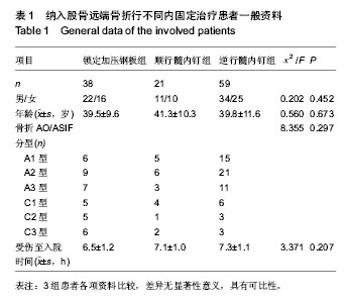
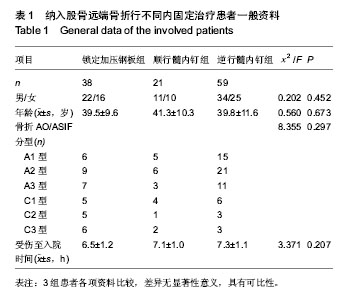
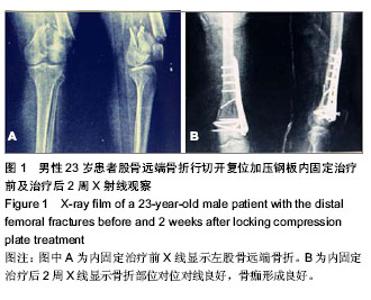
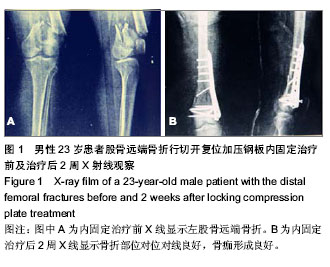
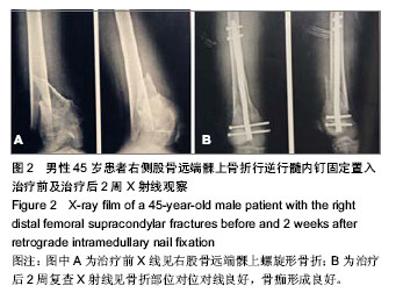
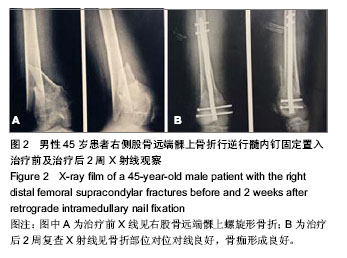
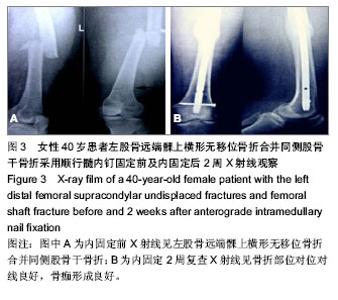
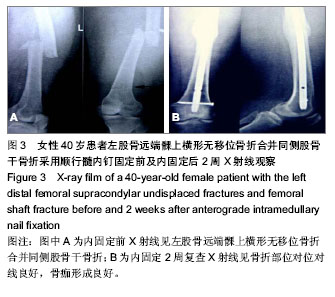
| [1] 张长青,施慧鹏.骨科专家病例解析丛书(创伤卷)[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2011:100.[2] 吴慧敏,文勇,刘治,等.单钢板与内外侧双钢板固定治疗股骨远端C3型骨折疗效比较[J].临床骨科杂志,2013,16(5):542-544.[3] 邓建龙,王剑敏,张茗慧,等.顺行髓内钉、逆行髓内钉及锁定加压钢板内固定治疗股骨远端骨折的对比研究[J].现代生物医学进展,2013,12(24):4687-4690.[4] 王剑,林洪伟.微创固定系统接骨板治疗股骨远端C型骨折的疗效分析[J].检验医学与临床,2013,10(15):1976-1977. [5] Van der Borght K, Wallinga AE, Luiten PG, et al. Morris water maze learning in two rat strains increases the expression of the polysialylated form of the neural cell adhesion molecule in the dentate gyrus but has no effect on hippocampal neurogenesis. Behav Neurosci. 2005;119(4):926-932.[6] 韩勇平,廖瑛,王帅.股骨远端骨折的内固定治疗[J].内蒙古中医药,2013,(31)9:53-54.[7] 孙健,蔡郑东,朱裕昌,等.LISS钢板在治疗股骨远端骨折畸形愈合的应用[J].南方医科大学学报,2010,30(5):1209-1213.[8] 关继奎,关雨,赵丽,等.内固定物置入治疗股骨远端骨折的生物力学变化与临床效果[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(13): 2439-2446.[9] Hak DJ,Nguyen J,Curtiss S,et al. Coronal fractures of the distal femoral condyle: a biomechanical evaluation of four internal fixationconstructs. Injury. 2005;36(9):1103-1106.[10] Zlowodzki M,Williamson S,Zardiackas LD,et al. Biome-chanical evaluation of the less invasive stabilization systemand the 95-degree angled blade plate for the internal fixa-tion of distal femur Fractures in human cadaveric boneswith high bone mineral density. J Trauma. 2006;60(4): 836-840.[11] 鲁迪,巴克利,莫兰.骨折治疗的AO原则[M].2版.上海:上海科学技术出版社,2010:53-67.[12] 李晗,王威,侯志勇,等.三种内固定方式治疗股骨远端骨折的疗效比较[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2012,14(11):950-953. [13] 王宝军,刘振宇,赵亮,等.三种内固定方法治疗股骨远端骨折的疗效分析[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2009,11(12):1118-1121.[14] Neubauer T. Distal femoral fractures. Unfallchirurg. 2012; 115(5): 433-449. [15] 关鹏飞,陈长河,李冀,等.倒置股骨远端外侧锁定板经皮微创内固定治疗复杂股骨粗隆下骨折[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2013, 28(8):771-772.[16] 唐虎子,郭鹏,马胜利,等. 微创内固定系统治疗股骨远端骨折[J]. 临床骨科杂志,2012,15(4):441-442.[17] 涂庆生,吴康蛊,余小容,等.锁定钢板与解剖型钢板治疗股骨远端骨折的临床疗效对比分析[J].中国医药指南,2012,10(24):18-19.[18] 张曦,许建湘,吕正祥,等.锁定加压钢板在胫骨远端骨折中的应用[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2007,9(2):196.[19] 买买提艾力•尼亚孜,艾合买提•吾买尔,买尔旦•买买提等.逆行髓内钉和钢板置入内固定治疗股骨远端骨折的比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(44):8201-8205. [20] 刘竹林,刘牛庆,李玉民,等.逆行交锁髓内钉与钢板治疗股骨干骨折临床疗效比较[J].南方医科大学学报,2010,30(5):1205-1206.[21] Vidovi? D, Matejci? A, Ivica M, et al. Approach to distal femur by osteotomy of the patellar distal pole and internal fixation with basket plate in complex articular fracture: report of five cases. Acta Clin Croat. 2013;52(1):113-118.[22] Zhang ZM, Liu J, Huang CX, et al. Treatment of type C3 distal femoral fractures with double-plating fixation via anteriormiddle approach. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2012;25(12): 1049-1052. [23] Barei DP, Beingessner DM. Open distal femur fractures treated with lateral locked implants: union, secondary bone grafting, and predictive parameters. Orthopedics. 2012;35(6): e843-846. [24] 俞新胜,肖波,汪普,等.微创锁定钢板治疗股骨远端C型骨折疗效分析[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2012,9(2):26-28.[25] 郝廷,余斌,郝增涛等.股骨远端微创锁定内固定钢板固定参数的三维数字化测量[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(13):2292-2295 [26] 张岩,杨铁毅,刘树义,等.有限元分析LISS-DF治疗股骨远端骨折近端螺钉单双皮质不同组合固定方式的应力分布[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2012,16(4):581-584.[27] 李景伟,王文志,冯世庆,等.闭合复位逆行交锁髓内钉治疗股骨远端骨折[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2012,20(2):181-183.[28] Kim J, Kang SB, Nam K, et al. Retrograde intramedullary nailing for distal femur fracture with osteoporosis. Clin Orthop Surg. 2012;4(4):307-312. [29] Horneff JG 3rd, Scolaro JA, Jafari SM, et al. Intramedullary nailing versus locked plate for treating supracondylar periprosthetic femur fractures. Orthopedics. 2013;36(5): e561-566.[30] Hohman DW, Affonso J, Budny J, et al. Calcaneal plate fixation of distal femoral fractures. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2012;41(3):140-143. [31] Khalil Ael-S, Ayoub MA. ghly unstable complex C3-type distal femur fracture: can double plating via a modified Olerud extensile approach be a standby solution? J Orthop Traumatol. 2012;13(4):179-188.[32] Ahmadi S, Shah S, Wunder JS, et al. The biomechanics of three different fracture fixation implants for distal femur repair in the presence of a tumor-like defect. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2013;227(1):78-86. [33] Heyworth BE, Hedequist DJ, Nasreddine AY, et al. Distal femoral valgus deformity following plate fixation of pediatric femoral shaft fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013;95(6): 526-533. |