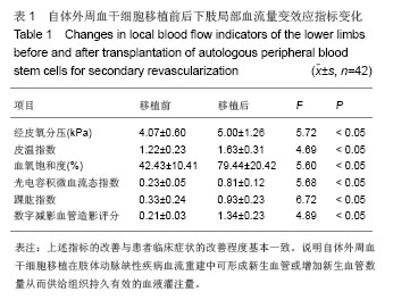
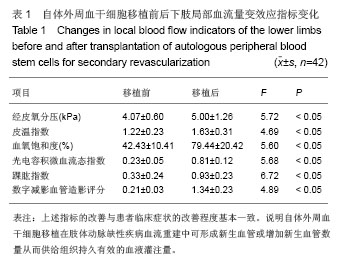
| [1]Huang P, Li S, Han M,et al. Autologous transplantation of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor-mobilized peripheral blood mononuclear cells improves critical limb ischemia in diabetes.Diabetes Care. 2005;28(9):2155-2160.
[2]黄平平,李尚珠,韩明哲,等.自体外周血干细胞移植治疗下肢动脉硬化性闭塞症[J].中华血液学杂志,2003,24(6):308-311.
[3]Oyibo SO, Jude EB, Tarawneh I,et al. A comparison of two diabetic foot ulcer classification systems: the Wagner and the University of Texas wound classification systems. Diabetes Care. 2001;24(1):84-88.
[4]刘政,张玥.血栓闭塞性脉管炎防治答疑[M]. 北京:人民军医出版社,2004:266-271.
[5]Isner JM, Asahara T. Angiogenesis and vasculogenesis as therapeutic strategies for postnatal neovascularization. J Clin Invest. 1999;103(9):1231-1236.
[6]杨镛,陆平,何晓明,等.人自体干细胞移植在重症肢体缺血血流重建中的疗效与评价[J].中国普外基础与临床杂志,2009,16(2): 115-118.
[7]谷涌泉,张健,齐立行,等.自体骨髓干细胞移植治疗慢性下肢缺血94例不同病变分期患者的效果比较[J].中国临床康复,2005, 9(38):7-10.
[8]谷涌泉,郭连瑞,张建,等.自体骨髓干细胞移植改善下肢严重缺血致运动功能障碍:15例报告[J].中国临床康复,2004,8(20): 3917- 3919.
[9]吴雁翔,杨晓凤,王红梅,等.干细胞治疗下肢缺血性疾病疗效观察[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2005,19(12):1019-1021.
[10]杨辉,邓显,施森,等.自体外周血干细胞移植联合血管腔内成形术治疗下肢缺血性疾病的疗效观察[J].实用医院临床杂志,2012, 9(5):96-98.
[11]李华,陈旭艳,冯亮华,等.自体外周血干细胞移植治疗糖尿病下肢缺血效果观察[J].中国综合临床,2011,27(9):958-961.
[12]郭亚娟,张玉顺,刘亚民,等.自体干细胞移植治疗下肢缺血性疾病6例[J].陕西医学杂志,2011,40(12):1636-1638.
[13]陈旭艳,李华,冯亮华, 等.自体外周血干细胞移植治疗下肢缺血性疾病[J].生物医学工程与临床, 2011,15(5):466-469.
[14]杜丽苹,李彦州,温志国.干细胞移植术治疗慢性下肢动脉闭塞性疾病91例研究报告[J].中医临床研究,2010,2(15):85.
[15]李环宇,胡何节,邓福生,等.自体外周血单个核细胞移植治疗下肢缺血27例[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(40):7572- 7575.
[16]杨辉,施森,钟武,等.自体外周血干细胞移植治疗下肢缺血性疾病14例[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(19):3581- 3584.
[17]苏旭,李滨,陈福真, 等.自体外周血干细胞移植术治疗重度下肢缺血19例临床分析[J].中国临床医学,2010,17(1):89-91.
[18]谷涌泉,张建,苏力,等.自体外周血单个核细胞移植治疗下肢缺血53例的临床研究[J].中华普通外科杂志,2006,21(12):848-851.
[19]闻进朝,黄平平.自体外周血单个核细胞移植治疗严重肢体缺血30例:3年安全性随访[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010, 14(45):8526-8530.
[20]杨国凯,杨镛,何晓明.外周血干细胞移植治疗血栓闭塞性脉管炎[J].中国微创外科杂志,2009,9(9):851-852.
[21]钱爱民,李晓强,段鹏飞,等.自体外周血干细胞移植治疗老年人慢性下肢缺血临床研究[J].南通大学学报:医学版, 2007,27(2): 109-110,112. |