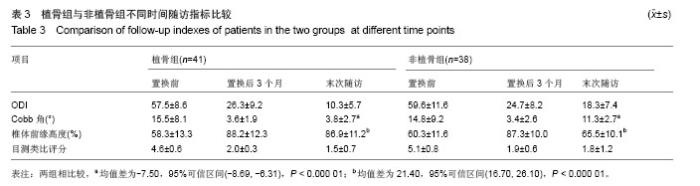
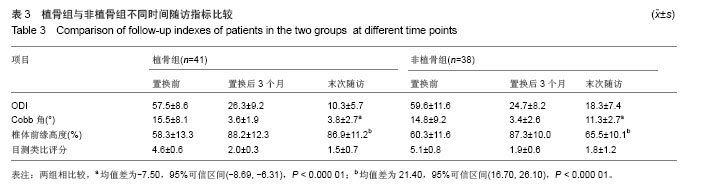
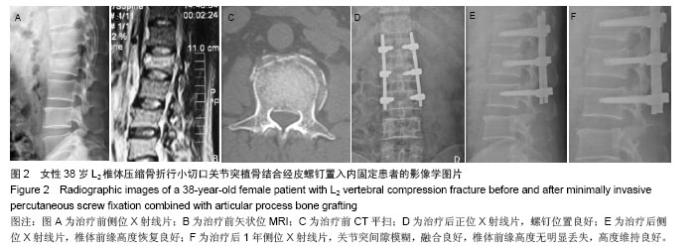
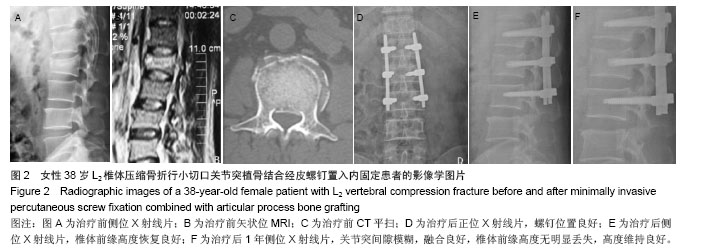
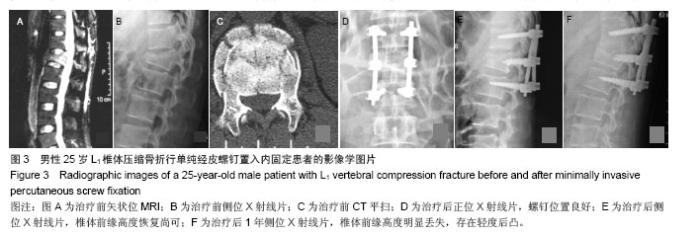
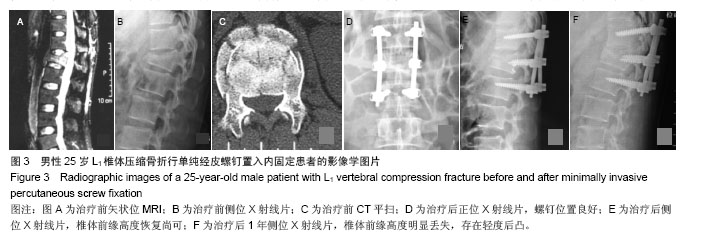
| [1]Kim DY, Lee SH, Chung SK, et al. Comparison of multifidus muscle atrophy and trunk extension muscle strength: percutaneous versus open pedicle screw fixation. Spine. 2005;30(1): 123-129.
[2]Huang TJ, Hsu RW, Li YY, et al. Less systemic cytokine response in patients following mieroendospie rersus open lumbar discectomy. Orthop Res. 2005;23(2):406-411.
[3]曾继伟. 微创与传统切开椎弓根螺钉内固定治疗胸腰椎骨折的疗效比较[J].实用临床医学,2014,15(11):71-72.
[4]蔡明,刘雅,贾小平,等.微创经皮椎弓根螺钉内固定术治疗胸腰椎骨折的临床观察[J].中国医药指南,2013,11(31): 442-443.
[5]罗鹏刚,熊浩,赖茂松,等.微创经皮与传统开放椎弓根螺钉内固定治疗胸腰椎骨折的临床研究[J]. 中国现代医生,2014,52(9): 11-14.
[6]朱勋兵,韩俊柱,王胜.微创经皮椎弓根置钉治疗无神经损伤胸腰椎骨折[J].中华全科医学,2014,12(8):1208-1210.
[7]叶军,于志勇,白龙,等.微创术式与传统术式治疗胸腰椎骨折的对照研究[J].中国现代医生,2012,50(23):144-145.
[8]杨雷,李家顺,贾连顺,等.经皮椎弓根螺钉技术的解剖学基础及其临床意义[J].中国临床解剖杂志,2002,22(1):86-88.
[9]Magerl F. External skeletal fixation of the lower thoracic and lumbar spine. Uhthoff HK, Stahl E.Current concepts of external fixation of fracture.New York: Springer-Verlag, 1982: 353-366.
[10]Mathews HH, Long BH.Endoscopy assisted percutaneous anterior interbody fusion with subcutaneous suprafascial internal fixation: evolution of technique and surgical considerations. Orthop Int Ed.1995;3:496-500.
[11]Foley KT, Gupta SK. Percutaneous pedicle screw fixation of the lumbar spine: preliminary clinical results. J Neurosurg. 2002; 97(1 Suppl):7-12.
[12]苗洁,李冠军,葛志强,等.微创经皮长尾定向椎弓根钉内固定术治疗胸腰椎骨折[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2012,27(11): 978-980.
[13]闫国良,纪振刚,高浩然,等.微创经椎间孔减压腰椎融合内固定术与传统后路开放手术治疗腰椎退变性疾病的疗效比[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2013,23(3):244-250.
[14]李峰,方苏亭,霍雄涛,等.小切口肌间隙入路在治疗胸腰椎骨折中的应用[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2013,21(8):18-20.
[15]Mahar A, Kim C, Wedemeyer M, et al. Short-segment fixation of lumbar burst fractures using pedicle fixation at the level of the fracture. Spine. 2007;32:1503-1507.
[16]张超,周临东,沈计荣.微创经皮技术治疗胸腰椎骨折进展[J].中国中西医结合外科杂志,2014,20(1):106-108.
[17]任亚军,张云庆,周枫,等.经多裂肌间隙微创椎弓根钉治疗胸腰椎骨折[J].实用骨科杂志,2014, 20(2):152-154.
[18]刘向阳,胡伟,吴建明,等.微创附加伤椎椎弓根内固定术治疗胸腰椎骨折[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2014,29(7):700-701.
[19]王洪伟,李长青,周跃,等.微创与传统附加伤椎经椎弓根钉内固定手术治疗胸腰椎骨折的疗效比较[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2010, 20(2): 112-116.
[20]王洪伟,李长青,周跃,等.附加伤椎固定的微创经皮椎弓根螺钉(Sextent)治疗胸腰椎骨折[J].中华骨科杂志,2010,12(2): 126-130.
[21]林鸿宽,周之平,曾峰.微创经伤椎置钉治疗胸腰椎骨折的疗效[J]. 实用临床医学,2013,13(2):51-53.
[22]李长青,罗刚,周跃,等.新型微创经皮椎弓根螺钉内固定治疗胸腰椎骨折[J].中华创伤杂志,2009,25(6):522-525.
[23]卢畅,杨明.后路经椎弓根内固定结合椎体成形术治疗老年人胸腰段脊椎骨折[J].中南大学学报:医学版,2009,34(2):181-184.
[24]贺健,蒋赞利,吴小涛,等.后路椎弓根固定结合伤椎椎弓根植骨治疗胸腰椎爆裂性骨折[J].中华临床医师杂志:电子版,2013,7(9): 3850-3854.
[25]闵少雄,靳安民,张辉,等.经椎弓根椎体内植入人工骨治疗多节段骨质疏松压缩性骨折[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2009,27(5): 606-609.
[26]陈宾,潘玉林,郭小伟,等.经皮微创与常规切开椎弓根螺钉内固定治疗不稳定性胸腰椎骨折的对比研究[J].中国骨与关节外科, 2014, 7(3):203-207. |