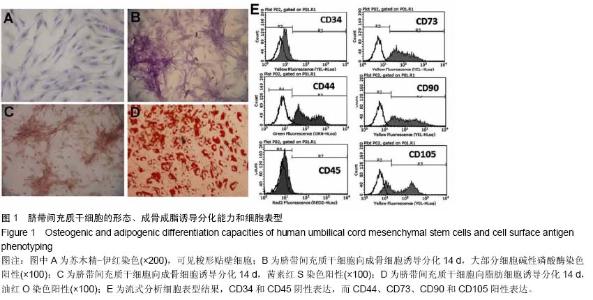
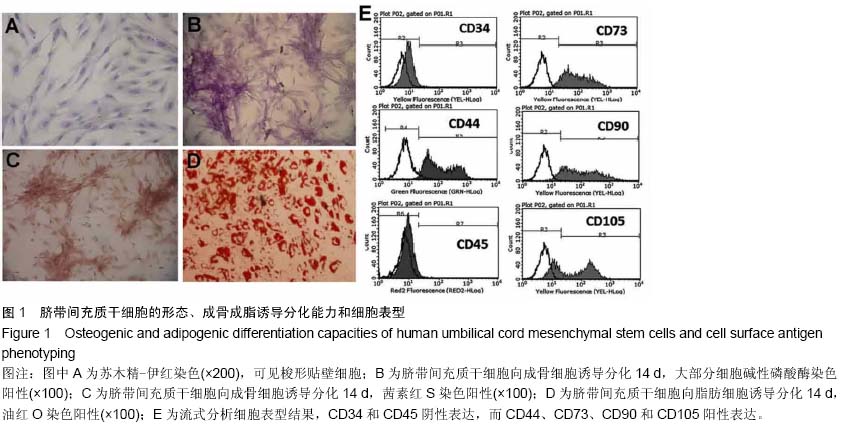
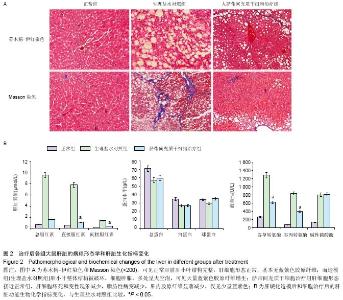
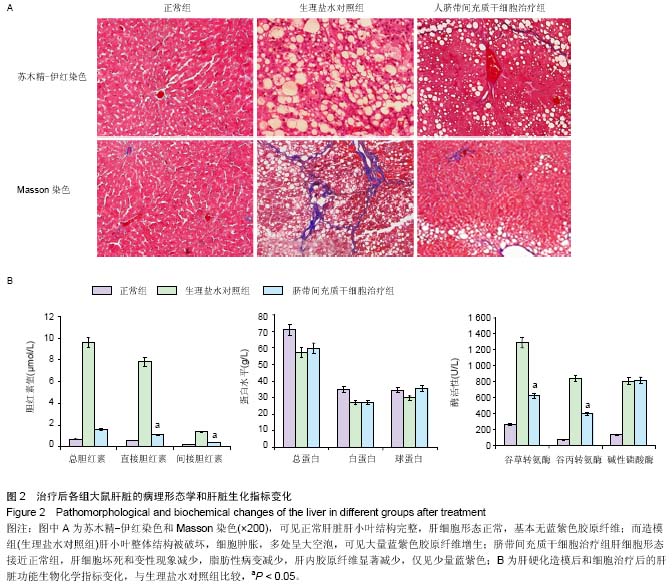
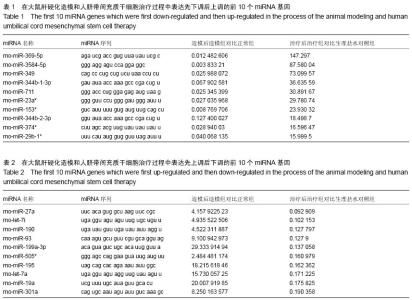
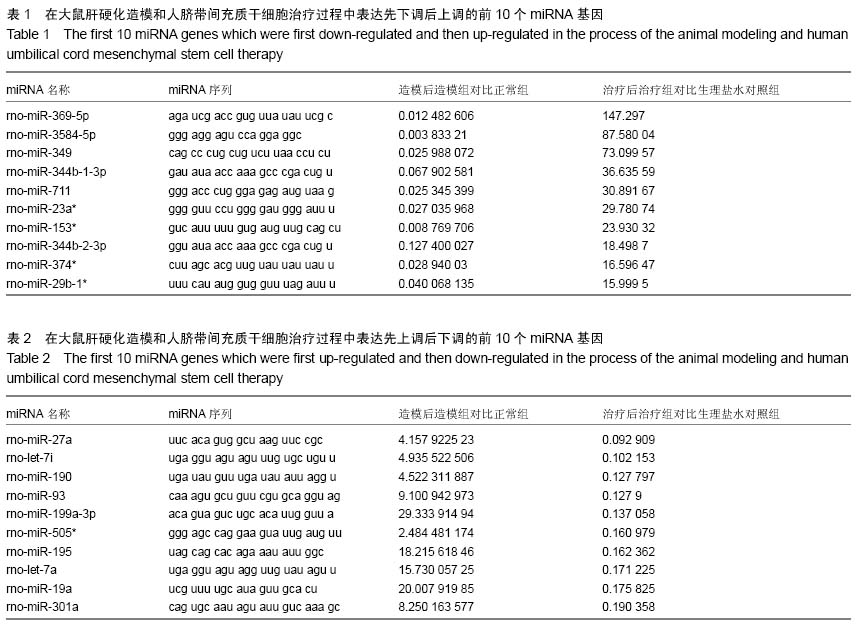
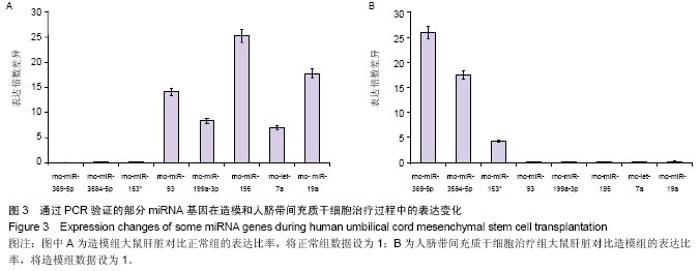
| [1] |
Cheng Gang, Huang Denggao, Liang Ying.
Hepatocyte-like cells derived from induced pluripotent stem cells inhibit liver fibrosis in rats
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(9): 1384-1389.
|
| [2] |
Wang Yifei, Song Yang, Guan Yongge, Xu Chunyan.
Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in a rat model of thin endometrium based on HOXA10 regulatory network
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(9): 1397-1402.
|
| [3] |
Zhang Deguo, Tan Xueying, Tang Nan, Huang Fei, Shi Guangjun.
Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation via the tail vein for acute liver failure in rats
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(9): 1416-1421.
|
| [4] |
Liu Meilin, Fu Songtao, Wang Peisen, Hao Ran, Chang Bingmei, Hou Xiuying.
Liposome prepared from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium for repair of skin wound in rats
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(5): 734-740.
|
| [5] |
Feng Fang, Dong Chenming, Chen Yu, Qi Yan.
Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for treating septic rats with acute respiratory distress syndrome and the underlying mechanism
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(5): 741-748.
|
| [6] |
Wei Dongjue1, Ye Dongmei2, Zhang Fengying1, Zhou Ying1, Wang Zhenchang3.
Changes of microcirculation disturbance in model rat liver treated with Rougan Huaxian Granule
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(3): 453-457.
|
| [7] |
Zhang Pin, Guo Ying, Gao Yajie, Wang Zhendong, Li Baiyi, Zhang Xiaomin, Niu Yuhu, Liu Zhizhen, Ma Lihui, Niu Bo, Guo Rui.
Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells promote myocardial repair after myocardial infarction under hypoxia
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(17): 2630-2636.
|
| [8] |
Guo Bo, Liu Jia, Cui Xiaolan, Shi Han, Zhang Sheyi, Wang Jia, Shan Xia, Wang Yizhong.
Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells combined with immunotherapy for the treatment of type 1 diabetic mice
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(13): 2016-2021.
|
| [9] |
Wang Yuxuan.
Combination of resveratrol and fetal liver stem cell transplantation for treatment of liver cirrhosis in rats
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(13): 2049-2054.
|
| [10] |
Liu Jian, Li Li, Wang Xiaochuan, Zhang Shengning, Li Laibang, Mang Yuanyi, Gao Yang, Chen Yonglin, Ren Gang, Li Wang.
Mild hypothermia combined with adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells protects hepatic function in hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(13): 2081-2087.
|
| [11] |
Zhang Yunke, Che Zhiying, Li Ke.
Effect of Buyang Huanwu Decoction combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on expression of tight junction proteins in the brain of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion rats
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(1): 55-60.
|
| [12] |
Ren Hao, Dong Jing, Liu Li-wei, Chen Zhao-lin, Pan Jin-jin, Chen Xi, Song Hai-yan, Zhang Jun-fei, Chen Cong-xin, Liu Bo.
Risk factors for hepatocellular carcinoma in hepatitis B cirrhosis patients given treatment with human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(9): 1350-1356.
|
| [13] |
Hu Ji-hong, Zhao Jing-miao, Wang Qiu-ping, Jia Jia, Lu Juan, Jin Hua, Hou Qian.
Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on voltage-gated K+ channel proteins and cytokines in the infarcted myocardium of rats
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(9): 1389-1394.
|
| [14] |
Gao Ming-long, Shi Shao-xia, Zhang Kun, Zhang Ying-dong, Li Na, Yu Ming, Wang Yong-liang.
Effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor-modified human amniotic membrane-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on learning and memory abilities of Alzheimer's disease rats
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(9): 1419-1424.
|
| [15] |
Shang Qing-qing, Zhou Jian-ye, Li Kai, Sun Jia-kang, Meng Jian, Li Jun.
Combination of hyaluronic acid and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells promotes cardiac function after myocardial infarction
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(5): 675-679.
|