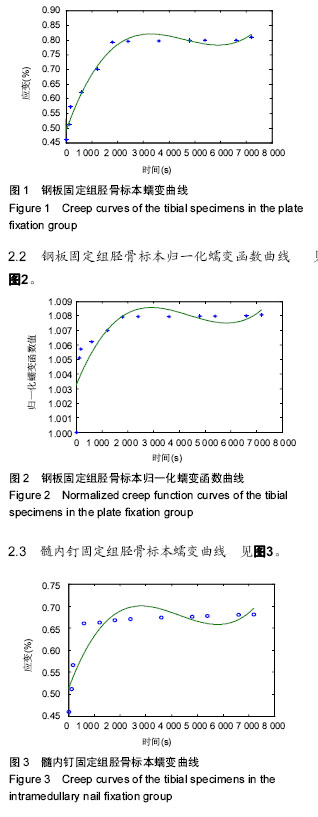
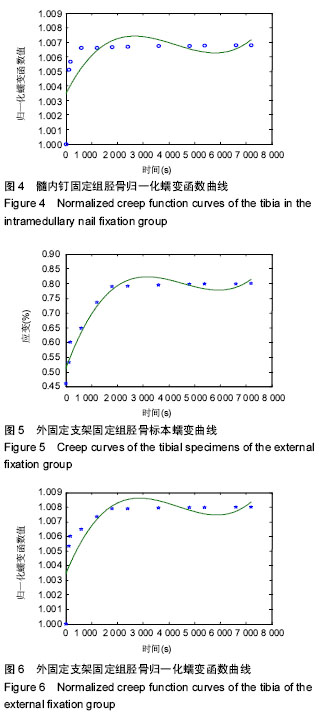
| [1] 迟佳囡,武子靖,付广龙.胫骨骨折内固定方法在三点受弯下的生物力学研究[C]. 呼和浩特:第十二届全国实验力学学术会议摘要集,2009.[2] 王亦璁.骨与关节损伤[M].3版.北京:人民卫生出版社, 1996:1060.[3] Shadgan B, Pereira G, Menon M, et al. Risk factors for acute compartment syndrome of the leg associated with tibial diaphyseal fractures in adults.J Orthop Traumatol. 2015;16(3):185-192.[4] Foote CJ, Guyatt GH, Vignesh KN, et al. Which Surgical Treatment for Open Tibial Shaft Fractures Results in the Fewest Reoperations. A Network Meta-analysis.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015;473(7): 2179-2192.[5] Dong W, Shi Z, Liu Z, et al. Design and clinical application of surgical device for closed reduction of tibial fracture.Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2013;27(11):1281-1285.[6] Tahririan MA, Ziaei E, Osanloo R.Significance of the position of the proximal tip of the tibial nail: An important factor related to anterior knee pain.Adv Biomed Res. 2014;3:119.[7] 闵竞,何盛江,郑华,等.交锁髓内钉早期动力化治疗对下肢骨折患者治疗效果的影响研[J].重庆医学,2013,42(25): 2988-2990.[8] 齐新文,王兆杰,邝立鹏,等. 急诊Sanatmetal交锁髓内钉治疗胫腓骨开放多段粉碎骨折的疗效[J].广东医学,2012, 33(21):3283-3285.[9] 刘印文,匡勇,顾新丰,等.手法闭合复位结合MIPPO技术治疗胫骨骨折56例临床研究[J].中国骨伤,2013,26(3): 248-251.[10] 王国利,张建华,张旭坤,等. LCP内固定治疗胫骨远端骨折过程中微创钢板内固定技术的应用[J].山东医药,2014, 54(3):79-81.[11] 楚万忠,谢新敏,刘华水,等.三种方法治疗胫骨远端骨折的比较[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2012 ,27(6):548-549.[12] 魏任远.胫骨中下段骨折的微创经皮钢板与切开复位内固定疗效比较[J]. 中国医药导报,2013,10(8): 46-47,50.[13] 陈科杰.微创经皮锁定加压钢板内固定术治疗胫骨中下段闭合性骨折疗效观察[J].现代实用医学,2013,25(9): 990-991.[14] 吴志峰,李艳玲,刘光耀,等.三种固定器械固定胫骨骨折的应力松弛实验[J].中国组织工程研究,2012, 16(9) :1605- 1608.[15] 黄俊武,王向阳,石成第,等.三种不同器械固定胫骨骨折的生物力学评价及临床意义[J].中华创伤骨科杂志2006, 8(7): 668-670.[16] 张翘,高明,李鹏,等.三种固定器械置入固定胫骨骨折的生物力学分析[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009, 13(35):3837-3870.[17] Zhang ZJ, Li YJ, Liu XG,et al.Human umbilical cord blood stem cells and brain-derived neurotrophic factor for optic nerve injury: a biomechanical evaluation. Neural Regen Res. 2015;10(7):1134-1138.[18] Wang Y, Li ZW, Luo M, et al. Biological conduits combining bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and extracellular matrix to treat long-segment sciatic nerve defects. Neural Regen Res. 2015;10(6):965-971. [19] Jin H, Yang Q, Ji F, et al. Human amniotic epithelial cell transplantation for the repair of injured brachial plexus nerve: evaluation of nerve viscoelastic properties. Neural Regen Res. 2015;10(2):260-265.[20] Uhthoff HK, Dubuc FL.Bone structure changes in the dog under rigid internal fixation. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1971;81:165-170. [21] Krettek C, Schandelmaier P, Miclau T, et al. Minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis (MIPPO) using the DCS in proximal and distal femoral fractures. Injury. 1997;28 Suppl 1:A20-30.[22] 林博文,肖德明,黎伟凡,等.微创经皮钢板固定治疗胫骨骨折[J].中华创伤杂志,2002,18(9):551-553.[23] 辛景义,鲁杰,魏万富,等.混合式外固定器结合有限内固定治疗胫骨远端骨折[J].中国骨科杂志,2006,26(9): 642-645. [24] Kumar P, Singh GK, Bajracharya S. Treatment of grade IIIB opens tibial fracture by Ilizarov hybrid external fixator. Kathmandu Univ Med J (KUMJ). 2007; 5(2):177-180.[25] Boenisch UW, de Boer PG, Journeaux SF. Unreamed intramedullary tibial nailing--fatigue of locking bolts. Injury. 1996;27(4):265-270.[26] 罗先正,张薇.髓内钉的生物力学设计[J].中华骨科杂志, 1997,17(4):272-275.[27] 周来喜,林本丹,钟志刚,等.胫骨三种固定器械的生物力学比较和临床研究[J].骨与关节损伤杂志,2000,15(6):428- 430. |