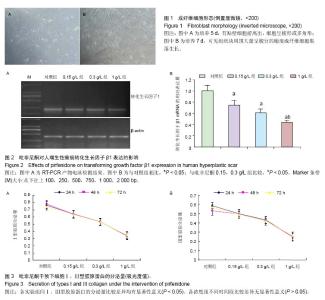
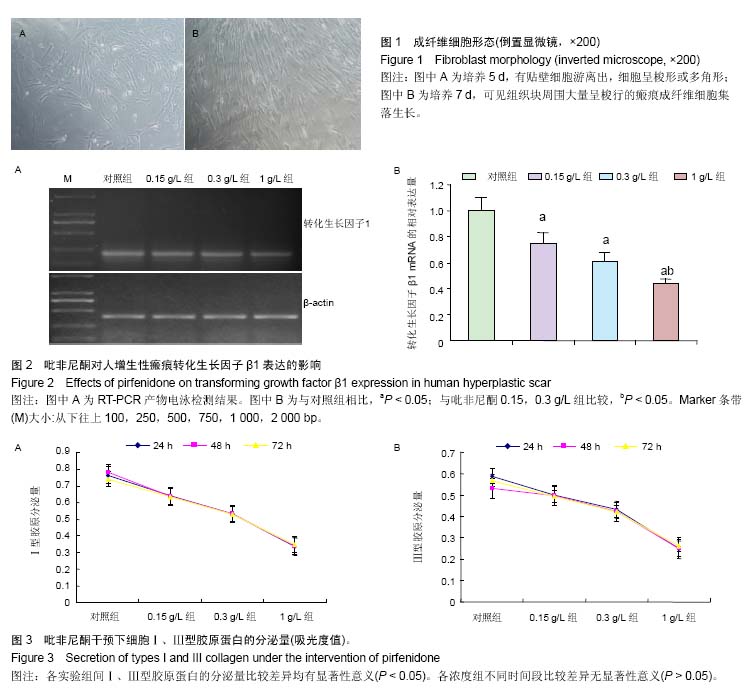
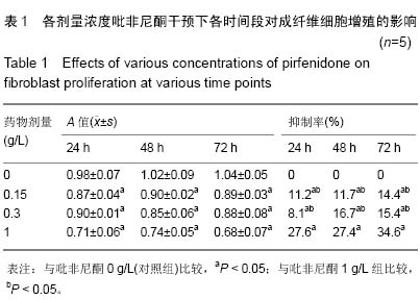
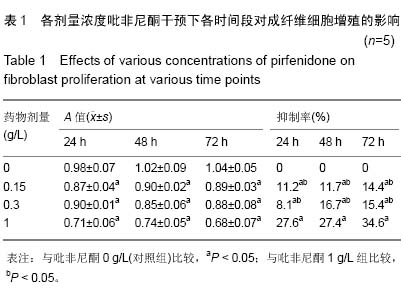
| [1] Monica CTB, Willem MVV, Magda MWU, et al. Prevention and curative management of hypertrophic scar formation. Burns. 2009;35(4):463-475.
[2] Verhaegen PD, van Zuijlen PP, Pennings NM, et al. Differences in collagen architecture between keloid, hypertrophic scar, normotrophic scar, and normal skin: An objective histopathological analysis. Wound Repair Regen. 2009;17(5):649-656.
[3] Corr DT, Hart DA. Biomechanics of Scar Tissue and Uninjured Skin. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2013;2(2):37-43.
[4] Tan J, Fu JF. Effects of pressure therapy on the proliferation and apoptosis of cells in hypertrophic scar of burn patients. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2013;29(6):509-515.
[5] Koike S, Akaishi S, Nagashima Y, et al. Nd: YAG Laser Treatment for Keloids and Hypertrophic Scars: An Analysis of 102 Cases. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2015;2(12):e272.
[6] Krakowski AC, Goldenberg A, Eichenfield LF, et al. Ablative fractional laser resurfacing helps treat restrictive pediatric scar contractures. Pediatrics. 2014;134(6):e1700-e1705.
[7] Capon A, Iarmarcovai G, Mordon S. Laser-assisted skin healing (LASH) in hypertrophic scar revision. J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2009;11(4):220-223.
[8] Huang L, Cai YJ, Lung I, et al. A study of the combination of triamcinolone and 5-fluorouracil in modulating keloid fibroblasts in vitro. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2013;66(9): 251-259.
[9] Jenwitheesuk K, Surakunprapha P, Jenwitheesuk K, et al. Role of silicone derivative plus onion extract gel in presternal hypertrophic scar protection: a prospective randomized, double blinded, controlled trial. Int Wound J. 2012;9(4): 397-402.
[10] Lu SW, Zhang XM, Luo HM, et al. Clodronate liposomes reduce excessive scar formation in a mouse model of burn injury by reducing collagen deposition and TGF-β1 expression. Mol Biol Rep. 2014;41(4):2143-2149.
[11] Cottin V, Maher T. Long-term clinical and real-world experience with pirfenidone in the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur Respir Rev. 2015;24(135):58-64.
[12] Jones MG, Fletcher S, Richeldi L. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: recent trials and current drug therapy. Respiration. 2013;86(5):353-363.
[13] Takano M, Yamamoto C, Yamaguchi K, et al. Analysis of TGF-β1- and drug-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cultured alveolar epithelial cell line RLE/Abca3. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2015;30(1):111-118.
[14] Kim ES, Keating GM. Pirfenidone: a review of its use in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Drugs. 2015;75(2):219-230.
[15] Wang Y, Wu Y, Chen J, et al. Pirfenidone attenuates cardiac fibrosis in a mouse model of TAC-induced left ventricular remodeling by suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome formation. Cardiology. 2013;126(1):1-11.
[16] Regulatory watch Pirfenidone: First drug for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis approved in Japan. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2008;7(12):966-967.
[17] Tzouvelekis A, Bonella F, Spagnolo P. Update on therapeutic management of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2015;3(11):359-370.
[18] Duck A, Pigram L, Errhalt P, et al. IPF Care: A Support Program for Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Treated with Pirfenidone in Europe. Adv Ther. 2015;32(2): 87-107.
[19] 吴尚辉,罗学滨,祝斌,等.人瘢痕组织成纤维细胞的培养[J].实用预防医学,2005,12(2):406-407.
[20] Lin X, Yu M, Wu K, et al. Effects of pirfenidone on proliferation, migration, and collagen contraction of human Tenon's fibroblasts in vitro. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2009;50(8): 3763-3770.
[21] Lee K, Young Lee S, Park SY et al. Antifibrotic effect of pirfenidone on human pterygium fibroblasts. Curr Eye Res. 2014;39(7):680-685.
[22] Ji X, Naito Y, Weng H, et al. Renoprotective mechanisms of pirfenidone in hypertension-induced renal injury: through anti-fibrotic and anti-oxidative stress pathways. Biomed Res. 2013;34(6):309-319.
[23] Choi J, Lee EH, Park SW, et al. Regulation of Transforming Growth Factor β1, Platelet-Derived Growth Factor, and Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor by Silicone Gel Sheeting in Early-Stage Scarring. Arch Plast Surg. 2015;42(1):20-27.
[24] Wu C, Jiang J, Boye A, etal. Compound Astragalus and Salvia miltiorrhiza extract suppresses rabbits' hypertrophic scar by modulating the TGF-β/Smad signal. Dermatology. 2014; 229(4):363-368.
[25] Kim WS, Lee JS, Bae GY, et al. Extract of Aneilema keisak inhibits transforming growth factor-β-dependent signalling by inducing Smad2 downregulation in keloid fibroblasts. Exp Dermatol. 2013;22(1):69-71.
[26] Dabiri G, Campaner A, Morgan JR, et al. A TGF-beta1- dependent autocrine loop regulates the structure of focal adhesions in hypertrophic scar fibroblasts. J Invest Dermatol. 2006;126(5):963-970.
[27] Li JH, Huang ZM, Du SH, et al. Effect of tensile stress on human heel skin fibroblast proliferation in vitro. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2014;27(10):838-842.
[28] Colwell AS, Phan TT, Kong W, et al. Hypertrophic scar fibroblasts have increased connective tissue growth factor expression after transforming growth factor-beta stimulation. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2005;116(5):1387-1392.
[29] 谢举临,利天增,祁少海,等.转化生长因子β1对培养的瘢痕成纤维细胞增殖的调控作用[J].中国组织化学与细胞化学杂志,2006, 15(1):31-33.
[30] Wu CF, Chiang WC, Lai CF, et al. Transforming growth factor β-1 stimulates profibrotic epithelial signaling to activate pericyte-myofibroblast transition in obstructive kidney fibrosis. Am J Pathol. 2013;182(1):118-131. |