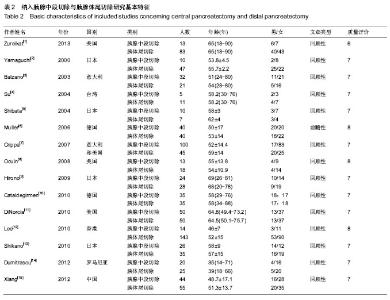
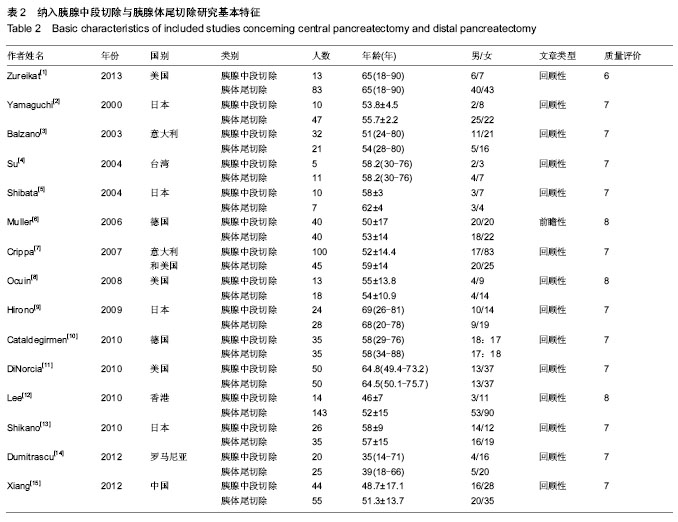
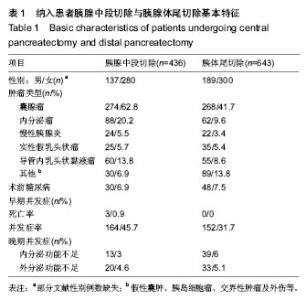
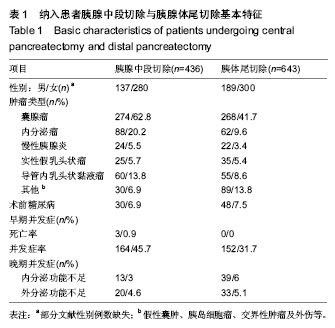
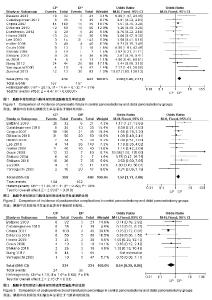
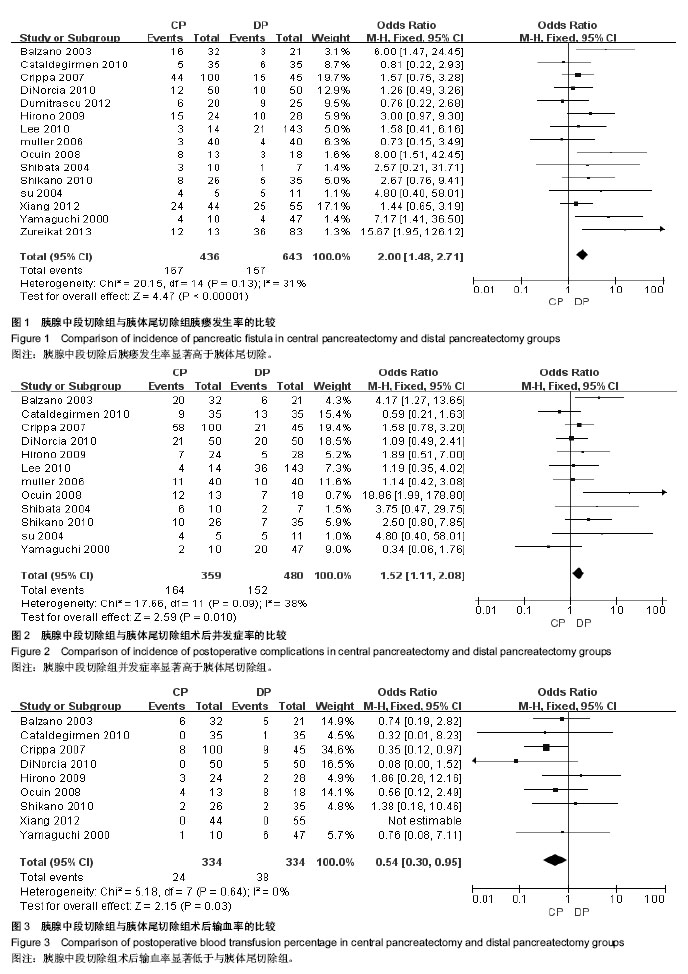
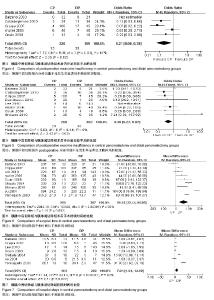
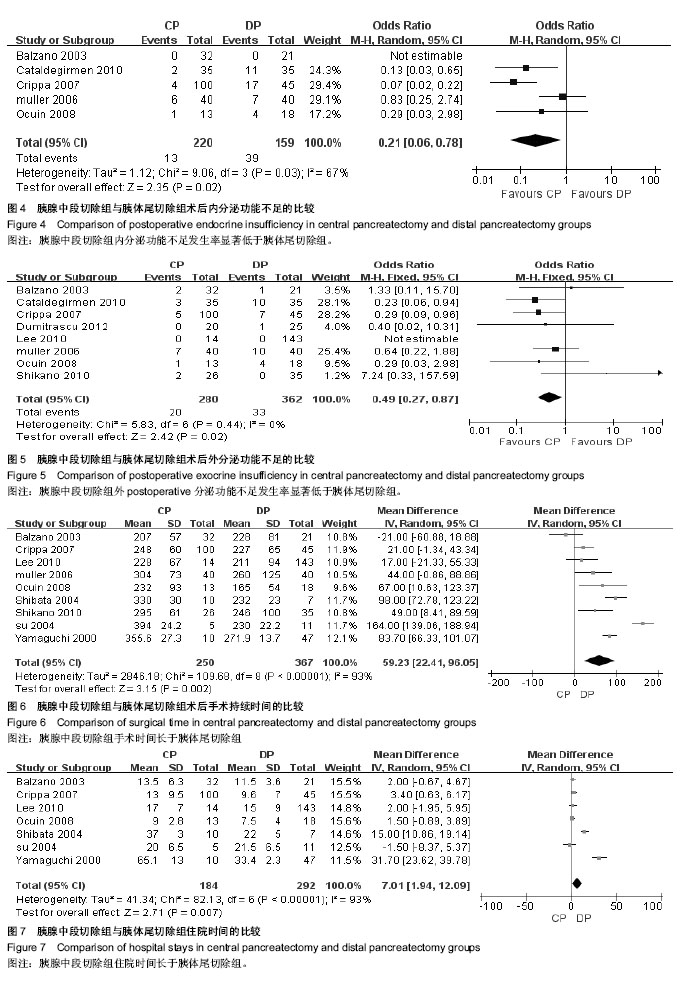
| [1] Zureikat AH, Moser AJ, Boone BA, et al. 250 robotic pancreatic resections: safety and feasibility. Ann Surg. 2013;258(4): 554-559; discussion 559-562.
[2] Yamaguchi K, Yokohata K, Ohkido M, et al. Which is less invasive--distal pancreatectomy or segmental resection? . Int Surg.2000;85(4):297-302.
[3] Balzano G, Zerbi A, Veronesi P, et al. Surgical treatment of benign and borderline neoplasms of the pancreatic body. Dig Surg. 2003;20(6):506-510.
[4] Su CH, Shyr YM, Lui WY, et al.Surgical treatment for serous cystadenoma of pancreas--segmental pancreatectomy or conventional resection? . Hepatogastroenterology. 2004; 51(56): 595-598.
[5] Shibata S, Sato T, Andoh H, et al.Outcomes and indications of segmental pancreatectomy. Comparison with distal pancreatectomy. Dig Surg. 2004;21(1):48-53.
[6] Muller MW, Friess H, Kleeff J, et al. Middle segmental pancreatic resection: An option to treat benign pancreatic body lesions. Ann Surg. 2006;244(6):909-918; discussion 918-920.
[7] Crippa S, Bassi C, Warshaw AL, et al. Middle pancreatectomy - Indications, short- and long-term operative outcomes. Annals of Surgery. 2007;246(1):69-76.
[8] Ocuin LM, Sarmiento JM, Staley CA, et al. Comparison of central and extended left pancreatectomy for lesions of the pancreatic neck. Ann Surg Oncol. 2008;15(8):2096-2103.
[9] Hirono S, Tani M, Kawai M, et al. A central pancreatectomy for benign or low-grade malignant neoplasms. J Gastrointest Surg. 2009;13(9):1659-1665.
[10] Cataldegirmen G, Schneider CG, Bogoevski D, et al. Extended central pancreatic resection as an alternative for extended left or extended right resection for appropriate pancreatic neoplasms. Surgery.2010;147(3): 331-338.
[11] DiNorcia J, Ahmed L, Lee MK, et al. Better preservation of endocrine function after central versus distal pancreatectomy for mid-gland lesions. Surgery. 2010;148(6):1247-1254; discussion 1254-1246.
[12] Lee SE, Jang JY, Hwang DW, et al. Clinical Efficacy of Organ-Preserving Pancreatectomy for Benign or Low-Grade Malignant Potential Lesion. J Korean Med Science. 2010; 25(1):97-103.
[13] Shikano T, Nakao A, Kodera Y, et al. Middle pancreatectomy: safety and long-term results. Surgery. 2010;147(1):21-29.
[14] Dumitrascu T, Scarlat A, Ionescu M, et al. Central pancreatectomy versus spleen-preserving distal pancreatectomy: a comparative analysis of early and late postoperative outcomes. Dig Surg. 2012;29(5):400-407.
[15] Xiang GM, Tan CL, Zhang H, et al. Central pancreatectomy for benign or borderline lesions of the pancreatic neck: a single centre experience and literature review. Hepatogastroenterology. 2012;59(116):1286-1289.
[16] Stang A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol. 2010;25(9): 603-605.
[17] Iacono C, Verlato G, Ruzzenente A, et al. Systematic review of central pancreatectomy and meta-analysis of central versus distal pancreatectomy. Br J Surg. 2013;100(7): 873-885.
[18] Bassi C, Dervenis C, Butturini G, et al. Postoperative pancreatic fistula: an international study group (ISGPF) definition. Surgery. 2005;138(1):8-13.
[19] Xu SB, Zhu YP, Zhou W, et al. Patients get more long-term benefit from central pancreatectomy than distal resection: A meta-analysis. Ejso. 2013;39(6):567-574.
[20] Kendall DM, Sutherland DE, Najarian JS, et al. Effects of hemipancreatectomy on insulin secretion and glucose tolerance in healthy humans. N Engl J Med 1990;322: 898-903.
[21] Kumar AF, Gruessner RW, Seaquist ER. Risk of glucose intolerance and diabetes in hemipancreatectomized donors selected for normal preoperative glucose metabolism. Diabetes Care 2008;31:1639-1643. |