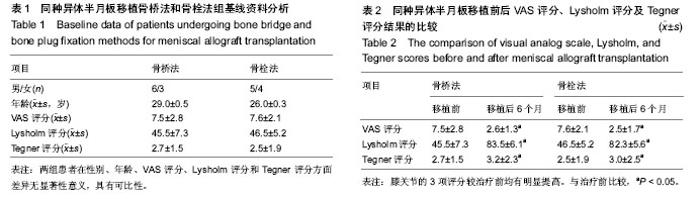
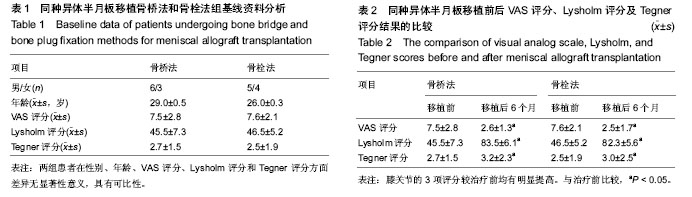
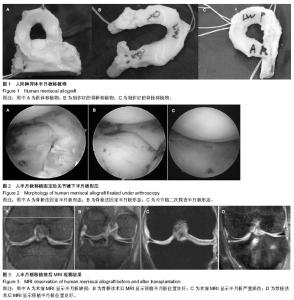
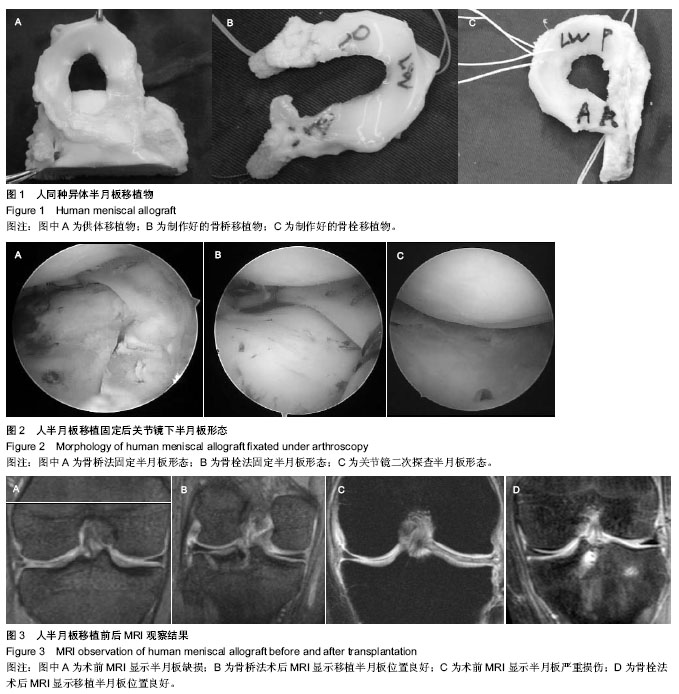
| [1] Lee AS, Kang RW, Kroin E, et al. Allograft meniscus transplantation.Sports Med Arthrosc. 2012;20(2):106-114.
[2] Vermesan D, Prejbeanu R, Laitin S, et al. Arthroscopic debridement compared to intra-articular eroids in treating degenerative medial meniscal tears. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.2013;17(23):3192-3196.
[3] Saltzman BM, Bajaj S, Salata M, et al. Prospective long-term evaluation of meniscal allograft transplantation procedure: a minimum of 7-year follow-up. J Knee Surg. 2012;25(2):165-175.
[4] Faivre B,Boisrenoult P,Lonjon G,et al.Lateral meniscus allograft transplantation: Clinical and anatomic outcomes after arthroscopic implantation with tibial tunnels versus open implantation without tunnels. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2014;100(3):297-302.
[5] Tegner Y, Lysholm J. Rating system in the evaIuation of knee liga-ment injur)r. Clin Orthop Relat Res.1984;198:43-49.
[6] Verdonk R,Volpi P,Verdonk P,et al.Indications and limits of meniscal allografts. Injury. Injury. 2013;44 Suppl 1:S21-27.
[7] Berhouet J, Marty F, Rosset P, et al. Meniscus matching: evaluation of direct anatomical, indirect radiographic, and photographic methods in 10 cadaver knees. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res.2013;99(3):291-297.
[8] Marcacci M, Zaffagnini S, Marcheggiani Muccioli GM, et al. Meniscal allograft transplantation without bone plugs: a 3-year minimum follow-up study. Am J Sports Med. 2012; 40(2):395-403.
[9] Lee YH, Caborn DN. A new technique for arthroscopic meniscus transplant using soft tissue fixation and anatomical meniscal root reinsertion. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2012;20(5):904-908.
[10] Ha JK, Sung JH, Shim JC, et al. Medial meniscus allograft transplantation using a modified bone plug technique: clinical, radiologic, and arthroscopic results. Arthroscopy. 2011;27(7): 944-950.
[11] Abat F, Gelber PE, Erquicia JI, et al. Suture-only fixation technique leads to a higher degree of extrusion than bony fixation in meniscalallograft transplantation.Am J Sports Med. 2012;40(7):1591-1596.
[12] Wang H, Gee AO, Hutchinson ID, et al. Bone Plug Versus Suture-Only Fixation of Meniscal Grafts: Effect on Joint Contact Mechanics During Simulated Gait. Am J Sports Med. 2014 Apr 28.
[13] Vundelinckx B, Vanlauwe J, Bellemans J. Long-term Subjective, Clinical, and Radiographic Outcome Evaluation of Meniscal Allograft Transplantation in the Knee. Am J Sports Med. 2014 Apr 23.
[14] Vundelinckx B, Bellemans J, Vanlauwe J. Arthroscopically assisted meniscal allograft transplantation in the knee: a medium-term subjective, clinical, and radiographical outcome evaluation.Am J Sports Med. 2010;38(11):2240-2247.
[15] Abat F, Gelber PE, Erquicia JI, et al. Prospective comparative study between two different fixation techniques in meniscal allografttransplantation.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013;21(7):1516-1522.
[16] Lee BS, Chung JW, Kim JM, et al. Morphologic changes in fresh-frozen meniscus allografts over 1 year: a prospective magnetic resonance imaging study on the width and thickness of transplants.Am J Sports Med. 2012;40(6):1384-1391.
[17] Carter T, Economopoulos KJ. Meniscal allograft shrinkage- MRI evaluation. J Knee Surg.2013;26(3):167-171.
[18] Koh YG, Moon HK, Kim YC, et al. Comparison of medial and lateral meniscal transplantation with regard to extrusion of theallograft, and its correlation with clinical outcome. J Bone Joint Surg Br.2012;94(2):190-193.
[19] Choi NH, Yoo SY, Victoroff BN.Position of the bony bridge of lateral meniscal transplants can affect meniscal extrusion. Am J Sports Med. 2011;39(9):1955-1959.
[20] Lee BS,Kim JM,Sohn DW,et al.Review of Meniscal Allograft Transplantation Focusing on Long-term Results and Evaluation Methods. Knee Surg Relat Res.2013;25(1):1-6.
[21] Roumazeille T,Klouche S,Rousselin B,et al. Arthroscopic meniscal allograft transplantation with two tibia tunnels without bone plugs: evaluation of healing on MR arthrography and functional outcomes. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013 Mar 19 |