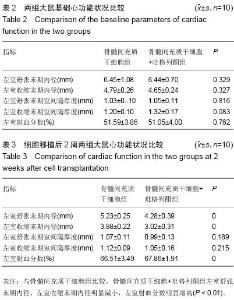
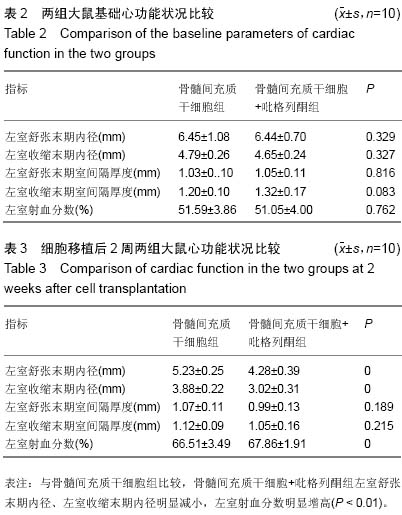
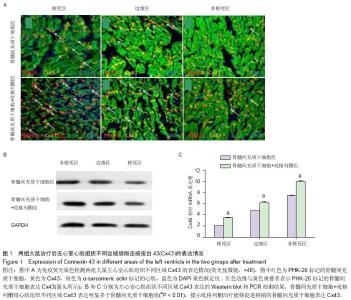
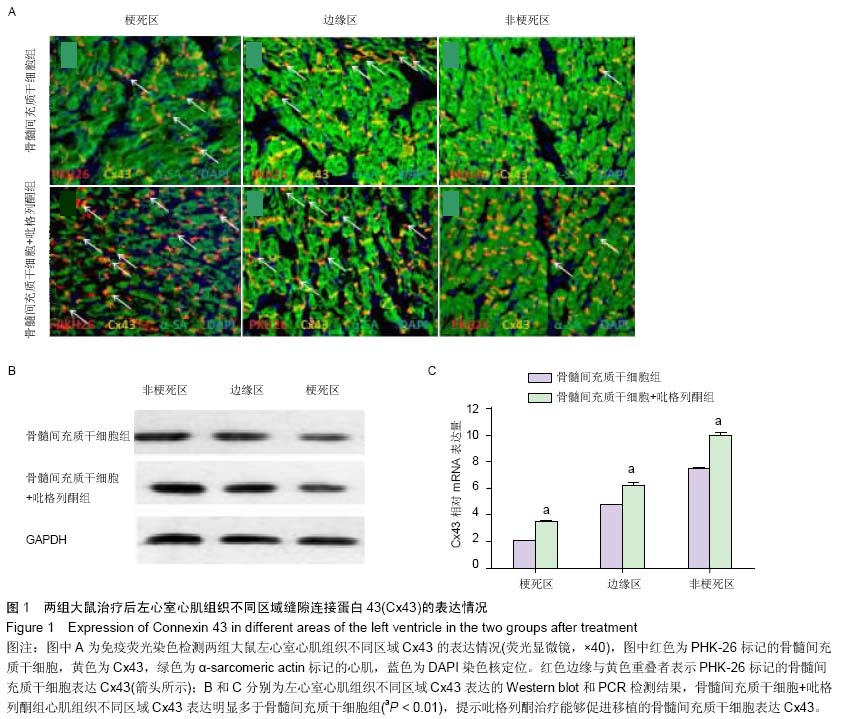
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (23): 3698-3704.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.23.016
Previous Articles Next Articles
Pioglitazone administration combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells transplantation improved the heart function of rats with myocardial infarction
Wu Quan-hua, Hou Jing-ying, Guo Tian-zhu, Zhong Ting-ting, Long Hui-bao, Xing Yue, Zhou Chang-qing, Zheng Shao-xin, Wang Tong
- Department of Emergency, Sun Yat-sen Memorial Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510120, Guangdong Province, China
-
Online:2015-06-04Published:2015-06-04 -
Contact:Wang Tong, M.D., Doctoral supervisor, Professor, Chief physician, Researcher, Department of Emergency, Sun Yat-sen Memorial Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510120, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Wu Quan-hua, Studying for master’s degree, Attending physician, Department of Emergency, Sun Yat-sen Memorial Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510120, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81070125, 81270213; the Science and Technology Plan of Guangdong Province, No. 2010B031600032; the Fundamental Research Funds for Young Teacher Culture in Sun Yat-sen University, No. 13ykzd16
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wu Quan-hua, Hou Jing-ying, Guo Tian-zhu, Zhong Ting-ting, Long Hui-bao, Xing Yue, Zhou Chang-qing, Zheng Shao-xin, Wang Tong. Pioglitazone administration combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells transplantation improved the heart function of rats with myocardial infarction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(23): 3698-3704.
share this article
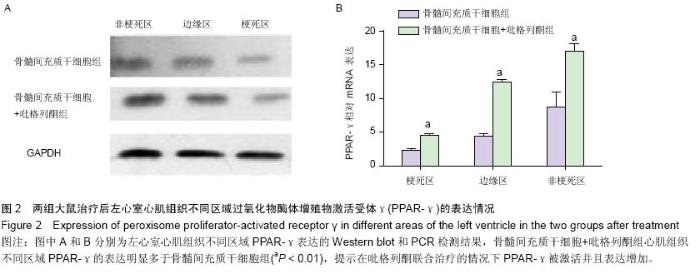
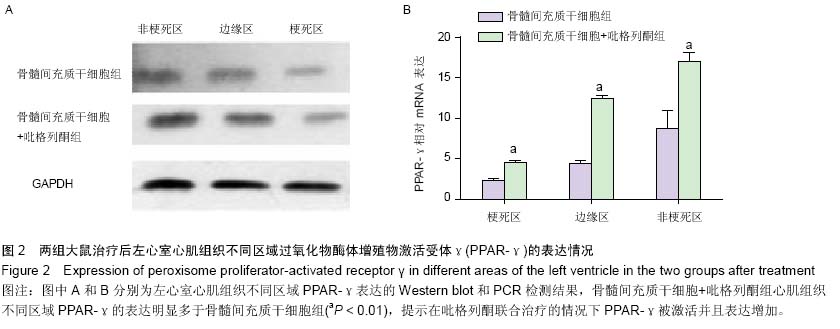
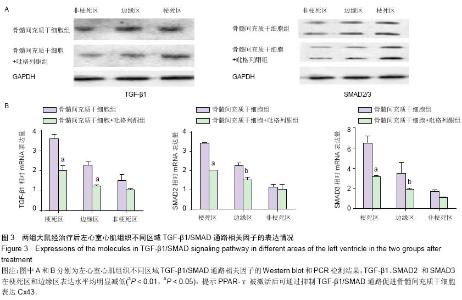
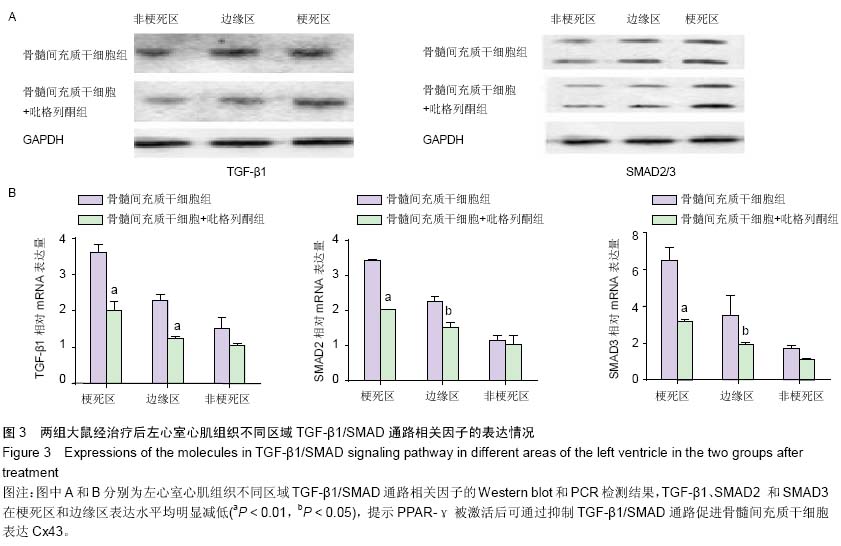
| [1] Pavo N, Charwat S, Nyolczas N, et al. Cell therapy for human ischemic heart diseases: critical review and summary of the clinical experiences. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2014;75:12-24. [2] Wen Z, Zheng S, Zhou C, et al. Repair mechanisms of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in myocardial infarction. J Cell Mol Med. 2011;15(5):1032-1043. [3] Wang T, Tang W, Sun S, et al. Intravenous infusion of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improves myocardial function in a rat model of myocardial ischemia. Crit Care Med. 2007;35(11):2587-2593. [4] Wang T, Tang W, Sun S, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells improve outcomes of cardiopulmonary resuscitation in myocardial infarcted rats. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2009;46(3): 378-384. [5] Wang T, Tang W, Sun S, et al. Improved outcomes of cardiopulmonary resuscitation in rats with myocardial infarction treated with allogenic bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Crit Care Med. 2009;37(3):833-839. [6] Xing Y, Hou J, Guo T, et al. microRNA-378 promotes mesenchymal stem cell survival and vascularization under hypoxic-ischemic conditions in vitro. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2014; 5(6):130. [7] Veeraraghavan R, Poelzing S, Gourdie RG. Old cogs, new tricks: a scaffolding role for connexin43 and a junctional role for sodium channels. FEBS Lett. 2014;588(8):1244-1248. [8] Severs NJ, Bruce AF, Dupont E, et al. Remodelling of gap junctions and connexin expression in diseased myocardium. Cardiovasc Res. 2008;80(1):9-19. [9] Wang D, Shen W, Zhang F, et al. Connexin43 promotes survival of mesenchymal stem cells in ischaemic heart. Cell Biol Int. 2010;34(4):415-423. [10] Taniguchi Ishikawa E, Gonzalez-Nieto D, Ghiaur G, et al. Connexin-43 prevents hematopoietic stem cell senescence through transfer of reactive oxygen species to bone marrow stromal cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109(23):9071- 9076. [11] Takada I, Makishima M. PPARγ ligands and their therapeutic applications: a patent review (2008 - 2014). Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2015;25(2):175-191. [12] Shinmura D, Togashi I, Miyoshi S, et al. Pretreatment of human mesenchymal stem cells with pioglitazone improved efficiency of cardiomyogenic transdifferentiation and cardiac function. Stem Cells. 2011;29(2):357-366. [13] Qi HP, Wang Y, Zhang QH, et al. Activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) through NF-κB/Brg1 and TGF-β1 pathways attenuates cardiac remodeling in pressure-overloaded rat hearts. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015; 35(3):899-912. [14] Jeon KI, Kulkarni A, Woeller CF, et al. Inhibitory effects of PPARγ ligands on TGF-β1-induced corneal myofibroblast transformation. Am J Pathol. 2014;184(5):1429-1445. [15] Copland IB, Lord-Dufour S, Cuerquis J, et al. Improved autograft survival of mesenchymal stromal cells by plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 inhibition.Stem Cells. 2009;27(2):467-477. [16] Lu F, Zhao X, Wu J, et al. MSCs transfected with hepatocyte growth factor or vascular endothelial growth factor improve cardiac function in the infarcted porcine heart by increasing angiogenesis and reducing fibrosis. Int J Cardiol. 2013; 167(6):2524-2532. [17] Yu YS, Shen ZY, Ye WX, et al. AKT-modified autologous intracoronary mesenchymal stem cells prevent remodeling and repair in swine infarcted myocardium. Chin Med J (Engl). 2010;123(13):1702-1708. [18] Usuda D, Kanda T. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors for hypertension. World J Cardiol. 2014;6(8): 744-754. [19] Lecarpentier Y, Claes V, Hébert JL. PPARs, Cardiovascular Metabolism, and Function: Near- or Far-from-Equilibrium Pathways. PPAR Res. 2010;2010. pii: 783273. [20] Nagashima A, Watanabe R, Ogawa M, et al. Different roles of PPAR-γ activity on physiological and pathological alteration after myocardial ischemia. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2012; 60(2):158-164. [21] Werner CM, Schirmer SH, Gensch C, et al. The dual PPARα/γ agonist aleglitazar increases the number and function of endothelial progenitor cells: implications for vascular function and atherogenesis. Br J Pharmacol. 2014;171(10):2685- 2703. [22] Zhao Q, Ye X. Additive value of adult bone-marrow-derived cell transplantation to conventional revascularization in chronic ischemic heart disease: a systemic review and meta-analysis. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2011;11(12):1569-1579. [23] Wang CH, Ciliberti N, Li SH, et al. Rosiglitazone facilitates angiogenic progenitor cell differentiation toward endothelial lineage: a new paradigm in glitazone pleiotropy. Circulation. 2004;109(11):1392-1400. [24] Zambrano S, Blanca AJ, Ruiz-Armenta MV, et al. L-carnitine attenuates the development of kidney fibrosis in hypertensive rats by upregulating PPAR-γ. Am J Hypertens. 2014;27(3): 460-470. [25] Fan F, Li Y, Duan X, et al. Rosiglitazone attenuates activation of human Tenon's fibroblasts induced by transforming growth factor-β1. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2012;250(8): 1213-1220. [26] Kim E, Fishman GI. Designer gap junctions that prevent cardiac arrhythmias. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2013;23(2): 33-38. [27] Hesketh GG, Shah MH, Halperin VL, et al. Ultrastructure and regulation of lateralized connexin43 in the failing heart. Circ Res. 2010;106(6):1153-1163. [28] Bacova B, Radosinska J, Knezl V, et al. Omega-3 fatty acids and atorvastatin suppress ventricular fibrillation inducibility in hypertriglyceridemic rat hearts: implication of intracellular coupling protein, connexin-43. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2010; 61(6):717-723. [29] Neuhaus J, Heinrich M, Schwalenberg T, et al. TGF-beta1 inhibits Cx43 expression and formation of functional syncytia in cultured smooth muscle cells from human detrusor. Eur Urol. 2009;55(2):491-497. [30] de Oliveira FL, Araújo-Jorge TC, de Souza EM, et al. Oral administration of GW788388, an inhibitor of transforming growth factor beta signaling, prevents heart fibrosis in Chagas disease. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2012;6(6):e1696. [31] Hou J, Wang L, Yan P, et al. Angiotensin II downregulates connexin 43 via TGF-β1 mediated signaling pathways in a rat model of myocardial infarction. Exp Clin Cardiol. 2014; 20(8): 2905-2940. |
| [1] | Jiang Tao, Ma Lei, Li Zhiqiang, Shou Xi, Duan Mingjun, Wu Shuo, Ma Chuang, Wei Qin. Platelet-derived growth factor BB induces bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to differentiate into vascular endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3937-3942. |
| [2] | Chen Yang, Huang Denggao, Gao Yuanhui, Wang Shunlan, Cao Hui, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Luo Siqin, Xiao Jingchuan, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes the proliferation and adhesion of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3949-3955. |
| [3] | Zhang Lishu, Liu Anqi, He Xiaoning, Jin Yan, Li Bei, Jin Fang. Alpl gene affects the therapeutic effect of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on ulcerative colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3970-3975. |
| [4] | Ruan Guangping, Yao Xiang, Liu-Gao Miyang, Cai Xuemin, Li Zian, Pang Rongqing, Wang Jinxiang, Pan Xinghua. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for traumatic systemic inflammatory response syndrome in tree shrews [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3994-4000. |
| [5] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [6] | Chen Lei, Zheng Rui, Jie Yongsheng, Qi Hui, Sun Lei, Shu Xiong. In vitro evaluation of adipose-derived stromal vascular fraction combined with osteochondral integrated scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3487-3492. |
| [7] | Wei Qin, Zhang Xue, Ma Lei, Li Zhiqiang, Shou Xi, Duan Mingjun, Wu Shuo, Jia Qiyu, Ma Chuang. Platelet-derived growth factor-BB induces the differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into osteoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2953-2957. |
| [8] | Chen Xiao, Guo Zhi, Chen Lina, Liu Xuanyong, Zhang Yihuizhi, Li Xumian, Wang Yueqiao, Wei Liya, Xie Jing, Lin Li. Factors affecting the mobilization and collection of autologous peripheral blood hematopoietic stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2958-2962. |
| [9] | Guo Zhibin, Wu Chunfang, Liu Zihong, Zhang Yuying, Chi Bojing, Wang Bao, Ma Chao, Zhang Guobin, Tian Faming. Simvastatin stimulates osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2963-2968. |
| [10] | Li Congcong, Yao Nan, Huang Dane, Song Min, Peng Sha, Li Anan, Lu Chao, Liu Wengang. Identification and chondrogenic differentiation of human infrapatellar fat pad derived stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2976-2981. |
| [11] | Gao Yuanhui, Xiang Yang, Cao Hui, Wang Shunlan, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang, Huang Denggao. Comparison of biological characteristics of adipose derived mesenchymal stem cells in Wuzhishan inbreed miniature pigs aged two different months [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2988-2993. |
| [12] | Cao Yang, Zhang Junping, Peng Li, Ding Yi, Li Guanghui. Isolation and culture of rabbit aortic endothelial cells and biological characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3000-3003. |
| [13] | Dai Min, Wang Shuai, Zhang Nini, Huang Guilin, Yu Limei, Hu Xiaohua, Yi Jie, Yao Li, Zhang Ligang. Biological characteristics of hypoxic preconditioned human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3004-3008. |
| [14] | Qin Yanchun, Rong Zhen, Jiang Ruiyuan, Fu Bin, Hong Xiaohua, Mo Chunmei. Chinese medicine compound preparation inhibits proliferation of CD133+ liver cancer stem cells and the expression of stemness transcription factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3016-3023. |
| [15] | Dai Yaling, Chen Lewen, He Xiaojun, Lin Huawei, Jia Weiwei, Chen Lidian, Tao Jing, Liu Weilin. Construction of miR-146b overexpression lentiviral vector and the effect on the proliferation of hippocampal neural stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3024-3030. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||