Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (22): 3287-3293.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.22.013
Previous Articles Next Articles
Correlation between reduction quality of femoral neck fracture and femoral head necrosis evaluated by three-dimensional measurement method
Zhang Li-peng1, Zhang Guo-ling2, Xu Wei1, Wang Dan1, Wang Wen-liang2
- 1Department of Pathogenic Biology and Immunology, Logistics University of People’s Armed Police Force, Tianjin 300000, China; 2Third Department of Joint, Affiliated Hospital of Logistics University of People’s Armed Police Force, Tianjin 300000, China
-
Revised:2016-04-11Online:2016-05-27Published:2016-05-27 -
About author:Zhang Li-peng, Master, Department of Pathogenic Biology and Immunology, Logistics University of People’s Armed Police Force, Tianjin 300000, China -
Supported by:the Key Scientific and Technological Support Project of Tianjin City, No. 13ZCZDSY01700
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Li-peng, Zhang Guo-ling, Xu Wei, Wang Dan, Wang Wen-liang. Correlation between reduction quality of femoral neck fracture and femoral head necrosis evaluated by three-dimensional measurement method[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(22): 3287-3293.
share this article
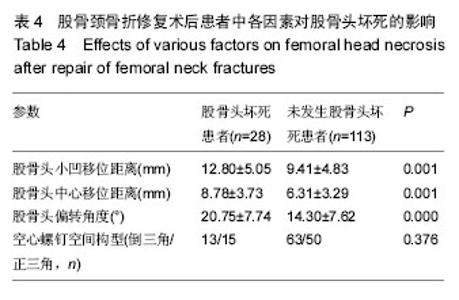
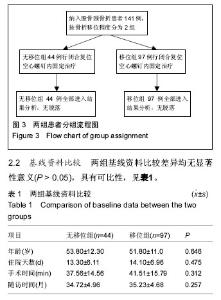
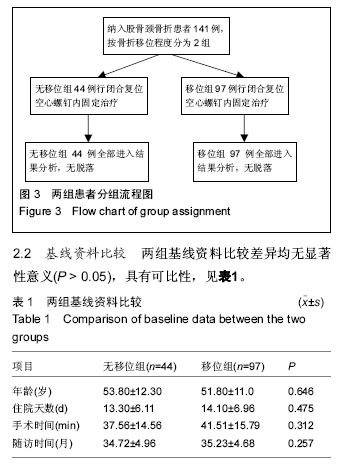
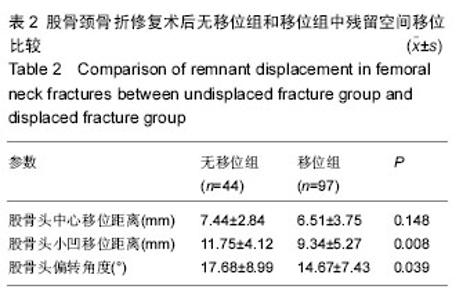
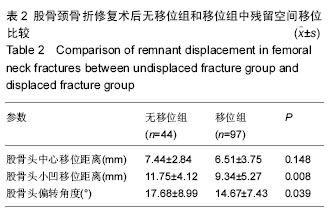
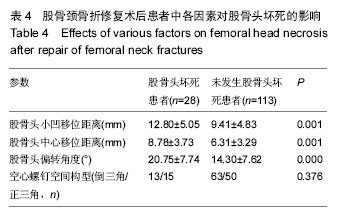
2.5 股骨头坏死患者与未发生股骨头坏死患者空间残留移位与置钉形状比较 本文中,股骨头坏死人群的股骨头中心移位距离、股骨头小凹移位距离、股骨头偏转角度均显著大于无患病人群,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。围手术时间在股骨头坏死人群人群和无患病人群中分别为(7.39±3.16) d和(8.42±5.86) d,差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。至于空间螺钉构型,76例倒三角空间构型中有13例发生股骨头坏死,65例正三角空间构型中有15例发生股骨头坏死。两种空间构型中,股骨头坏死发生率的差异无显著性意义(χ2=0.785,P=0.376),见表4。 2.6 不良事件 无移位型股骨颈骨折患者术后疼痛,2周后仍无法下地功能锻炼者4例,占9%,移位型股骨颈骨折者12例术后疼痛,占12%。术后8个月后仍出现骨折不愈合者,无移位组3例,占7%;移位组6例,占6%。进行至少25个月的随访后发现,无移位组出现股骨头坏死者7例,占16%;移位组21例,占22%。因无法忍受疼痛接受髋关节置换者,移位组中5例,移位组中14例,分别占各组患病人数的11%和14%。"
| [1] Fujimoto-Ibusuki K, Yamada Y, Hirai T, et al. [Perioperative Management of Elderly Patients Over 90 Years of Age with Femoral Neck/Trochanteric Fracture]. Masui. 2015;64(10):1040-1044. [2] Schoenfeld AJ, Weaver MJ, Power RK, et al. Does Health Reform Change Femoral Neck Fracture Care? A Natural Experiment in the State of Massachusetts. J Orthop Trauma. 2015;29(11):494-499. [3] Yu X, Zhao D, Huang S, et al. Biodegradable magnesium screws and vascularized iliac grafting for displaced femoral neck fracture in young adults. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2015;16:329. [4] Buecking B, Boese CK, Bergmeister VA, et al. Functional implications of femoral offset following hemiarthroplasty for displaced femoral neck fracture. Int Orthop. 2015. [5] 朱锋,徐耀增,耿德春,等.经皮加压钢板治疗股骨颈骨折的早期疗效[J]. 中华创伤杂志,2014,30(9):909-912. [6] Gehlen JM, Hoofwijk AG. Femoral neck fracture after electrical shock injury. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2010; 36(5):491-493. [7] 勘武生,黄方敏,郑琼,等.影响股骨颈骨折术后股骨头缺血性坏死的多因素分析[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2006,8(6): 520-523. [8] 孙辉,臧学慧,高立华,等.全髋关节置换与人工股骨头置换修复老年股骨颈骨折:18个月随访比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(53):8536-8541. [9] Cebatorius A, Robertsson O, Stucinskas J, et al. Choice of approach, but not femoral head size, affects revision rate due to dislocations in THA after femoral neck fracture: results from the Lithuanian Arthroplasty Register. Int Orthop. 2015;39(6):1073-1076. [10] Yeoh CJ, Fazal MA. ASA Grade and Elderly Patients With Femoral Neck Fracture. Geriatr Orthop Surg Rehabil. 2014;5(4):195-199. [11] Weil NL, van Embden D, Hoogendoorn JM. Radiographic fracture features predicting failure of internal fixation of displaced femoral neck fractures. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2015;41(5):501-507. [12] 封沙,潘福根,王忆茗,等.基于股骨头置换的多学科综合治疗老年陈旧性股骨颈骨折[J].中华创伤杂志, 2015,31(10): 921-924. [13] 杨磊,赵德伟,郭林,等.小切口外侧入路全髋关节置换术治疗老年股骨颈骨折的疗效[J].中国老年学杂志, 2012, 32(17):3797-3798. [14] 王奉雷. 空心钉锁定板治疗股骨颈骨折术后股骨头坏死的危险因素分析[J]. 重庆医学,2014,43(8):909-912. [15] Lazaro LE, Birnbaum JF, Farshad-Amacker NA, et al. Endosteal Biologic Augmentation for Surgical Fixation of Displaced Femoral Neck Fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2016;30(2):81-88. [16] 王本杰,赵德伟,郭林,等.带血管蒂髂骨瓣移位治疗股骨颈骨折术后股骨头缺血性坏死[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2011,25(5):526-529. [17] 汪松,马信龙,张弸羽,等. 利用有限元方法测定不同日常动作下坏死股骨头力学变化的研究[J].中华骨科杂志, 2015,35(9):962-969. [18] Xia X, Liu Z. [Advances on internal fixation treatment for femoral neck fracture in elderly patients]. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2014;27(8):706-708. [19] Inngul C, Enocson A. Postoperative periprosthetic fractures in patients with an Exeter stem due to a femoral neck fracture: cumulative incidence and surgical outcome. Int Orthop. 2015;39(9):1683-1688. [20] Freitas A, Maciel RA, Lima RA, et al. Mechanical analysis of femoral neck fracture fixation with dynamic condylar screw in synthetic bone. Acta Ortop Bras. 2014;22(5):264-268. [21] Avrahami D, Pajaczkowski JA. Femoral neck stress fracture in a female athlete: a case report. J Chiropr Med. 2012;11(4):273-279. [22] Shen JZ, Yao JF, Lin DS, et al. Hollow-bone-graft dynamic hip screw can fix and promote bone union after femoral neck fracture: an experimental research. Int J Med Sci. 2012;9(10):916-922. [23] 李波,邹正,罗文中.不同股骨颈骨折分型与中青年股骨颈骨折预后的相关性研究[J]. 重庆医学,2013,42(3): 297-298, 301. [24] Yoshimoto K, Nakashima Y, Nakamura A, et al. Neck fracture of femoral stems with a sharp slot at the neck: biomechanical analysis. J Orthop Sci. 2015;20(5): 881-887. [25] 刘福尧,刘承伟,吴声忠.不同置钉方式修复中青年移位型股骨颈骨折:复位质量及股骨头坏死率对比[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(31):4983-4988. [26] Palm H, Gosvig K, Krasheninnikoff M, et al. A new measurement for posterior tilt predicts reoperation in undisplaced femoral neck fractures: 113 consecutive patients treated by internal fixation and followed for 1 year. Acta Orthop. 2009;80(3):303-307. [27] Araujo TP, Guimaraes TM, Andrade-Silva FB, et al. Influence of time to surgery on the incidence of complications in femoral neck fracture treated with cannulated screws. Injury. 2014;45 Suppl 5:S36-S39. [28] Papadakis SA, Segos D, Kouvaras I, et al. Integrity of posterior retinaculum after displaced femoral neck fractures. Injury. 2009;40(3):277-279. [29] Liu C, Liu MT, Li P, et al. Efficacy evaluation for the treatment of subcapital femoral neck fracture in young adults by capsulotomy reduction and closed reduction. Chin Med J (Engl). 2015;128(4):483-488. [30] Javdan M, Bahadori M, Hosseini A. Evaluation the treatment outcomes of intracapsular femoral neck fractures with closed or open reduction and internal fixation by screw in 18-50-year-old patients in Isfahan from Nov 2010 to Nov 2011. Adv Biomed Res. 2013;2: 14. [31] Schweitzer D, Melero P, Zylberberg A, et al. Factors associated with avascular necrosis of the femoral head and nonunion in patients younger than 65 years with displaced femoral neck fractures treated with reduction and internal fixation. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2013; 23(1):61-65. [32] 王立强,李洋,刘成刚,等.老年股骨颈骨折患者关节置换术后病死率及危险因素分析[J].中华医学杂志, 2015,95(11): 832-835. [33] Tins B. Dislocation and spontaneous reduction of the femoral implant against the femoral neck in an infected metal on metal hip resurfacing with complex collection. Eur J Radiol. 2011;79(1):136-139. [34] Wang C, Xu GJ, Han Z, et al. Correlation Between Residual Displacement and Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head Following Cannulated Screw Fixation of Femoral Neck Fractures. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015; 94(47):e2139. [35] Yuan HF, Shen F, Zhang J, et al. Predictive value of single photon emission computerized tomography and computerized tomography in osteonecrosis after femoral neck fracture: a prospective study. Int Orthop. 2015;39(7):1417-1422. [36] Yang JJ, Lin LC, Chao KH, et al. Risk factors for nonunion in patients with intracapsular femoral neck fractures treated with three cannulated screws placed in either a triangle or an inverted triangle configuration. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013;95(1):61-69. [37] Wang JW, Li W, Xu SW, et al. [Sequential changes in biomechanical competence of femoral neck and marrow cavity of proximal femur in ovariectomized rats]. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2005; 34(5):432-435, 446. [38] Jiang H, Lei SF, Xiao SM, et al. Association and linkage analysis of COL1A1 and AHSG gene polymorphisms with femoral neck bone geometric parameters in both Caucasian and Chinese nuclear families. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2007;28(3):375-381. [39] Stone JD, Hill MK, Pan Z, et al. Open Reduction of Pediatric Femoral Neck Fractures Reduces Osteonecrosis Risk. Orthopedics. 2015;38(11): e983-e990. [40] 林庆波.全髋关节置换与空心螺钉置入内固定修复中老年股骨颈骨折:髋关节功能比较[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(35):5583-5587. [41] Nakamura G, Mihata T, Itami Y, et al. Locking plate fixation with femoral head allograft for treatment of nonunion of the surgical neck of the humerus: A case report. J Orthop Sci. 2015. |
| [1] | Shi Bin, An Jing, Chen Long-gang, Zhang Nan, Tian Ye . Influencing factors for pain after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 993-997. |
| [2] | Wang Xian-xun. Impact of local compression cryotherapy combined with continuous passive motion on the early functional recovery after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 998-1003. |
| [3] | Yuan Wei, Zhao Hui, Ding Zhe-ru, Wu Yu-li, Wu Hai-shan, Qian Qi-rong. Association between psychological resilience and acute mental disorders after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1015-1019. |
| [4] | Chen Qun-qun, Qiao Rong-qin, Duan Rui-qi, Hu Nian-hong, Li Zhao, Shao Min. Acu-Loc®2 volar distal radius bone plate system for repairing type C fracture of distal radius [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1025-1030. |
| [5] | Huang Xiang-wang, Liu Hong-zhe. A new low elastic modulus of beta titanium alloy Ti2448 spinal pedicle screw fixation affects thoracic stability: biomechanical analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1031-1035. |
| [6] | Xie Qiang. Three-dimensional finite element model for biomechanical analysis of stress in knee inversion and external rotation after posterior cruciate ligament rupture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1036-1040. |
| [7] | He Ze-dong, Zhao Jing, Chen Liang-yu, Li Ke, Weng Jie. Multilevel finite element analysis on the biological tribology damage of water on bone tissue [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1041-1045. |
| [8] | Jiang Zi-wei, Huang Feng, Cheng Si-yuan, Zheng Xiao-hui, Sun Shi-dong, Zhao Jing-tao, Cong Hai-chen,Sun Han-qiao, Dong Hang. Design and finite element analysis of digital splint [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1052-1056. |
| [9] | Wang Fei, Liu Zhi-bin, Tao Hui-ren, Zhang Jian-hua, Li Chang-hong, Cao Qiang, Zheng Jun, Liu Yan-xiong, Qu Xiao-peng. Clinical efficacy of preoperative osteotomy designs using paper-cut technology versus photoshop software for ankylosing spondylitis with kyphosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1057-1063. |
| [10] | Li Hui, Ma Jun-yi, Ma Yuan, Zhu Xu . Establishment of a three-dimensional finite element model of ankylosing spondylitis kyphosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1069-1073. |
| [11] | Ling Guan-han, Ou Zhi-xue, Yao Lan, Wen Li-chun, Wang Guo-xiang, Lin Heng-feng. Establishment of simulating three-dimensional model of China-Japan Friendship Hospital Classification for L type osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1074-1079. |
| [12] | Fu Wei-min, Wang Ben-jie. Assessing the degree of necrotic femoral head, and association of blood supply with pathlogical changes: study protocol for a diagnostic animal trial [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1086-1091. |
| [13] | Zhang Wen-qiang, Ding Qian, Zhang Na. Associations between alpha angle and herniation pit on oblique axial magnetic resonance imaging in asymptomatic hip joints of adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1098-1103. |
| [14] | Sun Xiao-xin1, Zhou Wei2, Zuo Shu-ping3, Liu Hao1, Song Jing-feng1, Liang Chun-yu1. Morphological characteristics for the magnetic resonance imaging assessment of discoid lateral meniscal tears in children [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1104-1109. |
| [15] | Lin Han-wen, Wen Jun-mao, Huang Chao-yuan, Zhou Chi, Tang Hong-yu. Correlation between the changes in lower limb power line and pain area in the knee osteoarthritis patients: imaging evaluation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1110-1114. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||