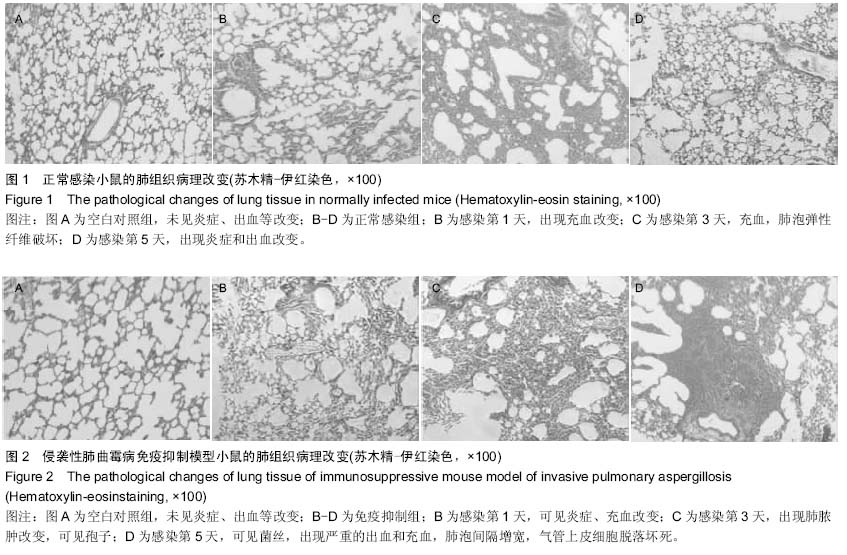
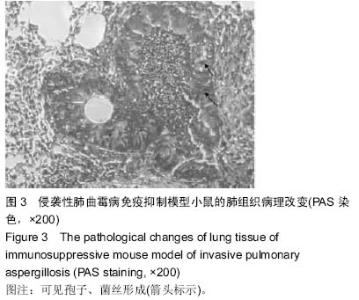
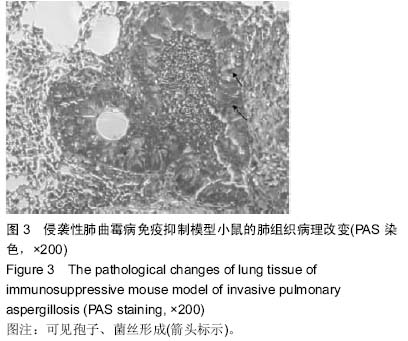
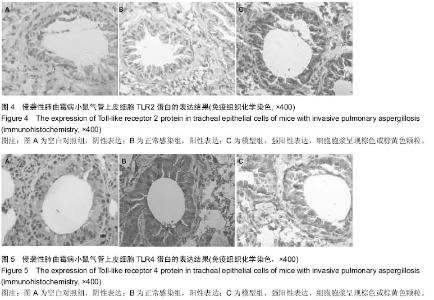
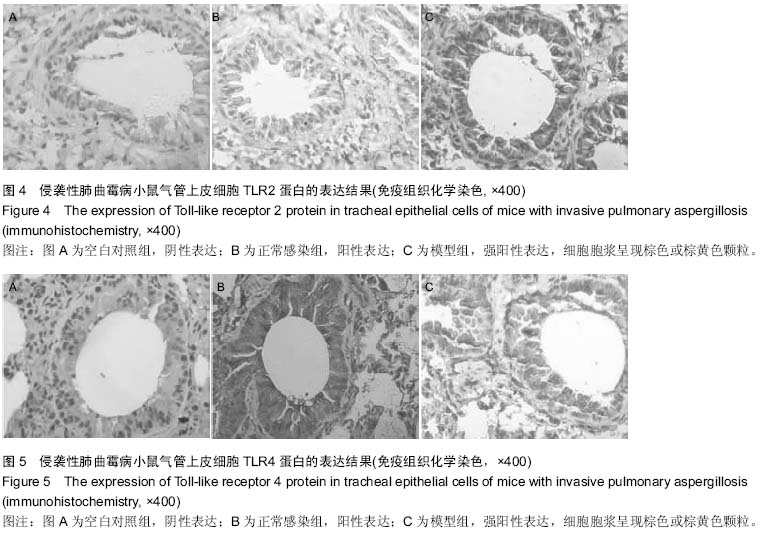
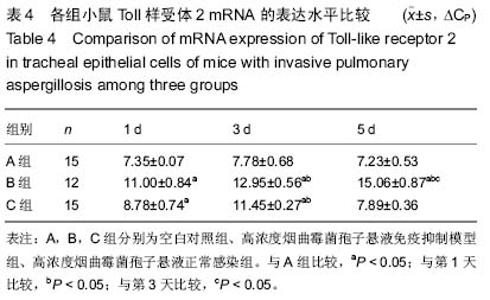
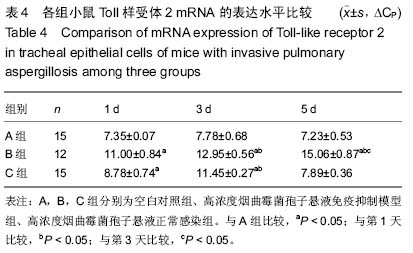
| [1] |
Mu Yufeng, Wei Lina, Wu Yong, Shao Anliang, Chen Liang, Qu Shuxin, Xu Liming.
Development and evaluation of alpha-galactosyl antigen-deficient rabbit model
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 281-285.
|
| [2] |
Fan Siqi, Zeng Ping, Nong Jiao, Liu Jinfu, Qian Xiaofen.
Effect of Tongluo Shenggu Capsule-containing serum on osteoclasts and Toll-like receptor 4/nuclear factor-kappa B signaling pathway
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(14): 2155-2160.
|
| [3] |
Yang Minjie, Liu Wei, Tu Hongfei, Li Li, Fei Sujuan.
Protective effect of crocin in ulcerative colitis rats and its related mechanism
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(29): 4673-4679.
|
| [4] |
Wang Zhen, Li Xiaolan, Liu Jianguo.
Insights into immunoregulatory properties of dental-derived mesenchymal stem cells in oral diseases
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(25): 4060-4067.
|
| [5] |
Huang Tian, Huang Xin, Lai Peilong, Geng Suxia, Chen Xiaomei, Wang Yulian, Guo Liyan, Zeng Gaochun, Han Fengzhen, Li Xiaohong, Du Xin, Weng Jianyu.
Interferon-gamma combined with lipopolysaccharide polarizes
human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells to a MSC2 phenotype
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(13): 2020-2027.
|
| [6] |
Feng Fang, Dong Chenming, Chen Yu, Qi Yan.
Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for treating septic rats with acute respiratory distress syndrome and the underlying mechanism
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(5): 741-748.
|
| [7] |
Xiang Xiaona, Yu Xi, Liu Yan, Jiang Hongying, He Chengqi, He Hongchen.
Pulsed electromagnetic fields and platelet rich plasma therapy for treatment of osteoarthritis: theoretical progress and clinical research
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(30): 4868-4874.
|
| [8] |
Feng Ruxue, Cai Rengang, Xie Dandan.
Lipopolysaccharide can influence and regulate proliferation and migration of dental pulp stem cells
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(29): 4688-4693.
|
| [9] |
Liu Jiao1, 2, 3, Qu Chongzheng2, 3, Xie Pingjin1, 2, 4, Ye Dalin1, 2, 4, Luo Zhen1, 2, 4, Liang Zhenghui1, 2, 5, Tao Jing2, 3, Jiang Ganghui2, 3 .
Changes of Toll-like receptor 4/myeloid differentiation factor 88 signal transduction in rat models of knee osteoarthritis treated with massage
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(19): 3019-3024.
|
| [10] |
Liu Ying, Gao Jie, Wu Bu-ling.
Expression of Toll-like receptor 4 in dental pulp stem cells under the stimulation of lipopolysaccharide and Streptococcus mutans
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(33): 5333-5337.
|
| [11] |
Xiong Le1, Zhang Bei1, Shen Ruo-wu2, Ji Ai-yu3, Sun Guang-qiang1, Bian Hong-lin3, Zhang Feng-yu1, Wang Yi1, Huang Heng4, Li Hua-qiao1, Zhou Shan-yu5, Shen Zhao-kang6, Wang Zhong1 .
Toll-like receptor 4 antagonist protects against Wallerian degeneration after peripheral nerve injury
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(42): 6308-6316.
|
| [12] |
Zhang Zi-li, Wang Gao-feng, Mei Dao-qi, Lin Peng-fei, Tian Ling.
TLR2 expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of Henoeh-Schonlein purpura children and its association with immune response
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(45): 7356-7361.
|
| [13] |
Zhao Jing, Yue Peng, Huang Jia-fang, Wang Yu-tao, Ma Ting, Chen Bao-rong.
MicroRNA-21 for regulation of TLR4 in Hela cells
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(2): 220-224.
|
| [14] |
Guo Zhen-xing, Chen Zhen-ping.
The role of Toll-like receptor 1 in the immunoregulatory regulation of Th17 cells by mesenchymal stem cells
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(6): 956-961.
|
| [15] |
Guo Zhen-xing, Chen Zhen-ping.
Role of Toll-like receptor 3 in the immunoregulatory function of embryonic bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on Th17 cells
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(45): 7217-7221.
|