Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (15): 2410-2414.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.15.022
Previous Articles Next Articles
Connective tissue growth factor in the intervertebral discs exerts an anabolic effect on the extracellular matrix
Wang Dong, Wang Li-chun
- Department of Orthopedics, Second Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150086, Heilongjiang Province, China
-
Revised:2015-03-14Online:2015-04-09Published:2015-04-09 -
Contact:Wang Li-chun, M.D., Chief physician, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Department of Orthopedics, Second Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150086, Heilongjiang Province, China -
About author:Wang Dong, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Orthopedics, Second Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150086, Heilongjiang Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Dong, Wang Li-chun. Connective tissue growth factor in the intervertebral discs exerts an anabolic effect on the extracellular matrix[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(15): 2410-2414.
share this article
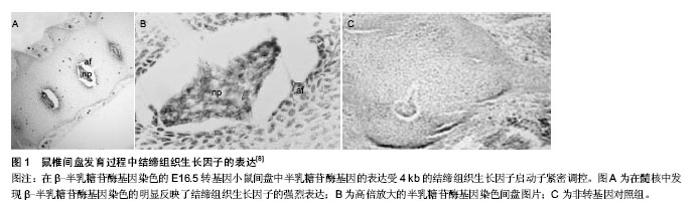
2.1 结缔组织生长因子概述及其生物学效应 由于结缔组织生长因子对细胞外基质的合成具有重要作用,因此在对椎间盘的立早基因结缔组织生长因子家族成员的研究中,对其研究较多[1]。结缔组织生长因子有如下4个结构域:胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白(IGFBP)结构域,C型血管假性血友病因子(VWC)结构域,血小板反应蛋白1(TSP-1)结构域以及含半胱氨酸的羧基端(CT)结构域。结缔组织生长因子凭借这4个结构域能够起到类似信号传感器或者调节器的作用,其与多种生长因子及细胞外基质蛋白相互配合,通过作用于细胞表面受体来对多种生物进程产生影响。结缔组织生长因子的很多功能都具有组织特异性;其既能够对细胞外基质的合成进行调节,也能促进血管的生成以及细胞的迁移、黏附、分化。 在脊椎动物发育到成熟的过程中,结缔组织生长因子被不同程度地表达,例如在梅克尔软骨、骨和间盘等骨组织中会被高度表达[2]。早期的胚胎发育过程中可以发现,结缔组织生长因子在原始组织(体节、底板、脊索)以及起源于此的几个表达相对旺盛的成熟组织中被高度表达[3]。Kawaki等[4]凭借体外实验验证了结缔组织生长因子对软骨细胞表型起到保护作用,并且能够促进生长板中的软骨分化。Geisinger等[5]的研究表明,结缔组织生长因子对成骨细胞的分化以及软骨内的成骨有促进作用,结缔组织生长因子可以在人体内将成骨细胞增殖、胶原蛋白沉积和矿化作用减少,在人体外将碱性磷酸酶,骨钙素水平降低。虽然有不少文章研究了结缔组织生长因子在其他组织中的功能和作用,但是对于结缔组织生长因子在间盘组织中的调节机制细节迄今为止依旧未被阐明。 2.2 间盘内结缔组织生长因子在发育过程中的表达与功能 椎间盘的结构比较复杂,而且属于多轴向活动性关节;其会分隔表面覆盖有软骨组织的相邻椎体,以支持一系列的肢体动作,同高生物学力量相适应[6]。间盘的外周围绕的纤维软骨环,其由紧密填充的Ⅰ型胶原纤维所构成,Ⅰ型胶原纤维会嵌插到相邻的上下软骨终板及椎体中。内纤维环则由Ⅱ型胶原纤维、聚焦蛋白聚糖以及多功能蛋白聚糖构成。纤维环和软骨终板包围着含有丰富聚焦蛋白聚糖及胶体样的髓核。髓核中没有血管,只有极少量的细胞,因此髓核中的细胞存活于一个极度缺氧和高渗的微环境之中[7]。完整的蛋白聚糖和胶原纤维支撑着间盘功能的正常运转,而间盘细胞的活性和维持基质稳定的能力敏感地受外界环境的刺激和诸如结缔组织生长因子等信号因子的影响。 如图1可以在处于发育过程中的E16.5转基因小鼠间盘明显地观察到结缔组织生长因子的表达[8]。Huang等[8]的研究表明,间盘组织中4 kb的结缔组织生长因子基因启动子的特异活性是相对稳定的。这证实了高等脊椎动物中,结缔组织生长因子在椎骨和间盘分节后起到了重要的作用。Erwin等[9]研究发现,结缔组织生长因子对髓核细胞生产聚焦蛋白聚糖有促进作用。Sakai等[10]的研究则显示,是脊索衍生出的所有髓核细胞。需要注意的是Tran等[11]的体外实验,其实验结果也表明脊索细胞所分泌的结缔组织生长因子能够刺激脊索细胞生成聚焦蛋白聚糖。最近,Tran等[12]的实验验证了结缔组织生长因子可以维持间盘组织基质成分的蛋白同化。出生后体内间盘结缔组织生长因子的稳定表达以及在结缔组织生长因子表达沉默的人髓核细胞外基质中[13],聚焦蛋白聚糖、Ⅰ型和Ⅱ型胶原的显著下降都表明结缔组织生长因子有益于维持基质的稳定[12]。因此,针对间盘退变过程微环境的改变是如何对基质稳定、细胞功能、关键基因的表达和调节产生影响的研究显得至关重要。"
| [1] Abbott RD, Purmessur D, Monsey RD,et al.Degenerative grade affects the responses of human nucleus pulposus cells to Link-N, CTGF, and TGFβ3. J Spinal Disord Tech.2013;26(3):E86-94. [2] Chiou M, Chao T, Wu J, et al. The physiological role of CTGF/CCN2 in zebrafish notochond development and biological analysis of the proximal promoter region. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006; 349:750-758. [3] Fernando CA, Conrad PA, Bartels CF, et al.Temporal and spatial expression of CCN genes in zebrafish. Dev Dyn. 2010; 239:1755-1767. [4] Kawaki H,Kubota S,Suzuki A,et al.Cooperative regulation of chondrocyte differentiation by CCN2 and CCN3 shown by a comprehensive analysis of the CCN family of proteins in cartilage. J Bone Miner Res. 2008; 23:1751-1764. [5] Geisinger MT, Astaiza R, Butler T,et al.Ets-1 is essential for connective tissue growth factor (CTGF/CCN2) induction by TGF-beta1 in osteoblasts. PLoS One. 2012;7:e35258. [6] Shapiro IM, Vresilovic EJ, Risbud MV.Is the spinal motion segment a diarthrodial polyaxial joint:what a nice nucleus like you doing in a joint like this? Bone. 2012; 50:771-776. [7] Risbud MV, Schaer TP, Shapiro IM. Toward an understanding of the role of notochordal cells in the adult intervertebral disc: from discord to accord. Dev Dyn. 2010; 239:2141-2148. [8] Huang B, Brugger SM, Lyons KM. Stage-specific control of connective tissue growth factor (CTGF/CCN2) expression in chondrocytes by Sox9 and beta-catenin. T J Biol Chem. 2010; 285:27702-27712. [9] Erwin WM, Ashman K, O’Donnel P, et al. Nucleus pulposus notochord cells secrete connective tissue growth factor and up-regulate proteoglycan expression by intervertebral disc chondrocytes.Arthritis Rheum. 2006; 54:3859-3867. [10] Sakai D, Nakamura Y, Nakai T, et al. Exhaustion of nucleus pulposus progenitor cells with ageing and degeneration of the intervertebral disc. Nat Commun.2012;3:1264.10.1038/ ncomms2226. [11] Tran CM, Smith HE, Symes A, et al. Transforming growth factor beta controls CCN3 expression in nucleus pulposus cells of the intervertebral disc. Arthritis Rheum. 2011; 63:3022-3031. [12] Tran CM, Fujita N, Huang BL, et al. HIF-1αand CCN2 form a Regulatory Circuit in Hypoxic Nucleus Pulposus Cells: CCN2 Suppresses HIF-1α Level and Transcriptional Activity. J Biol Chem. 2013 Mar 24.10.1074/jbc.M112.448860. [13] Hall-Glenn F, Lyons KM. Roles for CCN2 in normal physiological processes. Cell Mole Life Sci.2011; 68:3209-3217. [14] Peng B, Chen J, Kuang Z, et al. Expression and role of connective tissue growth factor in painful disc fibrosis and degeneration. Spine. 2009; 34:5178-182. [15] Tran CM,Schoepflin ZR, Markova D,et al. CCN2 Suppresses Catabolic Effects of Interleukin-1β through α 5β1 and αVβ3 Integrins in Nucleus Pulposus Cells: implications in intervertebral disk degeneration. J Biol. Chem.2014; 289: 7374-7487. [16] Liu Y, Li JM, Hu YG. Transplantation of gene-modified nucleus pulposus cells reverses rabbit intervertebral disc degeneration. Chin Med J (Engl).2011; 124(16):2431-2437. [17] Strassburg S, Richardson SM, Freemont AJ,et al.Co-culture in-duces mesenchymal stem cell differentiation and modulation of the degenerate human nucleus pulposus cell phenotype.Regen Med.2010;5(5):701-711. [18] 王飞. 腰椎间盘退变中软骨终板细胞的凋亡及CTGF对其保护作用的实验研究[D]. 南方医科大学, 2010. [19] Reich A, Maziel SS, Ashkenazi Z,et al.Involvement of matrix metal-loproteinases in the growth plate response to physiological mechanical load. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2010; 108(1):172-180. [20] Woods A, Pala D, Kennedy L, et al. Rac1 signaling regulates CTGF/CCN2 gene expression via TGFbeta/Smad signaling in chondrocytes. Osteoarthr Cartil. 2009; 17:406-413. [21] 李楠,修磊,关涛,等.TGF-β1和结缔组织生长因子在不同退变程度的腰椎间盘组织中的表达[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2014, 28(7):891-895. [22] Arnott JA, Zhang X, Sanjay A, et al. Molecular requirements for induction of CTGF expression by TGF-beta1 in primary osteoblasts. Bone. 2008; 42:871-885. [23] Tran CM, Markova D, Smith HE, et al. Regulation of CCN2/CTGF expression in the nucleus pulposus of the intervertebral disc: Role of smad and AP1 signaling. Arthritis Rheum. 2010; 62:1983-1992. [24] Xia W, Kong W, Wang Z, et al. Increased CCN2 transcription in keloid fibroblasts requires cooperativity between AP-1 and SMAD binding sites. Ann Surg. 2007;246:886-895. [25] Nakerakanti SS, Bujor AM, Trojanowska M. CCN2 is required for the TGF-βinduced activation of Smad1-Erk1/2 signaling network.PLoS one. 2011; 6:e21911-e21911. [26] Kawaki H, Kubota S, Suzuki A, et al. Differential roles of CCN family proteins during osteoblast differentiation: Involvement of Smad and MAPK signaling pathways. Bone. 2011; 49:975-989. [27] Abreu JG, Ketpura NI, Reversade B, et al. Connective-tissue growth factor (CTGF) modulates cell signalling by BMP and TGF-beta. Nat Cell Biol. 2002; 4:599-604. [28] Maeda A, Nishida T, Aoyama E, et al. CCN family 2/connective tissue growth factor modulates BMP signalling as a signal conductor, which action regulates the proliferation and differentiation of chondrocytes. J Biochem. 2009; 145:207-216. [29] Kroening S, Neubauer E, Wullich B, et al. Characterization of connective tissue growth factor expression in primary cultures of human tubular epithelial cells: modulation by hypoxia. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2010; 298:F796-806. [30] Kondo S, Kubota S, Mukudai Y, et al.Binding of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase to the cis-acting element of structureanchored repression in ccn2 mRNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011; 405:382-387. [31] Kroening S, Neubauer E, Wessel J,et al. Hypoxia interferes with connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) gene expression in human proximal tubular cell lines.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2009; 24:3319-3325. [32] Nishida T, Kondo S, Maeda A, et al. CCN family 2/connective tissue growth factor (CCN2/CTGF) regulates the expression of Vegf through Hif-1alpha expression in a chondrocytic cell line, HCS-2/8, under hypoxic condition. Bone. 2009; 44:24-31. [33] Eguchi T, Kubota S, Kawata K, et al. Novel transcription- factor-like function of human matrix metalloproteinase 3 regulating the CTGF/CCN2 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 2008; 28: 2391-2413. [34] Hiyama A, Sakai D, Risbud MV, et al. Enhancement of intervertebral disc cell senescence by WNT/β-catenin signaling-induced matrix metalloproteinase expression. Arthritis Rheum. 2010; 62:3036-3047. |
| [1] | Li Qinwen, Liang Jie, Wang Dongmei, Shang Zhenghui. Fibrotic changes in rat dorsal root ganglion following chronic sciatic nerve compression [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(29): 4686-4691. |
| [2] | Yang Zhen, Li Hao, Gao Cangjian, Fu Liwei, Tian Guangzhao, Zha Kangkang, Sun Zhiqiang, Li Xu, Guo Weimin, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Liu Shuyun, Lu Shibi, Guo Quanyi . Regulation of stem cells by transforming growth factor β3/polylactic acid-glycolic acid microspheres [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(28): 4540-4546. |
| [3] | Ren Jiangdong, Shalitanati • Wuermanbieke, Nuerailijiang • Yushan, Wuhuzi • Wulamu, Cao Li. Local injection of halofuginone into the subchondral bone relieves canine osteoarthritis by inhibiting transforming growth factor beta 1 signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(14): 2147-2152. |
| [4] | Li Hongchao, Wang Xi, Li Li, Li Zhenyu, Zang Zusheng, Zhou Heng, Wang Xiaojin, Chen Chengwei, Cheng Mingliang, Wu Jun, Jin Yinpeng, Fu Qingchun. Therapeutic effect of human adipose stem cells derived exosomes on carbon tetrachloride induced liver fibrosis in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(13): 1996-2004. |
| [5] | Shu Gao, Chen Xiaodong, Zhai Mingyu, Li Quanxiu, Liang Pengzhan, Yang Xuejun, Zhao Haibo, Yu Chenqiang, Bai Xueling, Li Long. Imaging evaluation and biomechanical characteristics of the novel intradiscal electrothermal annuloplasty in pigs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(8): 1214-1221. |
| [6] |
Wen Yi, Su Feng, Liu Su, Zong Zhiguo, Zhang Xin, Ma Pengpeng, Li Yuexuan, Li Rui, Zhang Zhimin.
Establishment of finite element model of L4-5 and mechanical analysis of degenerative intervertebral discs
|
| [7] | Zhang Wen1, Zhang Lei1, Ren Shouzhong1, Liu Risheng2 . Prednisolone inhibites osteoblast apoptosis induced by transforming growth factor beta activated kinase 1 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(23): 3630-3635. |
| [8] | Li Pengfei, Wang Tao, Ma Xinlong . Association between COL9A2 gene polymorphisms and intervertebral disc degeneration in Asian: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(20): 3275-3280. |
| [9] | Hu Guang, Zhang Kaiwei, Xu Yuankun. Lysophosphatidic acid affects the expression of connective tissue growth factor in osteoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(19): 2959-2964. |
| [10] | Chen Haitao, An Yuguang. Efficacy of specific versus non-specific cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors in the healing of rabbit models of tibial fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(15): 2385-2390. |
| [11] | Wang Yuxuan. Combination of resveratrol and fetal liver stem cell transplantation for treatment of liver cirrhosis in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(13): 2049-2054. |
| [12] | Chang Xiaopeng, Chen Tao, Zhao Yin, Liang Ming. Synergistic effect of bone morphogenetic protein 2 and transforming growth factor beta2 on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(1): 1-6. |
| [13] | Zhao Wenhui, Pi Hongtao, Feng Wanwen, Li Xiangdong, Wang Jianwei, Liu Yuepeng, Jiang Yang, Ma Jianxin, Xia Yayi, Wang Cuifang, Shao Linlin, Li Chunhui, Yu Hongyang, Liu Shanglin, Dong Yanbin, Ma Yahui. Contact or noncontact cocultures of articular chondrocytes with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells: cell proliferation and differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(1): 24-29. |
| [14] | Li Weiwei, Li Xiaofeng, Hou Ping, Li Jianping. CD4+T and Treg immunomodulatory functions after culture with the supernatant of human placenta mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(1): 85-89. |
| [15] | Peng Qiufeng, Gao Jingzhen, Ye Kui, Xing Aimin. Transplantation of endothelial progenitor cells with RNA interference targeting transforming growth factor beta1 inhibits pulmonary fibrosis in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(1): 90-95. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||