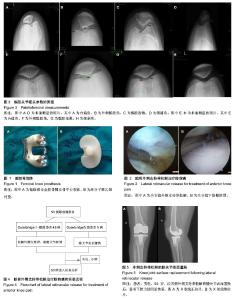
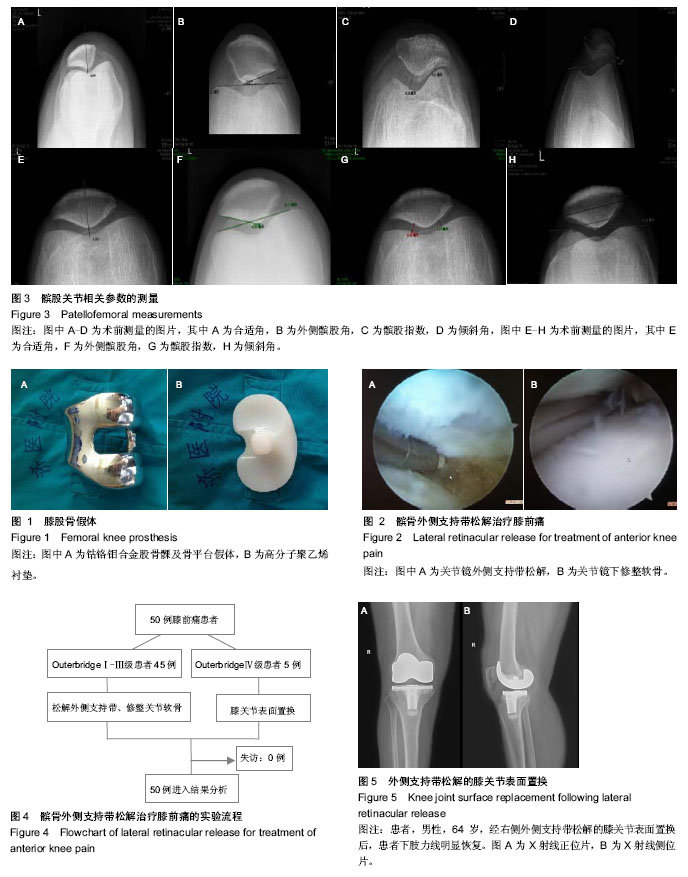
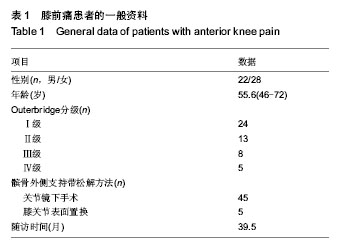
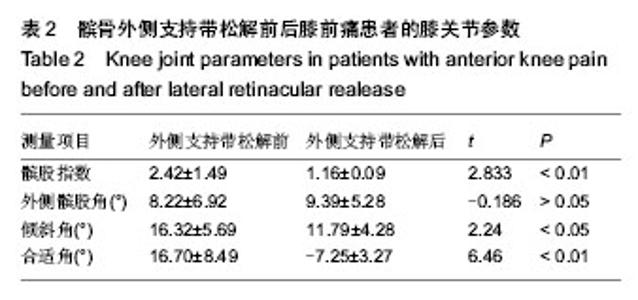
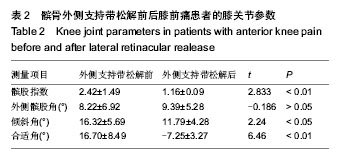
| [1] Outerbridge RE. The etiology of chondromalacia patellae. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1961;43-B:752-757.
[2] Maquet P. Advancement of the tibial tuberosity. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1976;(115):225-230.
[3] 李杭,林敏.髌股关节对称性与X线测量[J].浙江临床医学, 2003, 5(10):728-729.
[4] 吴海山,徐青镭.关节镜下支持带松解术治疗髌股关节紊乱的评价[J].中华矫形外科杂志,1995,2(3):148-149.
[5] 杨滨,谭洪波,杨柳,等.髌骨横轴-股骨通髁线角在评估髌股关节排列紊乱中的作用[J].中华骨科杂志,2009,29(2):108-111.
[6] 刘劲松,张道平.髌股外侧高压综合征的研究现状[J].中国骨伤, 2011,24(5):436-441.
[7] Ficat RP, Hungerford S. Disorders of the Patello-femoral Joint. Baltiomor: Williams and Wilkins,1977.
[8] Biliński P, Morasiewicz L, Czapiński J, et al. Radiologic analysis of the patello-femoral joint after treatment of patella fracture. Chir Narzadow Ruchu Ortop Pol. 1991;56(1-3):43-46.
[9] Arendt EA, Fithian DC, Cohen E. Current concepts of lateral patella dislocation. Clin Sports Med. 2002;21(3):499-519.
[10] 刘四海,刘克敏,王安庆,等.髌股关节对合关系的CT测量[J].中国康复理疗与实践,2009,15(11):1063-1064.
[11] 王思群,黄钢勇,俞永林,等.外侧支持带松解治疗髌股骨关节炎膝前痛[J].中国疼痛医学杂志,2011,17(6):325-328.
[12] 潘永谦,李健,林淦松,等.关节镜下联合手术治疗髌股关节紊乱症[J].中国内镜杂志,2000,6(5):59-60.
[13] 陈志超,顾祖超,李志力,等.关节镜下外侧支持带松解治疗髌骨外侧高压综合征[J].现代预防医学,2012,39(9):2321-2322.
[14] 韩建军,孙振杰,刘瑞波.关节镜术后膝前疼痛的原因分析[J].中国实用医药,2008,3(16):117-118.
[15] 陈昊,郭林,杨柳,等.膝关节镜动态监视下分级手术治疗髌股关节紊乱[C].第六届西部骨科论坛暨贵州省骨科年会论文汇编, 2010: 281.
[16] 杨景震,霍英杰,王成健,等.髌股关节紊乱的MRI表现与临床[J].放射性学实践,2011,26(7):753-755
[17] 张志杰,冯亚男,朱毅,等.髌股疼痛综合征的病因机制及治疗研究新进展[J].中国康复医学杂志.2012,27(4):384-386.
[18] Warden SJ, Hinman RS, Watson MA Jr, et al. Patellar taping and bracing for the treatment of chronic knee pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arthritis Rheum. 2008; 59(1):73-83.
[19] Post WR, Teitge R, Amis A. Patellofemoral malalignment: looking beyond the viewbox. Clin Sports Med. 2002;21(3): 521-546, x.
[20] Schutzer SF, Ramsby GR, Fulkerson JP. The evaluation of patellofemoral pain using computerized tomography. A preliminary study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1986;(204):286-293.
[21] Wilson T. The measurement of patellar alignment in patellofemoral pain syndrome: are we confusing assumptions with evidence? J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2007;37(6): 330-341.
[22] 张诚,王玉彬,单连良,等.关节镜下外侧支持带松解术联合髌骨外侧成形术治疗顽固性LPSC[J].山东医药,2012,52(10):41-42.
[23] 朱琦,王万春.髌股疼痛综合征病因学新观点[J].国际骨科学杂志, 2006,27(2):101-102.
[24] 李仕臣,王文革,田世坤,等.髌股关节参数在膝前疼痛中的意义[J].中国药物与临床,2011,11(9):1034-1035.
[25] 黄荣瑛,徐强,许勇刚,等.髌骨位姿异常对髌股关节接触影响的研究[J].航天医学与医学工程,2011,24(1):47-52.
[26] 史晨辉,王永,董金波,等.关节镜下外侧支持带松解治疗膝关节骨性关节炎[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2005,21(13):1679-1680.
[27] 王予彬,王惠芳,李文峰,等.关节镜下清理髌外侧支持带松解治疗膝关节骨性关节炎[J].中华矫形外科杂志,2003,12(11):829-830.
[28] 宣涛,徐斌,徐洪港,等.关节镜下射频汽化仪治疗髌股关节紊乱症[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2009,23(1):60-63.
[29] Thomeé R, Augustsson J, Karlsson J. Patellofemoral pain syndrome: a review of current issues. Sports Med. 1999; 28(4):245-262.
[30] Crossley K, Bennell K, Green S, et al. A systematic review of physical interventions for patellofemoral pain syndrome. Clin J Sport Med. 2001;11(2):103-110.
[31] Witvrouw E, Werner S, Mikkelsen C, et al. Clinical classification of patellofemoral pain syndrome: guidelines for non-operative treatment. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2005;13(2):122-130.
[32] Rixe JA, Glick JE, Brady J, et al. A review of the management of patellofemoral pain syndrome. Phys Sportsmed. 2013; 41(3):19-28.
[33] Nordentoft M. Prevention of suicide and attempted suicide in Denmark. Epidemiological studies of suicide and intervention studies in selected risk groups. Dan Med Bull. 2007;54(4): 306-369.
[34] Song CY, Lin JJ, Jan MH, et al. The role of patellar alignment and tracking in vivo: the potential mechanism of patellofemoral pain syndrome. Phys Ther Sport. 2011;12(3): 140-147.
[35] Smith TO, Davies L, Donell ST. The reliability and validity of assessing medio-lateral patellar position: a systematic review. Man Ther. 2009;14(4):355-362.
[36] 刘春龙,杜峰,余瑾,等.髌股关节疼痛综合征女性患者的髋关节肌力评测与分析[J].中国康复医学杂志,2012,27(6):570-571. |