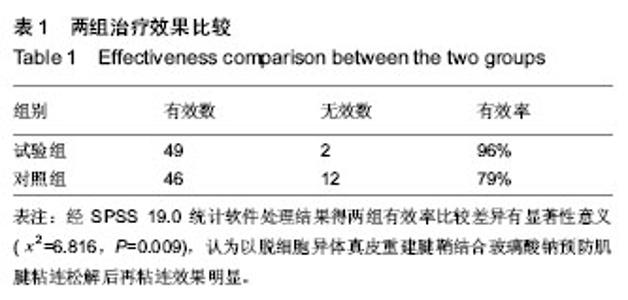
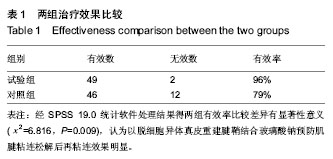
| [1] 刘昶,纪艳超.脱细胞真皮基质补片在腹部疝修补术中的应用[J].哈尔滨医科大学学报,2007,41(6):599-600.
[2] 王丽亚,董彦清,张鹏举,等.脱细胞异体真皮基质生物补片修补新生儿及婴幼儿组织缺损[J].上海交通大学学报:医学版, 2011, 31(1):115-117.
[3] 游艳琴,付晓宇,黄柯,等.脱细胞异体真皮组织补片在经阴道直肠阴道瘘修补术中的应用[J].中华妇产科杂志, 2012,47(12): 920-922.
[4] Shelton AA,Welton ML.Transperineal repair of persistent rectovaginal fistulas using an acellular cadaveric dermal graft (AlloDerm).Dis Colon Rectum. 2006;49(9):1454-1457.
[5] Nguyen MD,Chen C,Colako?lu S,et al.Infectious Complications Leading to Explantation in Implant-Based Breast Reconstruction With AlloDerm.Eplasty.2010;10:e48.
[6] Chun YS,Verma K,Rosen H,et al.Implant-based breast reconstruction using acellular dermal matrix and the risk of postoperative complications.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2010; 125(2):429-436.
[7] 刘广毅,杨军成.脱细胞异体真皮基质修复口腔组织缺损的疗效观察[J].四川医学,2012,33(7):1206-1207.
[8] 肖光礼,聂卫,高萍,等.脱细胞羊膜制备及生物学评价[J].临床医学工程,2009,16(1):1-5.
[9] 李开通,刘达恩.脱细胞异种(猪)真皮基质临床应用与研究进展[J].中国社区医师:医学专业,2012,14(6):13-14.
[10] 王志刚,陈秀英,刘韬,等.磨痂术与异种脱细胞真皮基质覆盖治疗深二度创面[J].内蒙古医学杂志,2010,42(5):535-537.
[11] 覃秋海,黄运严,边建民,等.脱细胞异种(猪)真皮早期覆盖治疗二度烧伤创面的临床研究[J].广西医学,2012,34(1):26-28.
[12] 杨辉,曾勉东.脱细胞异种真皮修复糖尿病足溃疡的疗效[J].实用医学杂志,2013,29(15):2587-2588.
[13] 王志勇,窦懿,廖镇江,等.异种脱细胞真皮基质膜修复全层皮肤损伤的疗效和安全性分析——多中心、随机、对照试验[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(40):783-7840.
[14] 刘汉辉,章莹,吴文,等.肌腱损伤修复过程及粘连的预防[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(50):9946-9949.
[15] Lundborg G,Rank F,Heinau B.Intrinsic tendon healing.A new experimental model.Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg. 1985; 19(2): 113-117.
[16] Lister GD.Cyclic stress analysis of flexor tendon repair.J Hand Surg Am.1991;16:701.
[17] Lundorg G.Tendon healing: Intrisinc mechanisms Tendon Surgery in the hand. The CV mosby comp-any.1987:54-60.
[18] 汤锦波,侍德,石井一郎.各种伤情下肌腱的愈合及粘连形成[J].中华手外科杂志,1992,8(1):31.
[19] Manske PR,Gelberman RH,Lesker PA.Flexor tendon healing. Hand Clin.1985;1(1):25-34.
[20] Szabo RM,Younger E.Effects of indomethacin on adhesion formation after repair of zone II tendon lacerations in the rabbit.J Hand Surg Am.1990;15(3):480-483.
[21] Moran SL,Ryan CK,Orlando GS,et al.Effects of 5-fluorouracil on flexor tendon repair.J Hand Surg Am.2000;25(2):242-251.
[22] 吴景明,余楠生,卢伟杰.显微外科技术修复Ⅱ区屈肌腱断裂[J].中华手外科杂志,2000,16(4):110-111.
[23] Kessler FB.Fascia Patch graft for a digital flexr sheath defect over Primary tendon repair in the chicken.J Hand Surg Am. 1986;11:241.
[24] 鲍卫汉,朱洪荫.自体筋膜移植物理性状的实验研究[J].中华外科杂志,1987,25(3):601.
[25] 陈青,王杰,秦光华,等.肌筋膜移植在肌腱损伤中的应用[J].手外科杂志,1990,6(12):18.
[26] 汤锦波,侍德.手指屈肌腱鞘的基础和临床研究[J].手外科杂志, 1990,6(21):39.
[27] Strauch B.The fate of tendon healing after re-storation of the integrity of the tendon sheath with autogenous vein grafts.J Hand Surg Am.1985;10:790.
[28] 焦文治,孙材江.手指屈肌腱修复中粘连防治研究进展[J].国外医学:创伤与外科基本问题分册,1985,2(3):157.
[29] 费起礼,孔令震,李兰平,等.聚乳酸薄膜预防肌腱粘连的研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,1992,6(2):65.
[30] 邵新中,凌彤,张煜.生物膜防止屈肌腱粘连的实验研究[J].中华外科杂志,1993,31(1):56-59.
[31] 王明民,侯希敏,孙树海,等.几丁聚糖影响肌腱愈合的实验研究及临床应用[J].中华创伤杂志,2001,17(1):38-41.
[32] 杨志,赵劲民,韦庆军,等.玻璃酸钠预防肌腱修复后粘连的实验研究[J].广西医科大学学报,2000,17(5):831-832.
[33] 姚学东,林其仁,施进兴,等.胶原酶预防聚集腱鞘内粘连的实验研究[J].福建医科大学学报,1999,33(2):529-531.
[34] 徐建光,顾玉东,王欢,等.透明质酸防止肌腱粘连的实验研究[J].中华外科杂志,1995,33(9):529-531.
[35] Moran SL,Ryan CK,Orlando GS,et al.Effects of 5-florouracil on flexor tendom repaie.J Hand Surg.2000;25:590-592.
[36] 凌沛学,贺艳丽,白若琬,等.玻璃酸钠结构及理化性质的研究进展[J],中国生化药物杂志,2000,21(3):152-155.
[37] 江少波,朱辉,李少伟,等.关节镜清理术并吗啡和玻璃酸钠注射治疗膝骨性关节炎42例[J].实用医学杂志,2007,23(2):211-212.
[38] 吴夏勃,蒋科卫,温建民,等.玻璃酸钠在膝骨关节病的临床应用[J].中国生化药物杂志,2005,26(3):176-177.
[39] 王希,袁君君,范全,等.玻璃酸钠治疗指屈肌腱腱鞘炎113例(129)指效果观察[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2006,14(13):1029-1030.
[40] 姜大伟,贾全章,侯明晓,等.伸指肌腱损伤后交指样显微编织缝合术加琉璃酸钠防粘连治疗的实验研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2009,17(14):1090-1092. |