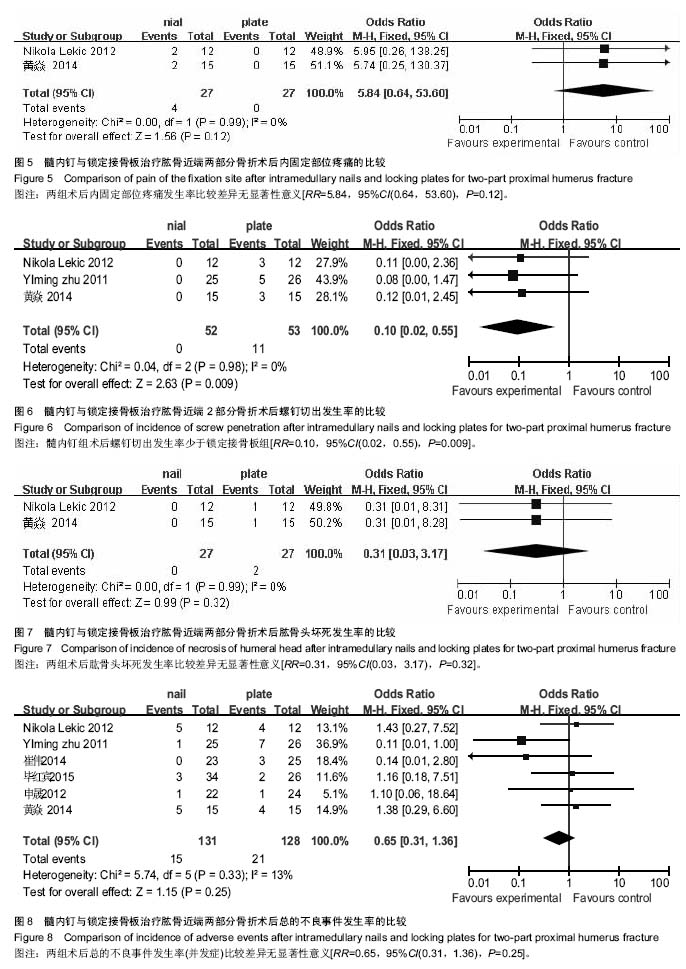
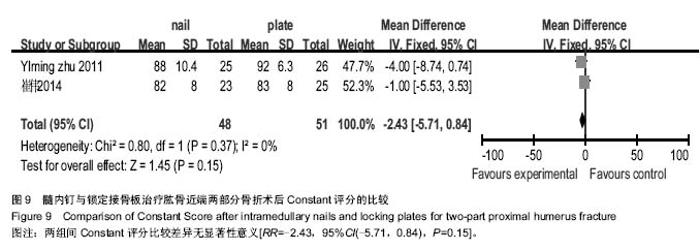
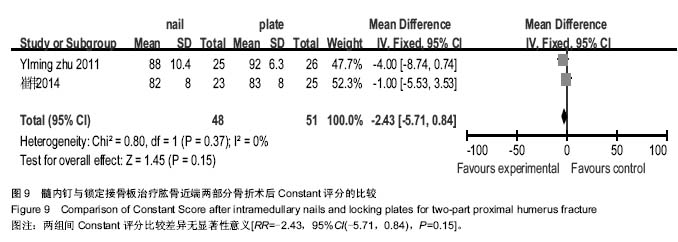
| [1] Lanting B,MacDermid J,Drosdowech D,et al.Proximal humeral fractures: a systematic review of treatment modalities.J Shoulder Elbow Surg.2008;17(1):42-54.[2] Horak J,Nilsson BE.Epidemiology of fracture of the upper end of the humerus.Clin Orthop Relat Res.1975;(112):250-253.[3] 文良元,薛庆云,黄公怡,等.老年肱骨近端骨折的内固定治疗[J].中华骨科杂志,2004,24(11):641-644.[4] 田伟,侯建文,王玺,等.锁定钢板治疗老年肱骨近端骨折效果观察[J].中国卫生标准管理,2015,6(21):22-23.[5] Konrad G,Bayer J,Hepp P,et al.Open reduction and internal fixation of proximal humeral fractures with use of the locking proximal humerus plate. Surgical technique. J Bone Joint Surg Am.2010;92 Suppl 1 Pt 1:85-95.[6] 吴在德.外科学[M].北京:人民出版社,2006:768.[7] 于志勇,白龙,叶军,等.锁定钢板与交锁髓内钉内固定治疗肱骨外科颈骨折的疗效比较[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2016,31(3): 260-262.[8] 董喆,王磊,马延辉,等.关节镜下经胫骨隧道入路与前内侧入路重建前交叉韧带效果的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2015, 19(51):8352-8358.[9] 刘向栋,王磊,董喆,等.大剂量甲基强的松龙冲击治疗成人急性脊髓损伤疗效的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(42): 6875-6881.[10] Alderson P,Green S,Higgins JPT.Cochrane Reviewers’ Handbook 4.2.2.In: The Cochrane Library. Chichester,UK: John Wiley & Sons,Ltd.2004.[11] 毕红宾,王永清,李毅,等.肱骨近端锁定钢板与髓内钉治疗老年肱骨近端二部分骨折疗效比较[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2015, 23(12): 34-37.[12] 申晟.锁定钢板与交锁髓内钉治疗老年肱骨近端二部分外科颈骨折的疗效分析[D].大连医科大学,2012.[13] 崔伟,吕杨训,贺行文,等.肱骨近端锁定钢板与髓内钉治疗肱骨外科颈骨折的临床对比研究[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2014, 29(1):41-43.[14] 黄焱,徐勇强,阎戈,等.髓内钉与锁定接骨板治疗肱骨近端2部分骨折的疗效比较[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2014,29(7): 725-726.[15] Lekic N,Montero NM,Takemoto RC,et al.Treatment of two-part proximal humerus fractures: intramedullary nail compared to locked plating.HSS J.2012;8(2):86-91.[16] Zhu Y,Lu Y,Shen J,et al.Locking intramedullary nails and locking plates in the treatment of two-part proximal humeral surgical neck fractures: a prospective randomized trial with a minimum of three years of follow-up.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93(2):159-168.[17] 陈耀龙,李幼平,杜亮,等.医学研究中证据分级和推荐强度的演进[J].中国循证医学杂志, 2008,8(2):127-133.[18] 陈亮清,白龙,于志勇,等.交锁髓内钉治疗肱骨近端骨折[J].临床骨科杂志,2014,17(6):712-714.[19] Foruria AM,Carrascal MT,Revilla C,et al.Proximal humerus fracture rotational stability after fixation using a locking plate or a fixed-angle locked nail: the role of implant stiffness.Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon).2010;25(4):307-311.[20] Yoon RS,Dziadosz D,Porter DA,et al.A comprehensive update on current fixation options for two-part proximal humerus fractures: a biomechanical investigation.Injury. 2014;45(3):510-514.[21] Papakonstantinou MK,Hart MJ,Farrugia R,et al.Prevalence of non-union and delayed union in proximal humeral fractures.ANZ J Surg.2016.doi: 10.1111/ans.13756. [Epub ahead of print].[22] Konrad G,Audigé L,Lambert S,et al.Similar outcomes for nail versus plate fixation of three-part proximal humeral fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res.2012;470(2):602-609.[23] 周福强,王秋梅,姚学军,等.肱骨近端严重粉碎骨折应用锁定钢板治疗的效果研究[J].世界最新医学信息文摘,2016,16(49):[24] Trepat AD,Popescu D,Fernández-Valencia JA,et al. Comparativestudy between locking plates versus proximal humeral nail for the treatment of 2-part proximal humeral fractures.Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol.2012;22(5):373-379.[25] 田伟,侯建文,王玺,等.锁定钢板治疗老年肱骨近端骨折效果观察[J].中国卫生标准管理, 2015,6(21):22-23.[26] 李永全,董荣华.肱骨近端骨折的治疗现状及研究进展[J].医学综述,2016,22(14):2788-2791.[27] 张楷利,冯刚.锁定加压钢板微创内固定技术治疗胫骨近端骨折临床观察[J].中国实用医药, 2016,11(22):73-74.[28] 陈建喜,徐朝和,张佳榕.肱骨近端骨折通过肱骨近端加压锁定钢板与传统钢板治疗的效果对比[J].中外医疗,2016,35(21):70-72. |