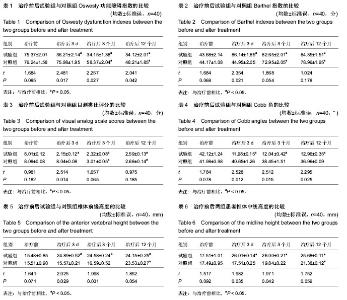
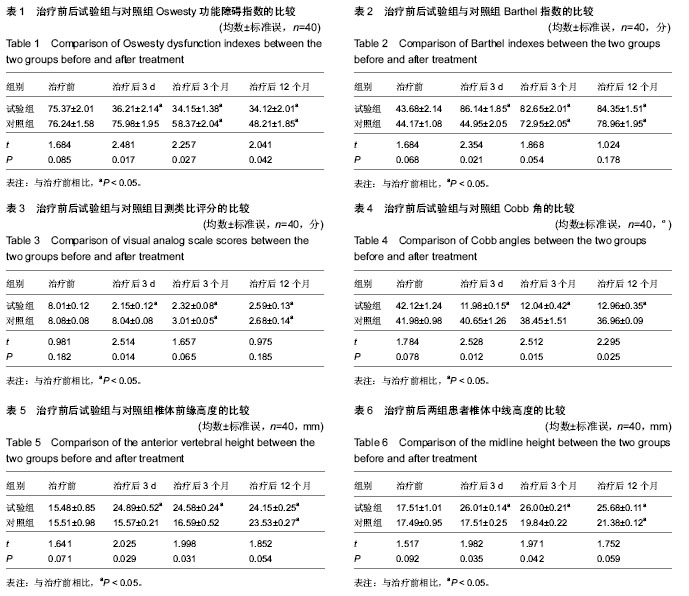
| [1] 邹可安.单、双侧入路PKP治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折的临床比较分析[D].福建医科大学,2012:36.
[2] 姜允琦,王会仁,董健.老年骨质疏松性椎体骨折的治疗[J].中华临床医师杂志(电子版),2013,7(19):8551-8554.
[3] 樊庆凯,龚维明,宁斌,等.PKP治疗骨质疏松性多节段椎体压缩性骨折的临床疗效[J].山东大学:医学版,2014,11(11):73-91.
[4] Wardlaw D,Van Meirhaeghe J,Ranstam J,et al.Balloon kyphoplasty in patients with osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures.Expert Rev Med Devices.2012;9(11): 423-436.
[5] 黄刚,陈海云,刘卓勋,等.经皮椎体成形术与经皮穿刺椎体后凸成形术治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折[J].南方医科大学学报, 2010,30(12):2729-2732.
[6] 关继奎,赵丽,姜屿,等.甲基丙烯酸甲酯骨水泥充填治疗骨损伤后的肺功能变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,18(6):4727-4732.
[7] 赵苏鸣,戴瑞茹,黄健,等.犬急性骨水泥肺栓塞的实验研究[J].介入放射学杂志,2012,21(1):55-60.
[8] 钱明,潘俊,孟斌,等.聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯骨水泥与Cortoss骨水泥生物力学性能及聚合温度比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2012, 15(4):2935-2938.
[9] Alvarez L,Perez-Higueras A,Quinones D,et al.Vertebroplasty in the treatment of vertebral tumors: postprocedural outcome and quality of life.Eur Spine J.2003;12(4):356-360.
[10] Chi JH,Gokaslan ZL.Vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty for spinal metastases.Curr Opin Support Palliat Care.2008; 2(1): 9-13.
[11] 陈文贵,肖立军,邓德礼,等.PKP治疗骨质疏松性多节段椎体压缩性骨折的临床应用研究[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2009,24(8): 702-704.
[12] 王文革,秦国强,李仕臣,等.PVP与PKP治疗骨质疏松性胸腰椎压缩性骨折的临床疗效观察[J].医学信息,2010,5(11):3073-3075.
[13] 李龙.单、双侧穿刺PKP治疗骨质疏松椎体压缩性骨折的对比分析[D].安徽医科大学学报,2010:46.
[14] 张萌.手法复位联合经皮椎体后凸成形术和椎体后凸成形术治疗老年骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折的比较研究[D].大连医科大学,2014:42.
[15] 方济,胡侦明,郝杰,等.聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯骨水泥对原代培养脊柱转移瘤细胞的影响和意义[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(21): 3828-3832.
[16] 张平,蒋成.经皮椎体后凸成形术治疗老年性胸腰椎骨质疏松压缩性骨折疗效观察[J].实用医院临床杂志,2013,10(6):129-130.
[17] 王志刚,李培春.经皮椎体后凸成形术治疗老年人骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折24例[J].浙江创伤外科,2013,18(6):867-868.
[18] 江兵,朱成润.经皮椎体成形术与经皮椎体后凸成形术治疗老年骨质疏松性椎体骨折的进展[J].中国现代医生,2013,51(34): 16-19.
[19] 王守赟,慈元,张光宇. 经皮椎体后凸成形术治疗骨质疏松性胸腰椎压缩性骨折的临床观察[J].中国现代医生,2012,50(25): 54-55.
[20] 江兵,刘立明,曹燕庆,等.椎体后凸成形术治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折[J].安徽医学,2010,31(3):233-234.
[21] 江兵,刘立明,曹燕庆,等.椎体后凸成形术治疗60 例骨质疏松性椎体骨折[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2012,37(5):447-448.
[22] 张淼荣,陈飞,荚鹏辉,等.椎体成形术及椎体后凸成行术治疗陈旧性骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折31例[J].福建医药杂志,2011, 33(1): 47-49. |