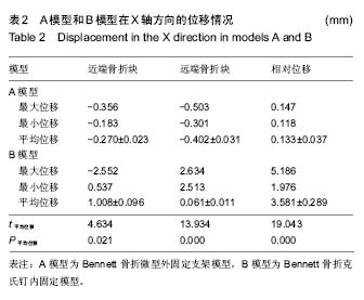
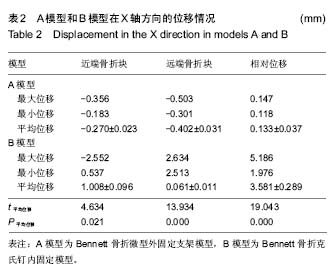
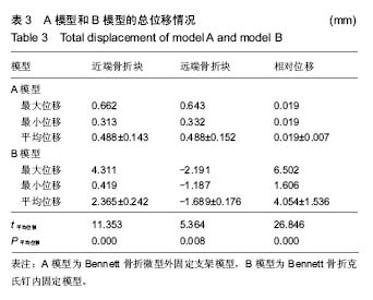
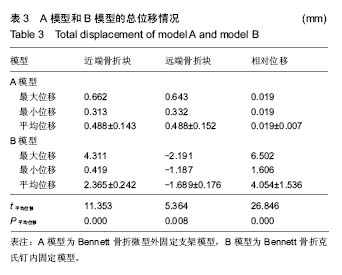
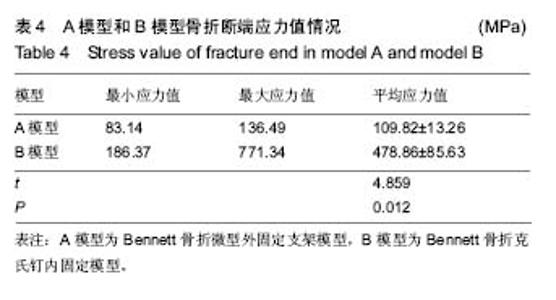
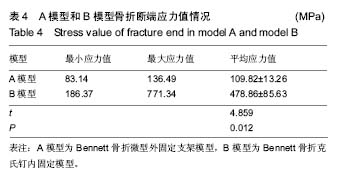
| [1] Middleton SD, McNiven N, Griffin EJ, et al.Long-term patient-reported outcomes following Bennett's fractures.Bone Joint J. 2015;97-B(7):1004-1006. [2] Evans P, Pervaiz K.Sport-specific commentary on Bennett and metacarpal fractures in football.Hand Clin. 2012; 28(3):393-394. [3] Clinkscales C.Sports-specific commentary on Bennett's fractures in professional basketball players: Bennettfractures and metacarpal fractures.Hand Clin. 2012;28(3):391-392. [4] Mahmoud M, El Shafie S, Menorca RM, et al.Management of neglected Bennett fracture in manual laborers by tension fixation.J Hand Surg Am. 2014;39(9):1728-1733. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2014.06.019. [5] 冯晰旻,田兴辉,姜荃月.不同手术方式对Bennett骨折远期疗效的影响[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2013,28(5):485-486.[6] 奕央华,杨亚杰.Bennett Rolando骨折的闭合复位内固定治疗[J].临床合理用药,2014,1(7): 158.[7] Bennani A, Zizah S, Benabid M, et al.The intermetacarpal double pinning in the surgical treatment of Bennett fracture (report of 24 cases).Chir Main. 2012;31(3):157-162.[8] 胥少汀,葛宝丰,徐印坎.实用骨科学[M].4版.北京:人民军医出版社,2014.[9] Deml C, Smekal V, Kastenberger T, et al.Pressure distribution in carpometacarpal joint, due to step-off in operatively treated Bennett'sfractures.Injury. 2014;45(10):1574-1578. [10] 刘德淮,庄小强,白宇,等.经皮克氏针固定微创治疗Bennett骨折[J].实用骨科杂志,2014,20(3):278-280.[11] 王学磊,康志秋.两种手术方法治疗Bennett骨折[J].实用手外科杂志,2014,2(28):176-179.[12] Pavi? R, Malovi? M.Operative treatment of Bennett's fracture. Coll Antropol. 2013;37(1):169-174.[13] Leclère FM, Jenzer A, Hüsler R, et al.7-year follow-up after open reduction and internal screw fixation in Bennett fractures.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2012;132(7):1045-1051. [14] Zhang X, Shao X, Zhang Z, et al.Treatment of a Bennett fracture using tension band wiring.J Hand Surg Am. 2012; 37(3):427-433.[15] 柳岩,牛杰,叶会跃,等.手法整复前臂石膏铁丝指夹板外固定治疗Bennett骨折[J].中医正骨,2013, 7(25):60-61.[16] 梁献丹,朱玉辉,吕游,等.闭合复位经皮穿针微创治疗新鲜Bennett骨折23例[J] .中国现代药物应用,2014,22(8): 14-15.[17] 汤样华,曾林如,徐灿达,等.微型外固定支架结合克氏针固定治疗Bennett骨折[J].中华手外科杂志,2012,28(6):372-373. [18] 王武,曹鹏.闭合复位第一、二掌骨间克氏针固定治疗Bennett骨折[J].中华手外科杂志,2013,29(6):383-384. [19] 王清义,张瑞云,关富龙,等.可吸收缝线钻孔环扎治疗Bennett骨折[J].中华手外科杂志,2011,27(5):319.[20] 沈华,沈尊理,马杰,等.空心拉力螺钉治疗Bennett骨折的临床研究[J].中华手外科杂志,2014,5(30): 365-367.[21] 朱宏伟,张旭,李彦闯,等,钢丝张力带治疗Bennett骨折[J].实用手外科杂志,2013,4(27): 364-365.[22] 曹克奎,衣英豪,王相如,等. 闭合复位克氏针内固定治疗Bennett骨折[J]. 西南国防医药,2013,23(5):522-524.[23] Elkins J, Marsh JL, Lujan T,et al.Motion Predicts Clinical Callus Formation: Construct-Specific Finite Element Analysis of Supracondylar Femoral Fractures.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2016;98(4):276-284. [24] Yu B, Chen WC, Lee PY,et al.Biomechanical comparison of conventional and anatomical calcaneal plates for the treatment of intraarticular calcaneal fractures - a finite element study.Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2016:1-8. [25] 支中正. 尺骨茎突骨折内固定对下尺桡关节稳定性影响的有限元分析[D].复旦大学,2013.[26] 张浩,朱建民,马南,等. 腕关节有限元骨性建模及力学分析[J]. 江苏大学学报(医学版),2013,23(1):53-56.[27] Mei ML, Chen YM, Li H,et al.Influence of the indirect restoration design on the fracture resistance: a finite element study. Biomed Eng Online. 2016;15(1):3. [28] 顾松,刘天苹,沈尊理,等. 基于有限元的第5掌骨颈骨折钢板螺钉内固定的生物力学分析[J]. 现代生物医学进展,2015,15(21): 4056-4059.[29] 谢世隆,方楚权,严瑾,等.微型外固定支架和克氏针治疗Bennett骨折的三维有限元分析[J].中国医药指南,2014,12(18): 185-185.[30] Harith H, Schmutz B, Malekani J,et al.Can we safely deform a plate to fit every bone? Population-based fit assessment and finiteelement deformation of a distal tibial plate.Med Eng Phys. 2016;38(3):280-285. [31] Nigil Haroon N, Szabo E, Raboud JM, et al. Alterations of bone mineral density, bone microarchitecture and strength in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: a cross-sectional study using high-resolution peripheral quantitative computerized tomography and finite element analysis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2015;17(1):377. [32] 陈延荣. 桡骨远端骨折畸形愈合后腕关节的生物力学变化[D].苏州大学,2013.[33] Varga P, Zysset PK, Schefzig P, et al.A finite element analysis of two novel screw designs for scaphoid waist fractures. Med Eng Phys. 2016;38(2):131-139. [34] Niort F, Godio-Raboutet Y, Torrents R, et al.Transmission of force to the hyoid bone during manual strangulation: Simulation using finiteelement numerical models.Forensic Sci Int. 2015;257:420-424. [35] Noda M, Saegusa Y, Takahashi M,et al.Biomechanical Study Using the Finite Element Method of Internal Fixation in Pauwels Type III Vertical Femoral Neck Fractures.Arch Trauma Res. 2015;4(3):e23167. [36] Liu XM, Pan CW, Wang GD, et al.Finite element analysis of the stability of combined plate internal fixation in posterior wall fracturesof acetabulum.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(8):13393- 13397. [37] Synek A, Chevalier Y, Baumbach SF,et al.The influence of bone density and anisotropy in finite element models of distal radius fractureosteosynthesis: Evaluations and comparison to experiments.J Biomech. 2015;48(15):4116-4123. |