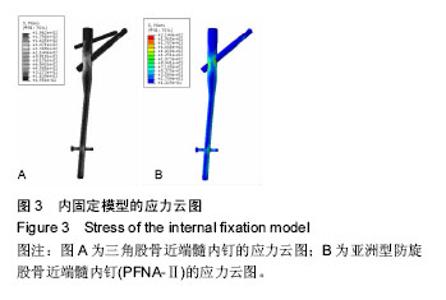
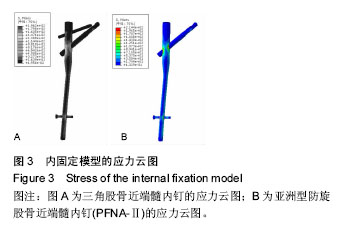
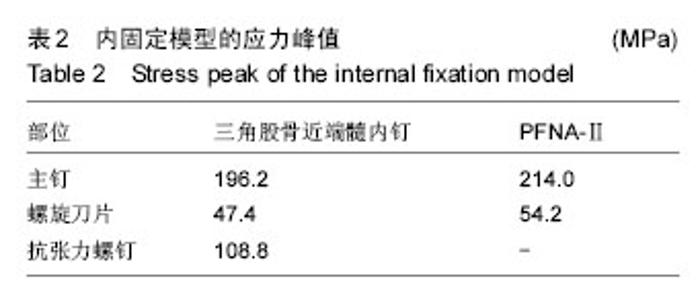
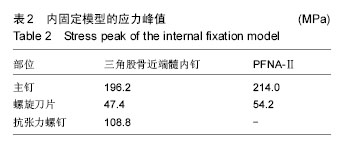
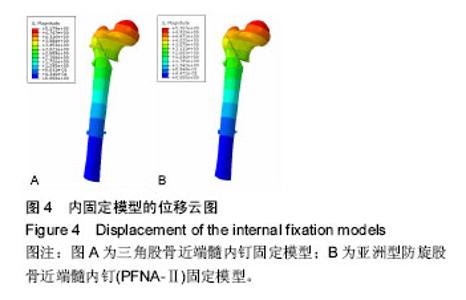
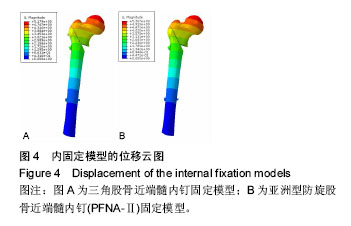
| [1] Wilk R,Skrzypek M,Kowalska M,et al.Standardized incidence and trend of osteoporotic hip fracture in Polish women and men:A nine year observation. Maturitas.2014;77(1):59-63.
[2] 沈宁江,林坚平,王广积,等.老年股骨转子间骨折不同手术方法比较研究[J].实用骨科杂志,2016, 22(1):6-10.
[3] Sadic S,Custovic S,Jasarevic M,et al.Proximal femoral nail antirotation in treatment of fractures of proximal femur.Med Arh.2014;68(3):173-177.
[4] 陈明,蔡郑东.股骨粗隆间骨折手术髓内固定和髓外固定治疗的比较[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2016,24(12):1131-1133.
[5] Sawaguchi T,Sakagoshi D,Shima Y,et al.Do design adaptations of a trochanteric nail make sense for Asian patients? Results of a multicenter study of the PFNA-II in Japan.Injury. 2014;45(10):1624-1631.
[6] 刘景一,杨晓飞,贺新兵,等.股骨近端螺旋刀片抗旋髓内钉治疗股骨粗隆间骨折的并发症及其防治[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2014,22(22):2105-2107.
[7] 茹江英,从宇,仓海斌,等.老年股骨粗隆间骨折PFNA内固定术后失效的翻修方法及效果分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2014,29(2):129-131.
[8] Grecu D, Pucalev I, Negru M,et al.Numerical simulations of the 3D virtual model of the human hip joint, using finite element method.Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2010;51(1): 151-155.
[9] Papini M,Zdero R,Schemitsch EH,et al.The biomechanics of human femurs in axial and torsional loading: comparison of finite element analysis, human cadaveric femurs, and synthetic femurs.J Biomech Eng. 2007;129(1):12-19.
[10] Helwig P,Faust G,Hindenlang U,et al.Finite element analysis of four different implants inserted in different positions to stabilize an idealized trochanteric femoral fracture. Injury. 2009;40(3):288-295.
[11] Audu ML,Davy DT.The influence of muscle model complexity in musculoskeletal motion modeling. Biomech Engr. 1985;107(2):147-157.
[12] Tada S,Stegaroiu R,Kitamura E,et al.Influence of implant designand bone quality on stress/strain distribution in bone around implants: a 3-dimensional finite element analysis.Int J Maxillofac Impants. 2003; 18(3):357-368.
[13] Kobayashi E,Wang TJ,Doi H,et al.Mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of Ti-6Al-7Nb alloy dental castings. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 1998;9(10):567-574.
[14] Eberle S,Gerber C,Von Oldenburg G, et al.A biomechanical evaluation of orthopaedic implants for hip fractures by finite element analysis and in-vitro tests. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2010;224(10):1141–1152.
[15] Goffin JM,Pankaj P,Simpson AH,et al.Does bone compaction around the helical blade of a proximal femoral nail anti-rotation (PFNA) decrease the risk of cut-out?: A subject-specific computational study. Bone Joint Res. 2013; 2(5):79-83.
[16] Niu E,Yang A,Harris AH,et al.Which Fixation Device is Preferred for Surgical Treatment of Intertrochanteric Hip Fractures in the United States? A Survey of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015; 473(11):3647-3655.
[17] 张金辉,张科学,张立海,等.老年股骨粗隆间骨折股骨近端抗旋髓内钉和股骨近端髓内钉InterTAN的选择和疗效评价[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2015,29(5):538-541.
[18] 冷云飞,于沈敏,蔡兵,等.防旋股骨近端髓内钉微创内固定治疗老年股骨转子间骨折[J]. 临床骨科杂志,2016,19(4): 469-470.
[19] Sadic S,Custovic S,Jasarevuc M, et al. Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation in Treatment of Intertrochanteric Hip Fractures: a Retrospective Study in 113 Patients.Med Arch. 2015;69(6):352-356.
[20] 陆晴友,李增春,李国风,等. PFNA及PFNAⅡ治疗股骨转子间骨折疗效分析[J]. 国际骨科学杂志,2011,32(1): 54-56.
[21] 王永安,顾龙殿,禹宝庆,等. PFNA内固定治疗股骨粗隆间骨折临床疗效观察[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2013, 28(6):514-516.
[22] 张世民,马卓,杜守超,等.股骨近端外侧壁的解剖学研究及其对转子间骨折内固定的意义[J].中国临床解剖学杂志, 2016,34(1):39-42.
[23] Brunner A, Büttler M, Lehmann U,et al.What is the optimal salvage procedure for cut-out after surgical fixation of trochanteric fractures with the PFNA or TFN? A multicentre study. Injury. 2016;47(2):432-438.
[24] Seyhan M,Turkmen I,Unay K,et al.Do PFNA devices and Intertan nails both have the same effects in the treatment of trochanteric fractures? A prospective clinical study. J Orthop Sci. 2015;20(6):1053-1056.
[25] Yu W,Zhang X,Wu R,et al.The visible and hidden blood loss of Asia proximal femoral nail anti-rotation and dynamic hip screw in the treatment of intertrochanteric fractures of elderly high- risk patients: a retrospective comparative study with a minimum 3 years of follow-up. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2016;17:269.
[26] Li J,Cheng L,Jing J.The Asia proximal femoral nail antirotation versus the standard proximal femoral antirotation nail for unstable intertrochanteric fractures in elderly Chinese patients.Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2015;101(2):143-146.
[27] 侯建伟,谢仁国,李玉前,等. PFNA-Ⅱ微创治疗老年骨质疏松性股骨粗隆间骨折的临床疗效[J].江苏医药,2015, 41(12):1460-1461.
[28] 杨飞,韩启明,杨凤明,等.老年股骨粗隆间骨折微创INTERTAN髓内钉与PFNA-Ⅱ髓内钉临床疗效分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2015,23(10):897-901.
[29] 辛培成,李明,赵德伟,等. ALCP、PFNA-Ⅱ、InterTan内固定治疗股骨粗隆间骨折的疗效比较[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2016,31(6):588-590.
[30] Tao YL, Ma Z, Chang SM.Does PFNA II avoid lateral cortex impingement for unstable peritrochanteric fractures? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013;471(4): 1393-1394.
[31] 王世斌,张亚峰. PFNA-Ⅱ治疗股骨粗隆间骨折的疗效分析[J].江苏医药,2012,38(23):2883-2884.
[32] Sitthiseripratip K,Van OH,Vander SJ,et al,Finite element study of trochanteric gamma nail for trochanteric fracture. Med Eng Phys. 2003;25(2): 99-106.
[33] Mueller TL,Christen D,Sandercott S,et al.Computational finite elementbone mechanics accurately predicts mechanical competence in the human radius of an elderly population.Bone. 2011; 48(6):1232-1238.
[34] 姜自伟,黄枫,庞智晖,等.股骨转子间骨折的“三角固定”理论[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2015,23(9):70-72.
[35] Lavini F,Renzi-Brivio L,Aulisa R,et al.The treatment of stable and unstable proximal femoral fractures with a new trochanteric nail: results of a multicentre study with the Veronail. Strategies Trauma Limb Recorstr. 2008;3(1):15-22.
[36] Tai CL,Chen WP,Chen HH,et al.Biomechanical optimization of different fixation modes for a proximal femoral L-osteotomy.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2009;10:112.
[37] 冯卫,郝廷,郝增涛,等.三种股骨近端髓内钉固定股骨转子间骨折的有限元分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2012, 20(8): 730-733. |