Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (39): 5885-5891.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.39.017
Previous Articles Next Articles
Comparison of 3.0T MRI and SPECT-CT in the diagnosis of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures
Ding Chao, Sun Qiang, Tang Cheng
- Nanjing Hospital Affiliated to Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210006, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Revised:2016-07-12Online:2016-09-23Published:2016-09-23 -
Contact:孙强,副教授,南京医科大学附属南京医院骨科,江苏省南京市 210006 -
About author:Ding Chao, Studying for master’s degree, Nanjing Hospital Affiliated to Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210006, Jiangsu Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Ding Chao, Sun Qiang, Tang Cheng. Comparison of 3.0T MRI and SPECT-CT in the diagnosis of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(39): 5885-5891.
share this article
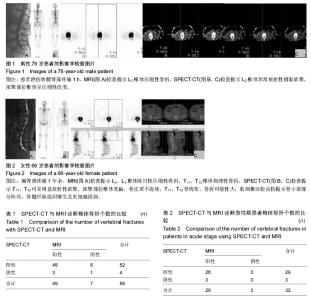
2.1 参与者数量分析 35例患者均进入结果分析。 2.2 责任椎体56个诊断结果 在35例病例中,以受累的胸腰椎体为统计单位,共有56个椎体确认责任椎体,其中MRI检查提示新鲜椎体骨折的共有49个节段;SPECT-CT检查提示新鲜椎体骨折的节段共有52个节段,其中两者检查相同椎体的有46节,见表1,图1。其中3个椎体在MRI检查下表现为阳性,在SPECT-CT检查为阴性结果;6个椎体在MRI检查下表现为阴性,在SPECT-CT检查为阳性结果。SPECT-CT检查的敏感度为92.86%(52/56),特异度为7.14%(4/56);MRI检查的敏感度为87.5%(49/56),特异度为12.5%(7/56)。以患者手术后疼痛是否缓解为标准,计算阳性预测值为93.88%(46/49),阴性预测值85.71%(6/7)。对二者进行Fisher精确检验方法比较结果,P=0.423,提示两种检验方法之间的差异不具有统计学意义,两种诊断方法效能相接近。"
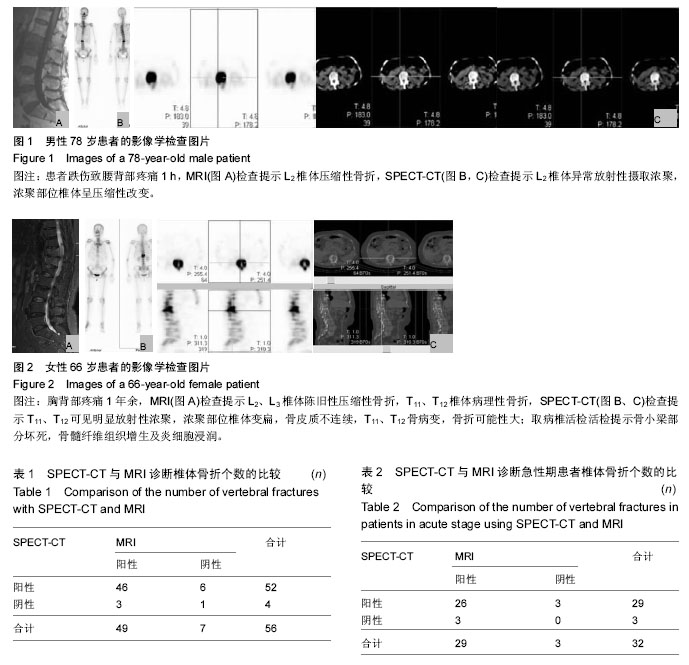
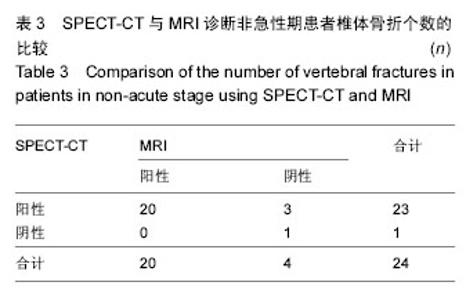
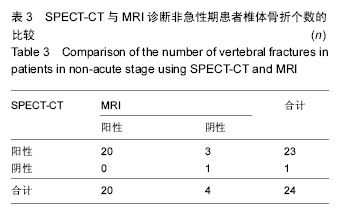
2.3 急性期22例骨折患者诊断结果 同样以受累胸腰椎体为统计单位,共有32个椎体确认为责任椎体,其中MRI符合骨质疏松性骨折诊断标准的共有29个节段;SPECT-CT检查诊断椎体骨折节段共有29个节段,其中两者检查相同椎体的有26节,见表2。其中3个椎体在MRI检查下表现为阳性,在SPECT-CT检查为阴性结果;3个椎体在MRI检查下表现为阴性,在SPECT-CT检查为阳性结果。SPECT-CT检查的敏感度为90.63%(29/32),MRI检查的敏感度为90.63%(29/32),特异度为9.38%(3/32)。以患者手术后疼痛是否缓解为标准,计算其阳性预测值为81.25%(26/32),阴性预测值100%(3/3)。两者进行Fisher精确检验比较结果,P=1,提示两种检验方法之间的差异不具有统计学意义,两种诊断方法效能相接近。 2.4 非急性期13例骨折患者诊断结果 10例亚急性期、3例愈合期,共有24个椎体确认为责任椎体,其MRI符合新鲜椎体骨折的共有20个节段;SPECT-CT检查诊断椎体骨折的节段共有23个节段,其中后两者检查相同椎体的有20节,见表3、图2。其中3个椎体在MRI检查下表现为阴性,在SPECT-CT检查为阳性结果。SPECT-CT检查的敏感度为95.83%(23/24),特异度为1.79%(1/24);MRI检查的敏感度为83.33%(20/24),特异度为16.67%(4/24)。 以患者手术后疼痛是否缓解为标准,计算其阳性预测值为100%(20/20),阴性预测值75%(3/4)。两者进行Fisher精确检验比较结果,P= 0.167,提示两种检验方法之间的差异不具有统计学意义,两种诊断方法效能相接近。"
| [1] Sun Q,Xu J,Zou XQ,et al.The efficacy of percutaneous kyphoplasty in relieving painful osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures.Chin J Osteoporos.2009;15: 820-824. [2] Werner CM,Osterhoff G,Schlickeiser J,et al.Vertebral body stenting versus kyphoplasty for the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a randomized trial.J Bone Joint Surg Am.2013;95: 577-584. [3] Pitton MB,Herber S,Koch U,et al.CT-guided vertebroplasty:analysis of technical results, extraosseous cement leakages,and complications in 500 procedures.Eur Radiol.2008;18(11):2568-2578. [4] Spiegl UJ,Beisse R,Hauck S,et al.Value of MRI imaging prior to a kyphoplasty for osteoporotic insufficiency fractures.Eur Spine J.2009;18(9): 1287-1292. [5] Papathanassion D,Bnma-Muraille C,Jouannaud C. Single-photon emission computer tomography combined with computer tomography(SPECT/CT) in bone diseases.Joint Bone Spine.2009;76(5): 474-480. [6] Hirschmann MT,Iranpour F,Davda K,et al. Combined single-photon emission computerized tomography and conventional computerized tomography (SPECT/CT): clinical value for the knee surgeons? Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc.2010;18: 341-345. [7] Husarik DB,Steinert HC.Single-photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography for sentinel node mapping in breast cancer.Semin Nucl Med.2007;37:29-33. [8] Do HM.Magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of patients for percutaneous vertebroplasty.Top Magn Reson Imaging.2000;11:235-244. [9] Baur A,Stäbler A,Arbogast S,et al.Acute osteoporotic and neoplastic vertebral compression fractures: fluid sign at MR imaging.Radiology.2002;225(3):730-735. [10] Netter F,Journo A,Mayer JC,et al.Apport de la TEMP-TDM en complément de la scintigraphie osseuse planaire dans la pratique courante du service de médecine nucléaire.Med Nucl.2008; 32: 76-84. [11] Bunyaviroch T,Aggarwal A,Oates ME.Optimized scintigraphic evaluation of infection and inflammation: role of single-photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography fusion imaging. Semin Nucl Med.2006;36(4):295-311. [12] Gaitanis IN,Hadjipavlou AG,Katonis PG,et al.Balloon kyphoplasty for the treatment of pathological vertebral compressive fractures.Eur Spine J.2005;14(3): 250-260. [13] van Dijk WA,Poeze M,van Helden SH,et al.Ten-year mortality among hospitalised patients with fractures of the pubic rami.Injury.2009;41:411-414. [14] Parmar R,Redfern DR,Hill JC. Comments on: role of bone scintigraphy.Ann R Coll Surg Engl.2006;88: 516-517. [15] Langdon J,Way A,Heaton S,et al.Vertebral compression fractures new clinical signs to aid diagnosis.Arm R Coll Surg Enngl.2010;92(2): 163-166. [16] Horger M,Bares R.The role of single-photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography in benign and malignant bone disease.Semin Nucl Med. 2006;36(4):286-289. [17] Hirschmann MT,Davda K,Rasch H,et al.Clinical value of combined single photon emission computerized tomography and conventional computer tomography (SPECT/CT) in sports medicine.Sports Med Arthrosc. 2011;19:174-181. [18] Navalkissoor S,Nowosinska E,Gnanasegaran G,et al. Single-photon emission computed tomography- computed tomography in imaging infection.Nucl Med Commun.2013;34:283-290. [19] 高化,李锦军,王炳强,等.磁共振成像与核素骨显像对骨质疏松性椎体骨折诊断的比较[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2011, 8(21):657-659. [20] Irani FG,Morales JP,Sabharwal T,et al.Successful treatment of a chronic post-traumatic 5-year-old osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture by percutaneous vertebroplasty.Br J Radiol.2005;78: 261-264. [21] Palestro CJ,Love C,Schneider R.The evolution of nuclear medicine and the musculoskeletal system.Radiol Clin N Am.2009;47:505-532. [22] Shen F,Yan ZQ,Guo CA,et al.Prediction of traumatic avascular necrosis of the femoral head by single photon emission computerized tomography and computerized tomography: an experimental study in dogs.Chin J Traumatol.2011;14(4):227-232. [23] More AE,Blake GM,Taylor KA,et al.Changes observed in radionuclide bone scans and after teriparatide treatment for osteoporosis.Eur J Nuel Med Mol Imaging. 2012;9(2):326-336. [24] Matin P.Bone scintigraphy in the diagnosis and management of traumatic injury.Semin Nucl Med. 1983; 13:104-122. [25] Bredella MA,Essary BA,Torriani M,et al.Use of FDG-PET in differentiating benign from maligant compression fractures.Skeletal Radiol.2008;37(5): 405-413. [26] Langdon J,Way A,Heaton S,et al.Vertebral compression fractures new clinical signs to aid diagnosis.Arm R Coll Surg Enngl.2010;92(2):163-166. [27] Zukotynski K,Curtis C,Grant FD,et al.The value of SPECT in the detection of stress injury to the pars interarticularis in patients with low back pain.J Orthop Surg Res. 2010;5:13. [28] Bayer LR,Widding A,Diemer H.Fifteen minutes bone scintigraphy in patients with clinically suspected scaphoid fracture and normal x-rays.Injury.2000;31: 243-248. [29] Ohishi T,Takahashi M,Yamanashi A,et al.Sequential changes of bone metabolism in normal and delayed union of the spinel.Clin Orthop Relat Res.2008;466: 402-410. [30] 江晓兵,莫凌,姚珍松,等.SPECT、SPECT-CT 与 MRI 对新鲜骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的诊断价值[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2013,23(10):891-897. |
| [1] | Shi Bin, An Jing, Chen Long-gang, Zhang Nan, Tian Ye . Influencing factors for pain after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 993-997. |
| [2] | Wang Xian-xun. Impact of local compression cryotherapy combined with continuous passive motion on the early functional recovery after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 998-1003. |
| [3] | Yuan Wei, Zhao Hui, Ding Zhe-ru, Wu Yu-li, Wu Hai-shan, Qian Qi-rong. Association between psychological resilience and acute mental disorders after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1015-1019. |
| [4] | Chen Qun-qun, Qiao Rong-qin, Duan Rui-qi, Hu Nian-hong, Li Zhao, Shao Min. Acu-Loc®2 volar distal radius bone plate system for repairing type C fracture of distal radius [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1025-1030. |
| [5] | Huang Xiang-wang, Liu Hong-zhe. A new low elastic modulus of beta titanium alloy Ti2448 spinal pedicle screw fixation affects thoracic stability: biomechanical analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1031-1035. |
| [6] | Xie Qiang. Three-dimensional finite element model for biomechanical analysis of stress in knee inversion and external rotation after posterior cruciate ligament rupture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1036-1040. |
| [7] | He Ze-dong, Zhao Jing, Chen Liang-yu, Li Ke, Weng Jie. Multilevel finite element analysis on the biological tribology damage of water on bone tissue [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1041-1045. |
| [8] | Jiang Zi-wei, Huang Feng, Cheng Si-yuan, Zheng Xiao-hui, Sun Shi-dong, Zhao Jing-tao, Cong Hai-chen,Sun Han-qiao, Dong Hang. Design and finite element analysis of digital splint [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1052-1056. |
| [9] | Wang Fei, Liu Zhi-bin, Tao Hui-ren, Zhang Jian-hua, Li Chang-hong, Cao Qiang, Zheng Jun, Liu Yan-xiong, Qu Xiao-peng. Clinical efficacy of preoperative osteotomy designs using paper-cut technology versus photoshop software for ankylosing spondylitis with kyphosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1057-1063. |
| [10] | Li Hui, Ma Jun-yi, Ma Yuan, Zhu Xu . Establishment of a three-dimensional finite element model of ankylosing spondylitis kyphosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1069-1073. |
| [11] | Ling Guan-han, Ou Zhi-xue, Yao Lan, Wen Li-chun, Wang Guo-xiang, Lin Heng-feng. Establishment of simulating three-dimensional model of China-Japan Friendship Hospital Classification for L type osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1074-1079. |
| [12] | Fu Wei-min, Wang Ben-jie. Assessing the degree of necrotic femoral head, and association of blood supply with pathlogical changes: study protocol for a diagnostic animal trial [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1086-1091. |
| [13] | Zhang Wen-qiang, Ding Qian, Zhang Na. Associations between alpha angle and herniation pit on oblique axial magnetic resonance imaging in asymptomatic hip joints of adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1098-1103. |
| [14] | Sun Xiao-xin1, Zhou Wei2, Zuo Shu-ping3, Liu Hao1, Song Jing-feng1, Liang Chun-yu1. Morphological characteristics for the magnetic resonance imaging assessment of discoid lateral meniscal tears in children [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1104-1109. |
| [15] | Lin Han-wen, Wen Jun-mao, Huang Chao-yuan, Zhou Chi, Tang Hong-yu. Correlation between the changes in lower limb power line and pain area in the knee osteoarthritis patients: imaging evaluation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1110-1114. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||