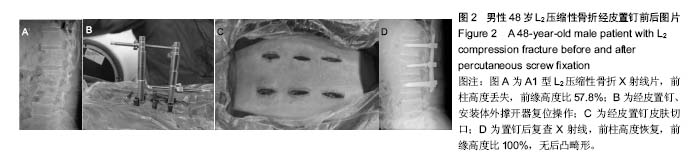
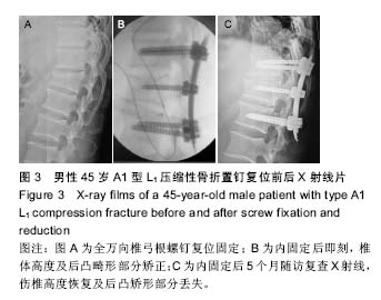
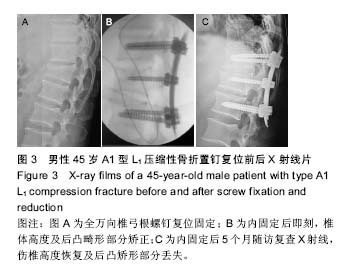
| [1] Dahdaleh NS,Smith ZA,Hitchon PW.Percutaneous pedicle screw fixation for thoracolumbar fractures.Neurosurg Clin N Am.2014;25(2):337-346.[2] Grossbach AJ,Dahdaleh NS,Abel TJ,et al.Flexion-distraction injuries of the thoracolumbar spine: open fusion versus percutaneous pedicle screw fixation.Neurosurg Focus. 2013; 35(2):E2.[3] Lee ST,Chen JF. Closed reduction vertebroplastry for the treatment of osteoporosis vertebral compression fracture. Technique note.J Neurosurg.2004:100(4Sppl): 392-396.[4] Foley KT,Gupta SK. Percutaneous pedicle screw fixation of the lmnhar spine:preliminary clinical results.Neurosurg. 2002;97(Suppl 1):7-12.[5] Foley KT,Gupta SK,Justs JR,et al.Pereutaneous pedicle serew fixation of the lumbar spine.Neurosurg Focus.2001; 10(4): E10.[6] Ni WF,Huang YX,Chi YL,et al.Percutaneous pedicle screw fixation for neurological intact thoracolumbar burst fractures.J Spinal Disord Tech.2010;23(8):530-537.[7] Blondel B,Fuentes S,Pech-Gourg G,et al.Percutaneous management of thoracolumbar burst fractures:Evolution of techniques and strategy.Orthop Traumatol Surg Res.2011; 97:527-532. [8] Stanford RE,Loefler AH,Stanford PM,et al. Multiaxial pedicle screw designs:static and dynamic mechanical testing. Spine. 2004;29(4):367-375.[9] 刘程俊,顾祖超,张宇.Sextant内固定系统修复腰椎骨折:伤椎前后缘高度比及后凸Cobb角变化[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015, 19(4):548-553.[10] 王洪伟,李长青,周跃,等.微刨与传统开放附加伤椎经椎弓根螺钉内固定手术治疗胸腰椎骨折的疗效比较[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2010,20(2):112-116.[11] 王洪伟,李长青,周跃,等.附加伤椎固定的微创经皮椎弓根螺钉(Sextant)治疗胸腰椎骨折[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2010, 12(2): 18-22.[12] Wang HW,Li CQ,Zhou Y,et al.Percutaneous pedicle screw fixation through the pedicle of fractured vertebra in the treatment of type A thoracolumbar fractures using Sextant system:an analysis of 38 cases.Chin J Traumatol.2010; 13(3):137-145.[13] Gelb D,Ludwig S,Karp JE,et al. Successful treatment of thoracolumbar fractures with short-segment pedicle instrumentation.J Spinal Disord Tech.2010;23(5): 293-301.[14] 钱济先,纪振钢,高浩然,等.微创经皮并结合伤椎椎弓根螺钉固定治疗胸腰椎骨折[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2013,21(16): 1591-1596.[15] 刘斌,董健文,戎利民,等.微创经皮椎弓根螺钉治疗无神经症状的Magerl A3型胸腰椎骨折[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2012,14(9): 772-777.[16] 王春,林永绥,刘清平,等.经皮长尾可折U形空心椎弓根钉系统固定治疗胸腰椎骨折的疗效评估[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2012, 22(7):627-633.[17] Anekstein Y,Brosh T,Mirovsky Y.Intermediate screws in short segment pedicular fixation for thoracic and lumbar fractures: a biomechanical study.J Spinal Disord Tech.2007;20(1):72-77.[18] 胡海刚,谭伦,林旭,等.经伤椎椎弓根植骨置钉后路复位内固定术治疗胸腰椎骨折[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2011,21(8): 663-668.[19] 常锐,王丰爱,王海霞,等. 伤椎置短钉技术治疗胸腰椎爆裂骨折的疗效分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2014,22(8):683-686.[20] 高浩然,赵海恩,钱澍,等.经皮螺钉置入固定结合关节突植骨修复胸腰椎骨折:建立伤椎长久稳定性[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015, 19(17): 2688-2693.[21] Mahar A,Kim C,Wedemeyer M,et al.Short¬-segment fixation of lumbar burst fractures using pediele fixation at the level of the fracture.Spine.2007;32(14):1503-1507.[22] Shepard MF,Davies MR,Abayan A,et al.Effects of polyaxial pedicle screws on lumbar construct rigidity.J Spinal Disord Tech.2002;15(3):233-236.[23] Stanford RE,Loefler AH,Stanford PM,et al. Multiaxial pedicle screw designs: static and dynamic mechanical testing.Spine. 2004;29(4):367-375.[24] Kuklo TR, Potter BK, Polly DW, et al. Monaxial versus multiaxial thoracic pedicle screws in the correction of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine. 2005;30(18): 2113-2120.[25] 李方财,陈其昕,陈维善,等.经皮椎弓根螺钉内固定结合椎体内植骨治疗胸腰椎骨折[J].中华骨科杂志,2011,31(10):1066-1071.[26] Tannous O, Jazini E, Weir TB, et al.Facet Joint Violation during Percutaneous Pedicle Screw Placement: A Comparison of Two Techniques.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2016 Dec 2.[27] Gazzeri R.Percutaneous Pedicle Screw Fixation Technique in the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine-Tips and Tricks.Surg Technol Int. 2016 Apr;28:303-310.[28] Li K, Li Z, Ren X,et al.Effect of the percutaneous pedicle screw fixation at the fractured vertebra on the treatment of thoracolumbar fractures.Int Orthop. 2016;40(6):1103-1110. [29] McAnany SJ, Overley SC, Kim JS,et al.Open Versus Minimally Invasive Fixation Techniques for Thoracolumbar Trauma: A Meta-Analysis.Global Spine J. 2016;6(2):186-194.[30] Zairi F, Vielliard MH, Bouras A,et al.Long-segment percutaneous screw fixation for thoracolumbar spine metastases: a single centre experience.J Neurosurg Sci.2015 Oct 6. [31] Giorgi H, Blondel B, Adetchessi T,et al.Early percutaneous fixation of spinal thoracolumbar fractures in polytrauma patients.Orthop Traumatol Surg Res.2014;100(5):449-454. [32] Vanek P, Bradac O, Konopkova R, et al.Treatment of thoracolumbar trauma by short-segment percutaneous transpedicular screw instrumentation: prospective comparative study with a minimum 2-year follow-up.J Neurosurg Spine. 2014;20(2):150-156. [33] Citak M, Stubig T, Kendoff D, et al.Navigated minimally invasive thoracolumbar pedicle screw placement with flat panel 3-D imaging. A feasibility study.Technol Health Care. 2010;18(2):101-110. |