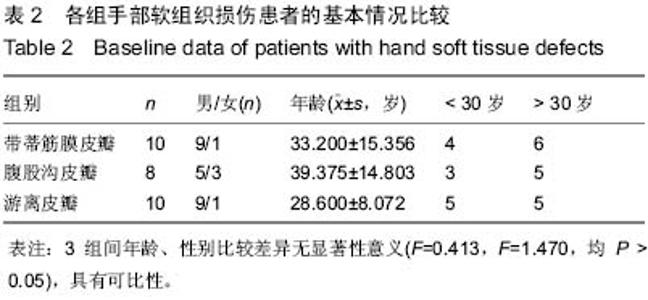
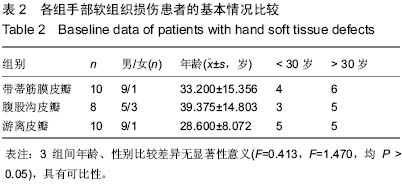
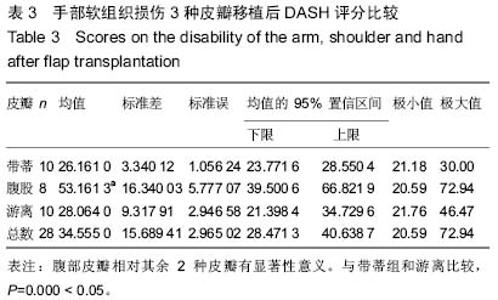
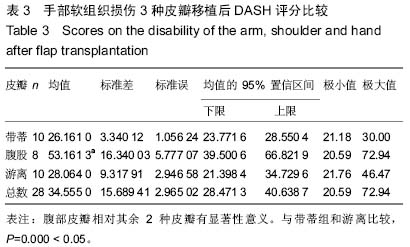
| [1] Wood J.Fisson and extroversion of the bladder with epispadias with the results of 8 cases treated by plastic operations.Med Chir Trans.1869;2:85.
[2] Davis JS.The use of the podunculated flap in reconstructive surgery. Ann Surg.1918;68:221.
[3] Germany W ,Finesilver EM,Davis JS. Estabishment of circulation in tubed skin flaps.Arch Surg.1933;26:27.
[4] McGregeor IA,Jachson IT.The extend role of the deltoppectoral flap.Br J Plast Surg.1970;23:173.
[5] Shaw DT,Payne RL.One stage tubed abdominal flaps.Sur Gynecol Obstet 1946;83:205.
[6] McGregeor IA,Jachson IT. The groin flap. Br J Plast Surg 1970;25:3.
[7] McGregeor IA,Morgan RG.Axial and random pattern flaps.Br J Plast Surg 1973;26:202
[8] Carrel A.La technique operative des anastomoses vascular res et la transplantation des visscere.Lyon Med.1920;98:859.
[9] Carrel A.Results of the transplantation of blood vessels, organs and limbs. JAMA.1908;51:1662.
[10] Jacobson JH. Suarez EL.Microsurgery in the anastomosis of small vessels. Surg Forum.1960;11:243.
[11] Bunche HJ,Schulz WP.Total ear reimplantation in the rabbit utilizing microminiature vascular anastomoses.Br J Plast Surg.1966;19:15.
[12] Bunche HJ, Bunche CM,Schulz WP.Immidiate Nicoladoni procedures in the rhesus mongkey, or hallax-to-hand transplantation, utilizing microminiature vascular anastomoses.Br J Plast Surg.1966;19:332.
[13] Strauch B,Murray DE. Transfer of composite graft with immediate suture anastomosis of vascular pedicle measuring less than 1 mm in external diameter using microsurgical techniques.Plast Reconstr Surg.1967; 40:325.
[14] Kaplan EN,Bunche HJ, Murray DE.Distant transfer of cutaneous island flaps in humans by microvascular anastomosis.Plast Reconstr Surg.1973;52:301.
[15] Taylor GI, Daniel RK.The free flap:composite tissue trausfer by vascular anastomosis.Aust NZJ Surg.1973;43:1.
[16] 郑和平,徐永清,张世民.皮神经营养血管皮瓣[M].天津:天津科技出版社,2009:2-4,45.
[17] 范存义,柴益民.实用四肢显微外科.上海:上海交通大学出版社, 2009:4-5,74-75.
[18] Wei FC,Mardinis,Free-style free flaps.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2004;114:910-916.
[19] Lister GD,McGregor IA,Jackson IT.The groin flap in the hand injuries.Injury 1973;4:229.
[20] Colson P, Houot R, Gangolphe M, et al. Use of thinned flaps (flap grefts) in reparative hand surgery.Ann Chir Plast.1967;12: 298.
[21] 蒙家辉,张文作,曾业龙,等,腹部超薄皮瓣修复手部创面的远期疗效分析.中华手外科杂志,2009,25(5):29.
[22] 常建琪,贺晓黎,张示峰.带蒂真皮下血管网皮瓣急诊修复手部创面.实用手外科杂志,2002,16(2):87-88.
[23] Smith PJ.The rascular basis of exial pattern flaps.Br J Plast Surg 1973;26:150.
[24] 官士兵,孙文海,李淑媛,等.髂腹股沟皮瓣联合股部皮瓣带蒂瓦合移植在手部大面积套脱伤治疗中的应用[J].中华手外科杂志, 2009, 25(2):81-83.
[25] 王淑娟,李晓莉,张宏山,等.腹部超薄皮瓣对手背创面急诊修复[J].河北医药,2012,34(10):1549.
[26] 蔺慧,孙雪生,李强,等.分段夹蒂法行腹部皮瓣早期断蒂的临床应用[J]. 实用骨科杂志,2013,19(4):379-380.
[27] 邢大勇,张洪艳.腹部超薄皮瓣在复杂手外伤中的应用[J].中国医药指南,2012,10(12):615-616
[28] 张昌军.腹部超薄皮瓣在手外伤中的应用分析[J].中国医学工程, 2013,21(6):148-149.
[29] Franco.D, Almeida G, Arnaut M Jr,et al.Analysis of the use of fascicutaneous flaps for immediate vulvar reconstruction.Rev Col Bras Cir.2012;39(1):54-59.
[30] 姚伟涛,蔡启卿,等.筋膜皮瓣修复四肢关节周围肿瘤术后巨大创面的应用研究[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2013,2(11): 618-622.
[31] Chan J K, Harry L, Williams G, et al. Soft-tissue recongstruction of open fractures of the lower limb: muscle versus fasciotaneous flaps. Plast Reconstr Surg,2012; 130(2): 284e-295e.
[32] Wei FC, Jain V, Ceilk N, et al. Have we found an idieal soft tissue flap? An experience with 672 anterolateral soft thigh flaps.Plast Reconstr.2002;109(7): 2219-2226.
[33] Gedebou TM, Wei FC,Linch. Clinical experience of 1284 free anterolateral thigh flaps.Handchir Mikrochir Plast Chir.2002; 34(4):239-244.
[34] 寿建国,张继东.不带筋膜且一期修薄的股前外侧穿支皮瓣修复四肢远端组织缺损.[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2013,28(1): 93-94.
[35] 邓小花,王海波.游离股前外侧皮瓣修复下肢皮肤软组织的临床应用[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2014,29(1):96-97.
[36] 谭屏,汤玉泉,曾凯生,等. 游离股前外侧穿支皮瓣修复大面积皮肤软组织缺损的临床研究[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2014, 29(增1):100-101.
|