| [1] 王奔,葛振新,杨国跃,等.髓内与髓外固定修复股骨转子间骨折的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(4):736-743.
[2] 梁昌详,郑晓青,昌耘冰,等.精确定位防旋髓内钉置入治疗股骨转子间骨折[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(17):2685-2690.
[3] 蒋正武,赵越,胡志毅.不同内固定方法治疗老年不稳定性股骨转子间骨折的疗效比较[J].南京医科大学学报:自然科学版,2013, 12(57):1735-1737.
[4] Little NJ, Verma V, Fernando C, et al. A prospective trial comparing the Holland nail with the dynamic hip screw in the treatment of intertrochanteric fractures of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2008;90(8):1073-1078.
[5] Saudan M, Lübbeke A, Sadowski C, et al. Pertrochanteric fractures: is there an advantage to an intramedullary nail?: a randomized, prospective study of 206 patients comparing the dynamic hip screw and proximal femoral nail. J Orthop Trauma. 2002;16(6):386-393.
[6] Elis J, Chechik O, Maman E, et al. Expandable proximal femoral nails versus 95° dynamic condylar screw-plates for the treatment of reverse oblique intertrochanteric fractures. Injury. 2012;43(8):1313-1317.
[7] Hong JY, Suh SW, Park JH, et al. Comparison of soft-tissue serum markers in stable intertrochanteric fracture: dynamic hip screw versus proximal femoral nail—A preliminary study. Injury. 2011;42(2):204-208.
[8] Rupprecht M, Grossterlinden L, Ruecker AH, et al. A comparative biomechanical analysis of fixation devices for unstable femoral neck fractures: the Intertan versus cannulated screws or a dynamic hip screw. J Trauma. 2011; 71(3):625-634.
[9] Audigé L, Hanson B, Swiontkowski MF. Implant-related complications in the treatment of unstable intertrochanteric fractures: meta-analysis of dynamic screw-plate versus dynamic screw-intramedullary nail devices. Int Orthop. 2003; 27(4):197-203.
[10] 黄诚,付聪聪,黄相杰.DHS和PFNA治疗老年骨质疏松性转子间骨折的临床疗效对比[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2014,22(6): 568-570.
[11] 董桂贤,张宁,孙建华,等.股骨近端锁定钢板和股骨近端髓内钉治疗老年股骨转子间骨折比较[J].临床骨科杂志,2010,13(6):640- 641.
[12] 朱俊锋,周根来,董大海.PFNA-Ⅱ治疗老年股骨转子间EVANSⅠ、Ⅱ型骨折后早期负重锻炼的疗效观察[J].浙江创伤外科, 2013,18(2):189-190.
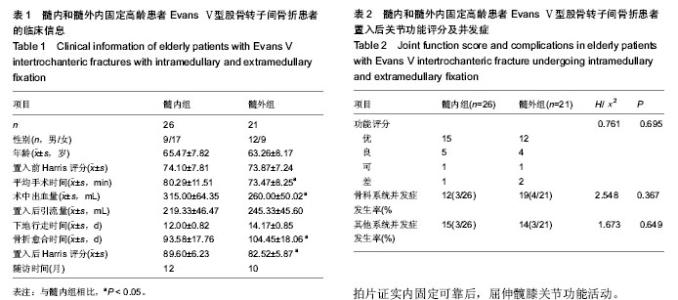
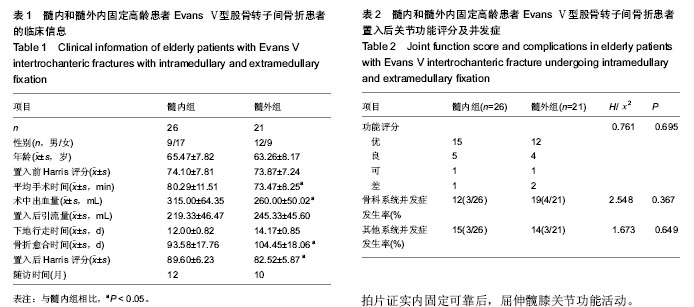
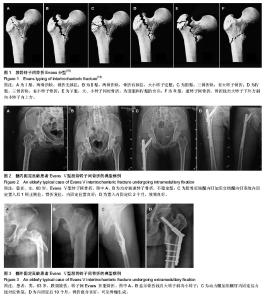
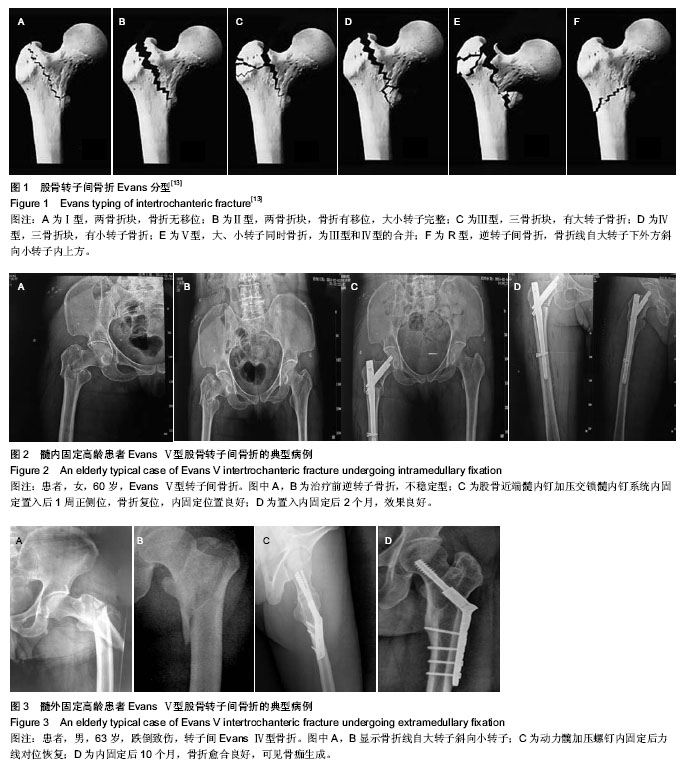
[13] 刘永刚,裴国献,王丹,等.股骨转子间骨折Evans-Jensen分类数字化模型的建立及意义[J].南方医科大学学报,2009,29(10): 2088-2090.
[14] 陈兴华,刘涛,黄珍谷.长、短股骨近端防旋髓内钉固定股骨转子间骨折的对比[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(4):595-600.
[15] 张一鹏,刘伟新,梁献会.DHS治疗股骨转子间骨折失败原因分析[J].实用骨科杂志,2014,20(2):165-168.
[16] Zachert G, Rapp M, Eggert R, et al. Additional Tension Screws Improve Stability in Elastic Stable Intramedullary Nailing: Biomechanical Analysis of a Femur Spiral Fracture Model. Eur J Pediatr Surg. 2014. in press.
[17] Ruecker AH, Rupprecht M, Gruber M, et al. The treatment of intertrochanteric fractures: results using an intramedullary nail with integrated cephalocervical screws and linear compression. J Orthop Trauma. 2009;23(1):22-30.
[18] 黄杰峰,邓友章,万凌屹.髋部骨折与老年骨质疏松[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2006,10(40):127-129.
[19] Shen L, Zhang Y, Shen Y, et al. Antirotation proximal femoral nail versus dynamic hip screw for intertrochanteric fractures: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled studies. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2013;99(4):377-383.
[20] 杨民,马军,王国选,等.DHS和PCCP治疗Evans-JensenⅠ、Ⅱ型股骨粗隆间骨折的疗效分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2011, 26(12):1108-1109.
[21] 周强,陆骅,俞思明,等.动力髋结合转子稳定钢板与Gamma钉内固定治疗股骨转子间骨折的比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2014, 18(9):1441-1446.
[22] Calderón A, Ramos T, Vilchez F, et al. Proximal femoral intramedullary nail versus DHS plate for the treatment of intertrochanteric fractures. A prospective analysis. Acta Ortop Mex. 2013;27(4):236-239.
[23] Gorodnichenko AI, Uskov ON, Platonov II. Intramedullary ostheosynthesis of femoral acetabular fractures in elderly patients. Khirurgiia (Mosk). 2013;(6):55-58.
[24] Huang Y, Zhang C, Luo Y. A comparative biomechanical study of proximal femoral nail (InterTAN) and proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures. Int Orthop. 2013; 37(12):2465-2473.
[25] Haidukewych GJ, Berry DJ. Hip arthroplasty for salvage of failed treatment of intertrochanteric hip fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85-A(5):899-904.
[26] Drobniewski M, Sibiński M, Plebański R, et al. Breakage of the prosthesis steam as a rare complication of total hip replacement. Chir Narzadow Ruchu Ortop Pol. 2010;75(1): 53-56.
[27] 岳建明,郝斌,杨亚军,等.股骨粗隆型人工股骨头置换术治疗高龄Evans-JensonⅢ型股骨粗隆间骨折临床探讨[J].宁夏医科大学学报,2011,33(9):872-874.
[28] 章玉冰,戎祖华,张俊德,等.G.T.F.柄人工髋关节置换治疗高龄股骨转子间骨折(Evans Ⅲ型)疗效分析[J].临床医学工程,2012, 19(11):1919-1920. |