Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (11): 1739-1744.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.11.019
Previous Articles Next Articles
Arthroscopic glenoid labrum repair and combined joint capsule and partial subscapularis suture for recurrent anterior shoulder dislocation
Xu Bin, Tu Jun
- Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230022, Anhui Province, China
-
Revised:2015-02-02Online:2015-03-12Published:2015-03-12 -
About author:Xu Bin, Master, Chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230022, Anhui Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xu Bin, Tu Jun. Arthroscopic glenoid labrum repair and combined joint capsule and partial subscapularis suture for recurrent anterior shoulder dislocation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(11): 1739-1744.
share this article
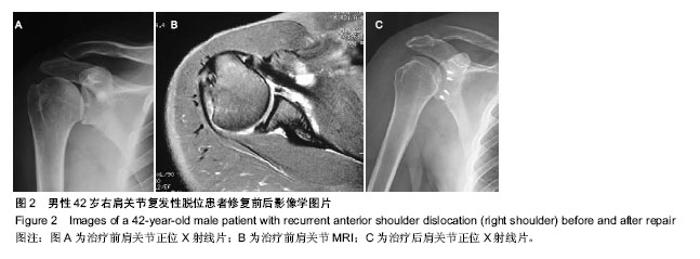
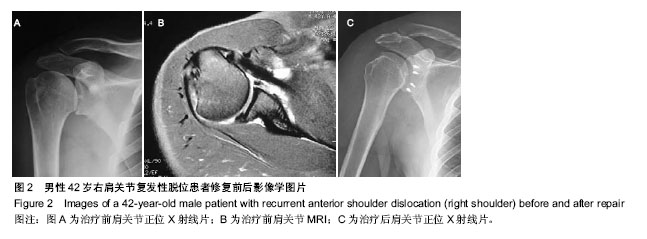
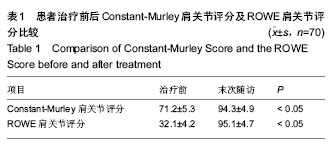
2.1 参与者数量分析 按意向性处理,纳入70例复发性肩关节脱位患者,修复术后均完成随访,未出现失访现象。 2.2 随访结果 70例患者经过11-46个月的随访,治疗后肩关节稳定性均恢复,未再发生脱位。末次随访肩关节ROWE评分上升到(95.1±4.7)分,其中稳定性项目评分所有患者均为50分;Constant-Murley肩关节评分上升到(94.3±4.9)分, 两项评分均较治疗前明显增高(P < 0.05,见表1)。70例患者中65例患者肩关节活动度恢复基本正常,5例患者肩关节活动度轻度受限,以外展、外旋为主,但活动度在正常活动度的50%以上,能够满足日常生活及工作的活动需要。所有患者均未遗留明显的肩关节疼痛症状,均能正常工作和生活。 2.3 典型病例 男性患者,42岁,因“外伤致右肩关节脱位7年反复发作十余次”来本科就诊,诊断“右肩关节复发性脱位,右肩关节Hill-sachs损伤,右肩前下盂唇损伤”。在本科术前评估中明确该患者存在肱骨头软骨缺损但未达20%,肩关节前下盂唇损伤,但未达25%,符合研究标准(图2A,B)。治疗前对患者一般情况、Constant-Murley肩关节评分、肩关节ROWE评分进行详细记录。修复术中将患者前下盂唇彻底松解并与部分肩胛下肌腱、关节囊一起缝合固定于前下盂唇(图2C)。修复术后常规康复方案指导康复锻炼。共随访12个月,肩关节Constant-Murley肩关节评分由治疗前的70分上升到92分,ROWE评分由治疗前25分上升到95分,肩关节未再发生脱位,关节活动度基本正常,能够完成日常工作和生活中所需要的肩关节活动,无显著疼痛,患者回到原工作岗位。 2.4 不良事件 1例63岁女性患者在修复手术结束后出现急性肺水肿,经呼吸机辅助呼吸、消肿对症治疗后迅速康复,治疗后第2天症状完全消失,第3天患者下地活动,第7天顺利出院。有5例患者在修复术后出现肘部或前臂皮肤水泡,在反复仔细查找原因后认定是在手术过程中等离子消融刀的引流管引出的高温灌注液滴落至皮肤导致热灼伤所致,后经改进未再发生类似并发症。所有患者灼伤处皮肤经积极治疗后迅速康复。无其他明显不良事件出现。 "
| [1] Shields E, Mirabelli M, Amsdell S, et al. Functional and imaging outcomes of arthroscopic simultaneous rotator cuff repair and bankart repair after shoulder dislocations. Am J Sports Med. 2014;42(11):2614-2620.
[2] 黄华杨,郑小飞,张余,等.关节镜下非打结型缝合锚钉修补Bankart损伤治疗复发陛肩关节前脱位[J].中华骨科杂志,2008, 28(11):912-916.
[3] 姜春岩,冯华,洪雷,等.复发性肩关节前脱位的关节镜治疗[J].中华骨科杂志,2005,25(6):321-325.
[4] 闫辉,崔国庆,王健全,等.关节镜下Bankart修复术治疗肩关节复发性前脱位:手术效果及复发危险因素分析[J].中华外科杂志, 2011,49(7):597-602.
[5] 刘玉杰,蔡谞,王志刚,等.关节镜下可吸收铆钉固定修复Bankart损伤[J]. 中华外科杂志,2005, 43(16):1072-1074.
[6] Aslani H,Zafarani Z, Ebrahimpour A, et al. Early clinical results of arthroscopic remplissage in patients with anterior shoulder instability with engaging hill-sachs lesion in iran. Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2014;2(1):43-46.
[7] Horst K, Von Harten R, Weber C, et al. Assessment of coincidence and defect sizes in Bankart and Hill-Sachs lesions after anterior shoulder dislocation: a radiological study. Br J Radiol. 2014;87(1034):20130673.
[8] Di Giacomo G, De Vita A, Costantini A, et al. Management of humeral head deficiencies and glenoid track. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2014; 7(1):6-11.
[9] Argintar E,Heckmann N, Wang L,et al.The biomechanical effect of shoulder remplissage combined with Bankart repair for the treatment of engaging Hill-Sachs lesions. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2014.
[10] Rhee YG, Cho NS, Yoo JH, et al. Filling Index Score of Remplissage (FISOR):a useful measurement tool to evaluate structural outcome afterremplissage. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2014. pii S1058-2746(14)00497-2.
[11] Longo UG, Loppini M,Rizzello G,et al.Remplissage, humeral osteochondral grafts, weber osteotomy, and shoulder arthroplasty for the management of humeral bone defects in shoulder instability: systematic review and quantitative synthesis of the literature. Arthroscopy. 2014;30(12):1650-1666.
[12] McCabe MP,Weinberg D, Field LD,et al.Primary versus revision arthroscopic reconstruction with remplissage for shoulder instability with moderate bone loss. Arthroscopy. 2014;30(4):444-450.
[13] Omi R, Hooke AW,Zhao KD,et al.The effect of the remplissage procedure on shoulder range of motion: a cadaveric study. Arthroscopy. 2014;30(2):178-187.
[14] Flinkkilä T, Sirniö K.Open Latarjet procedure for failed arthroscopic Bankart repair. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2015;101(1):35-38.
[15] Fedorka CJ, Mulcahey MK.Recurrent anterior shoulder instability: a review of the Latarjet procedure and its postoperative rehabilitation. Phys Sportsmed. 2015;19:1-7.
[16] Balestro JC, Young A, Maccioni C,et al.Graft osteolysis and recurrent instabilityafter the Latarjet procedure performed with bioabsorbable screw fixation. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2014. pii: S1058-2746(14)00425-X.
[17] Abdelhady A, Abouelsoud M, Eid M. Latarjet procedure in patients with multiple recurrent anterior shoulder dislocation and generalized ligamentous laxity. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2014.
[18] Maiotti M, Massoni C.Arthroscopic augmentation with subscapularis tendon in anterior shoulder instability with capsulolabral deficiency. Arthrosc Tech. 2013;2(3):e303-310.
[19] Savoie FH 3rd, O'Brien MJ. Anterior instability in the throwing shoulder. Sports Med Arthrosc. 2014;22(2):117-119.
[20] Ozorak M, Kokavec M, Svec A. Arthroscopic management of anterior instability of the shoulder. Ortop Traumatol Rehabil. 2014;16(2):111-118.
[21] Bessière C, Trojani C, Carles M, et al.The open latarjet procedure is more reliable in terms of shoulder stability than arthroscopic bankart repair. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014; 472(8):2345-2351.
[22] Shibata H, Gotoh M, Mitsui Y,et al.Risk factors for shoulder re-dislocation after arthroscopic Bankart repair. J Orthop Surg Res. 2014;9(1):53.
[23] Neoral P, Holibka R, Kalina R, et al.Arthroscopic stabilisation of the shoulder. Risk factors for its failure. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2014;81(1):51-56.
[24] Provencher MT, Frank RM, Leclere LE, et al. The Hill-Sachs lesion: diagnosis, classification, and management. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2012;20(4):242-252.
[25] Boileau P, Thélu CÉ, Mercier N,et al.bristow-latarjet combined with bankart repair restores shoulder stability in patients with glenoid bone loss. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;472(8): 2413-2424.
[26] Agneskirchner JD, Lafosse L.Transfer of the coracoid process in recurrent anterior instability of the shoulder joint. The arthroscopic Latarjet procedure. Oper Orthop Traumatol. 2014; 26(3):296-306.
[27] Buza JA 3rd, Iyengar JJ, Anakwenze OA,et al.Arthroscopic Hill-Sachs remplissage: a systematic review. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014;96(7):549-555.
[28] Ko SH,Shin SM,Jo BG.Outcomes of minimally 1 year follow-up for the arthroscopic Remplissage technique with Hill-Sachs lesion. J Orthop. 2013;10(1):41-45.
[29] Garcia GH,Park MJ,Baldwin K,et al.Comparison of arthroscopic osteochondral substitute grafting and remplissage for engaging Hill-Sachs lesions. Orthopedics. 2013;36(1):e38-43.
[30] Leroux T, Bhatti A,Khoshbin A,et al.Combined arthroscopic Bankart repair and remplissage for recurrent shoulder instability. Arthroscopy. 2013;29(10):1693-1701.
[31] Wolf EM,Arianjam A. Hill-Sachs remplissage, an arthroscopic solution for the engaging Hill-Sachs lesion: 2- to 10-year follow-up and incidence of recurrence. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2014;23(6):814-820.
[32] Trivedi S, Pomerantz ML, Gross D, et al.Shoulder instability in the setting of bipolar (glenoid and humeral head) bone loss: the glenoid track concept. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;472(8): 2352-2362.
[33] Mohtadi NG, Chan DS, Hollinshead RM, et al.A randomized clinical trial comparing open and arthroscopic stabilization for recurrent traumatic anterior shoulderinstability: two-year follow-up with disease-specific quality-of-life outcomes. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014;96(5):353-360.
[34] Friedman LG, Griesser MJ, Miniaci AA, et al.Recurrent instability after revision anterior shoulder stabilization surgery. Arthroscopy. 2014;30(3):372-381.
[35] Zhang AL, Montgomery SR, Ngo SS, et al. Arthroscopic versus open shoulder stabilization: current practice patterns in the United States. Arthroscopy. 2014;30(4):436-443.
[36] Atalar AC, Bilsel K, Eren I, et al. Modified Latarjet procedure for patients with glenoid bone defect accompanied with anterior shoulder instability. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2013;47(6):393-399.
[37] Noonan B, Hollister SJ, Sekiya JK, et al. Comparison of reconstructive procedures for glenoid bone loss associated with recurrent anterior shoulder instability. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2014;23(8):1113-1119.
[38] Degen RM,Giles JW,Johnson JA.Remplissage versus latarjet for engaging Hill-Sachs defects without substantial glenoid bone loss: a biomechanical comparison. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;472(8):2363-2371.
[39] Moran CJ, Fabricant PD, Kang R, et al. Arthroscopic double-row anterior stabilization and bankart repair for the "high-risk" athlete. Arthrosc Tech. 2014;3(1):e65-71.
[40] Gamulin A, Dayer R, Lübbeke A, et al. Primary open anterior shoulder stabilization: a long-term, retrospective cohort study on the impact of subscapularis muscle alterations on recurrence. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2014;15:45. |
| [1] | Chen Qun-qun, Qiao Rong-qin, Duan Rui-qi, Hu Nian-hong, Li Zhao, Shao Min. Acu-Loc®2 volar distal radius bone plate system for repairing type C fracture of distal radius [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1025-1030. |
| [2] | Jia Yan-bo, Liang Zi-hong, Ren Yi-zhong, Han Chang-xu, Kong Ling-yue, Eerduntu. Tibial avulsion fractures of anterior cruciate ligament repaired with Arthrex sutures passing through combining free knotting technique [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(3): 367-372. |
| [3] | Qiu Hao, Lu Min-peng, Dong Jing, Zhang Zhong-zu, Chu Tong-wei, Wang Qun-bo, Quan Zheng-xue, Jiang Dian-ming. Subtotal corpectomy and reconstruction with titanium mesh cage implantation and pedicle screw fixation through posterior approach in treatment of thoracolumbar burst fracture or thoracolumbar fracture dislocation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(53): 7932-7938. |
| [4] | Abudunaibi•Aili, Zhang Hong-qi, Huang Wei-min, Li Lei, Tian Hui-zhong. Special formed titanium mesh cages for treating spinal tuberculosis via one-stage posterior approach [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(48): 7192-7199. |
| [5] | Zhang Wei, Tang Zai-xiang, Geng De-chun, Zhu Feng, Dong Han-qing, Wang Yi-jun, Xu Yao-zeng. Multiple linear regression analysis of hip function and vitamin D levels before and after hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(44): 6557-6563. |
| [6] | Zhai Peng-fei, Liu Wei, Sun Zhi-ming, Zhang Xue-li. Adjacent segment degeneration after anterior cervical corpectomy and fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(35): 5216-5223. |
| [7] | Wu Shu-hong. Dual fixed anchor biomechanics and application in front of recurrent shoulder dislocation with severe bone defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(35): 5231-5236. |
| [8] | Lu Ning, Yang Yang. Unicompartmental knee replacement for medial compartmental knee osteoarthritis: a four to six-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(31): 4575-4581. |
| [9] | Zhao Gang, Zhou Ying-jie, Wang Xu-ke. RTS versus SEXTANT percutaneous pedicle screw fixation for unstable thoracolumbar fractures under minimally invasive technology: recovery of the height of the vertebral body [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(22): 3255-3262. |
| [10] | Zhang Li-peng, Zhang Guo-ling, Xu Wei, Wang Dan, Wang Wen-liang. Correlation between reduction quality of femoral neck fracture and femoral head necrosis evaluated by three-dimensional measurement method [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(22): 3287-3293. |
| [11] | Chen Rong-bo, Hou Na, Wang Ren, He Ming, Wang Er-feng, Zhang Wei-tao, Li Xiao-jian, Li Xian-zhi . Total knee arthroplasty for the treatment of bilateral knee rheumatoid arthritis in the same period [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(4): 493-498. |
| [12] | Wang Jian-yuan, Deng Qiang, Sheng Wei-bin, Lu Yong-jiang. Restoration of fracture and dislocation of lower cervical spine: bone graft fusion and cervical stability [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(4): 522-530. |
| [13] | Shen Cang-hai, Feng Yong-jian, Wang Li-guo, Yang Cheng, Peng Ning-ning, Wang Gui-jiang, Guo Xu . Conservative treatment of mild ossification of cervical posterior longitudinal ligament: prognostic factors and timing of surgical repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(4): 531-536. |
| [14] | Wang Bin, Gao Yi, Xu Jian-da, Xie Zi-kang, Shen Peng-fei, Zheng Chong, Qu Yu-xing. Adjustable and ordinary locking compression plates for the repair of osteoporotic distal radius fractures: comparison of radial length and wrist function recovery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(4): 584-589. |
| [15] | Li Tie-bin, Zhang Hai-qing. Memory alloy osteosynthesis plate fixation for flail chest injuries: 1-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(4): 601-605. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||