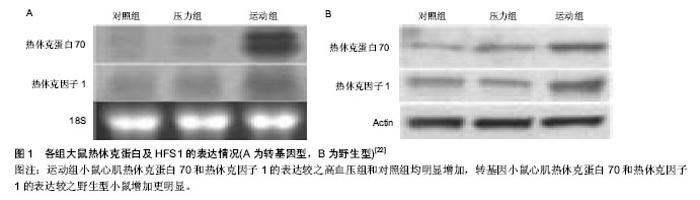
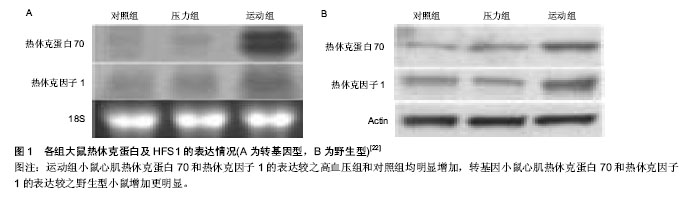
| [1] Snoeckx LH,Cornelussen RN,Van Nieuwenhoven FA,et al.Heat shock proteins and cardiovascular pathophysiology. Physiol Rev.2001;81(4):1461-1497.
[2] Latchman DS.Review: Heat shock proteins and cardiac prote-tion.Cardiovasc Res.2001;51(4):637-646.
[3] Snoeckx LH, Cornelussen RN, Van Nieuwenhoven FA,et al.Heat shock proteins and cardiovascular pathophysiology. Physiol Rev.2001;81:1461-1497.
[4] 王凤阳,张学林.热休克蛋白(Hsp72)与运动训练的研究进展[J].北京体育大学学报,2004,27(4):493-495.
[5] Tokor H,Mina minor T,Komuror I.Role of heat shock transcriptional factor 1 and heat shock proteins in cardiac hypertrophy.Trends Cardiovascr Med.2008;18(3):88-93.
[6] Ritossa FM.A new puffing pattern inducell by temperature shock and DNP in D rosophila Experientia.1962;18(1): 571-573.
[7] Tissieres A,Mitcheli HK,Tracy UM.Protein synthesis in salivary glangs of Drosophila melanogaster,Relation to chromosomal puffs.mol Biol.1974;84:389-398.
[8] 黄勇.运动与热休克蛋白[J].山西师大体育学院学报研究生论文专刊,2007,3(22):97-99.
[9] Kampinga HH, Hageman J, Vos MJ, et al.Guidelines for the nomenclature of the human heat shock proteins. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2009;14(1):105-111.
[10] Maglara AA, Vasilaki A, Jackson MJ, et al.Damage to Decloping mouse skeletal muscle mytubes in Culture proectiveef-fect of heat shock protines. Physiol. 2003;(3): 837-846.
[11] 杨德洪,陈佩杰.运动应激与热休克蛋白的表达[J].中国临床康复,2002,6(23):3554-3555.
[12] Yamaguchi H, Osaki T, Kai M, et al.Immune Response against a Cross-Reactive Epitope on the Heat Shock Protein60 Homologue of Helicobacter pylori.Infection and Immunity.2000;68(6):3448-3454.
[13] 金怡,江钟立,招少枫,等.低强度运动对糖尿病大鼠心肌细胞凋亡的保护作用[J].中国康复医学杂志,2009,24(1):15-19.
[14] Huang CC,Lin TJ,Chen CC,et al.Endurance training accelerates exhaustive exercise-induced mitochondrial DNA deletion and apoptosis of left ventricle myocardium in rats.Eur J Appl Physiol.2009;107(6):697-706.
[15] 王诚,王军力.热休克蛋白在运动医学界的研究进展[J].解放军体育学院学报,2004,23(1):99-102.
[16] Taylor RP, Starnes JW.Reactive oxygen species are not a required trigger for exercise-induced late preconditioning in the rat heart.Physiol Regul Integr\Comp Physiol.2012;303(9): 68-74.
[17] Marshall HC, Ferguson RA, Nimmo MA, et al.Human resting extracellular heatshock protein72 concentration decreases during the initial adaptation to exercise in a hot humid environment.Cell Stress & Chaperones.2006;11(2):129-134.
[18] Febbraio MA, Mesa JL, Chung J, et al.Glucose ingestion attenuates the exercise –induced increase incirculating heat shock protein72 andHeat shock protein60 in humans. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2004;9(4):390-396.
[19] 陈艳,任建生.不同负荷训练对大鼠心肌细胞热休克蛋白70表达的影响[J].通化师范学院学报,2009,30(2):58-60.
[20] Milne KJ,Noble EG.Exercise-induced elevation of HSP70 is intensity dependent.J Appl Physiol.2002;93(2):561-568.
[21] Liu Y,Lormes W,Wang L,et al.Different skeletal musclHSP70 responses to high-intensity strength training and low-intensity endurance training.Eur J Appl Physiol.2004;91(3):330-335.
[22] 杨兵生,刘强,毛威,等.适应性心肌肥大机制中热休克蛋白及其转录因子1的正向调控作用[J].浙江医学,2011,33(4):35-39.
[23] Salo DC.Hsp and otherpossible heat shock oroxidative stress proteins are induced in skeletal muscle heart and liver during exercise.Free Rad BiolMed.1991;11:239-246.
[24] Taylor RP,Harris MB,Starnes JW.Acute exercise can im-prove cardioprotection without increasing heat shock protein content. Am J Physiol.1999;276:1098-1102.
[25] 李爱萍,崔书强,徐金成,等.高温环境下急性力竭运动对大鼠心肌HSP70及血浆心钠素的影响[J].中国运动医学志,2010,29(2): 188-191.
[26] Locke M.The cellular stress response to exercise:role of stress proteins.Exerc Sport Sci Rev.1997;25:105-136.
[27] 陈佩杰,魏勇,杨德洪,等.不同强度运动后大鼠心肌细胞热休克蛋白72mRNA的表达[J].中国运动医学志,2004,23(6):624-628.
[28] Klang J,Tsokos G.Heats hock protein 70kDa: molecular biology[J].Biochemistry And Physiology Pharmacol Ther. 1998;(80):183-201.
[29] 胡亚哲,陈艳,扈诗兴,等.运动训练诱导大鼠心肌细胞热休克蛋白70表达[J].中国运动医学志,2009,28(5):561-563.
[30] 扈盛,胡亚哲.热休克蛋白70在末端病中表达的研究[J].中国运动医学杂志,2002,21(3):232-234.
[31] 史绍蓉,刘田,龚丽,等.递增负荷训练对大鼠心室肌蛋白质组影响的研究[C].北京:第八届全国体育科学大会,2007.
[32] Brown CR.The constitutive and stress inducible forma of HSP70 ex-hibit functional similarities and interact with one another in an ATP- dependant fashion.J cell Biol.1993;120: 1101-1112.
[33] Samelman TR.Heat shock protein expression is increased in cardial and skeletal muscles of Fischer 344 tats after endurance training.Expphysiol.2000;51:92-102.
[34] Demirel H, Powers S, Cailland C, et al. Exercise training reduces myocardial lipid peroxidation following short-term ischemia Powersreferfusion.Med sci sports Exerc.1998;(30): 1211-1216.
[35] Powers SK, Demirel HA ,Vincent HK, et al. Exercise trainin improves myocardial tolerance to in vivo ischemia - reperfusion in the tat.Jphysiol.1998;(275):1468-1477.
[36] 袁爱国.运动心脏重塑过程中大鼠左室肌蛋白质组差异表达的研究[D].长沙:湖南师范大学,2008.
[37] 刘建荣.运动心脏重塑过程中大鼠心房肌的比较蛋白质组学研究[D].长沙:湖南师范大学,2008.
[38] 魏勇,陈佩杰,杨德洪,等.不同周期运动后大鼠心肌细胞热休克蛋白72 mRNA的表达[J].中国运动医学杂志,2003,22(2):129-132.
[39] 凡启为,肖国强.运动对骨骼肌、心肌中热休克蛋白表达影响的研究进展[J].体育学刊,2005,12(5):123-125.
[40] 彭峰林,张林,邓树勋.间歇运动对缺血再灌注大鼠心肌HSP70表达的影响[J].西安体育学院学报,2009,26(5):565-569.
[41] Suzuki K,Murtuza B,Sammut IA, et al.Heat shock protein72 enhances manganese superoxide dismutase activity during myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury,associated with mitochondrial protection and apoptosis reduction. Circulation. 2002;106(supp[I]):270-276.
[42] Moran M, Delgado J,Gonzalez B,et al. Responses of rat my-ocardial antioxidant defenses and heat shock protein HSP72 induced by 12 and 24-week treadmill training.Acta Physiol Scand.2004;180(2):157-166.
[43] Lunz W,Davel AP,Rossoni LV,et al.L-NAME treatment enhances exercise-induced content of myocardialheat shock protein72 (Hsp72) in rats.Cell Physiol Biochem.2011;27(5): 479-486.
[44] Cernila B, Cresnar B, Breskvar K.Molecular characterization of genes encoding cytosolic Hsp70s In the zygomycete fungus Rhizopus nigricans.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2003;8(4): 317-328.
[45] Milne KJ, Wolff S, Noble EG,et al. Myocardialaccumulation and localization of the inducible 70-kDa heat shock protein, Hsp70, following exercise.Appl Physiol 2012;113(6):53-60.
[46] 陆阿明,陆爱云.运动与热休克蛋白表达[J].上海体育学院学报, 2002,26(3):35-38.
[47] Korzeniowska Kubacka I.Physical training as an effective way to protect the heart against ischaemia.Kardiol Pol.2011;69(3): 75-79.
[48] 蔡爱芳,葛新发,侯晓晖,等.应激蛋白在运动应激中的研究进展[J].武汉体育学院学报,2003,37(6):37-40. |