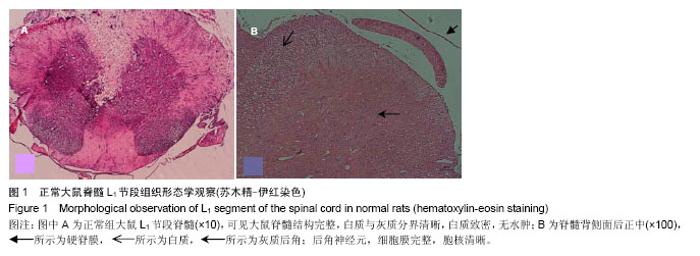
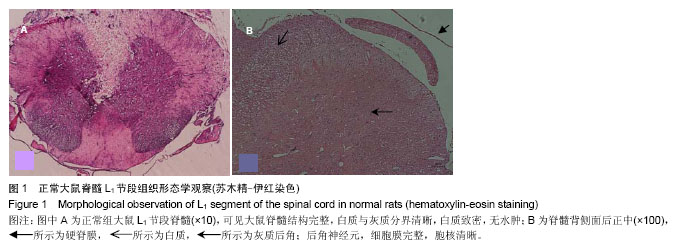
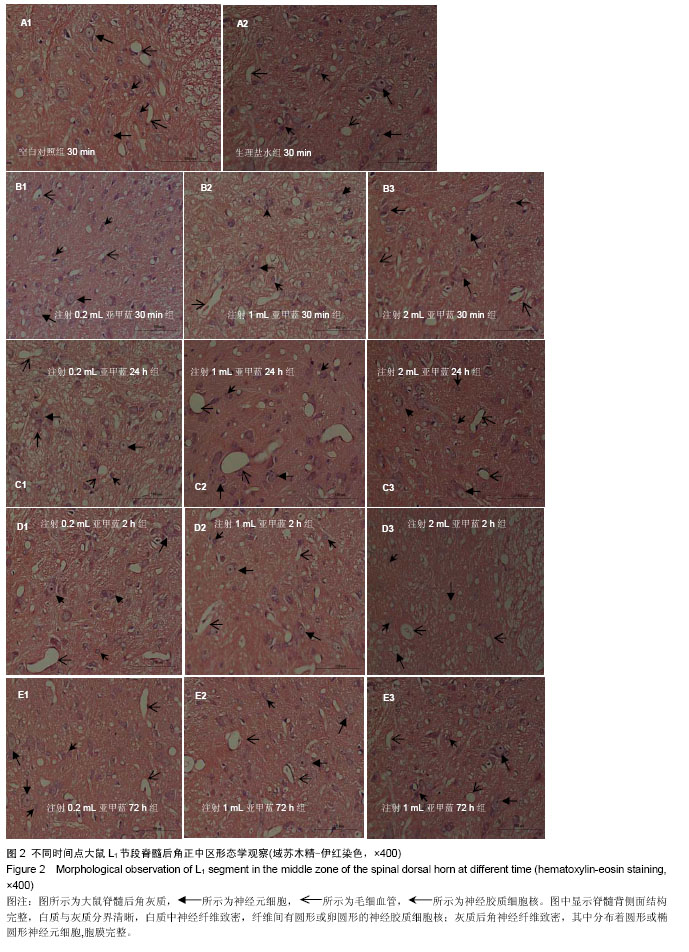
| [1] 黄映善.亚甲蓝硬膜外腔注射对术后疼痛疗效的临床研究[J]. 广西医学,1997,19(4):554.
[2] 职良喜.复方亚甲蓝液穴位注射治疗第三腰椎横突综合症30例[J]. 江苏中医药,2003,24(3):38.
[3] Crock HV.A reappraisal of intervertebral disc lessions.Mel J Aust.1970;(20):983-989.
[4] Park WM, McCall W, OBrien JP, et al. Fissuring of the posteriorannulus fibrosus in the lumbar spine. Br J Radiol. 1979;52(617):382-387.
[5] 杨惠林.全国腰椎退行性疾患座谈会会议纪要[J].中华骨科杂志, 2006,10(9):711-716.
[6] Nakamura A, Fujita M, Shiomi H. Involvement of endogenous nitric oxide in the mechanism of bradykinin-induced peripheral hyperalgesia.Br J Pharmacol.1996;117 (3): 407-412.
[7] 彭宝淦,吴闻文,侯树勋,等.腰椎间盘内破裂的诊断和治疗[J].中华外科杂志, 2003, 41(6): 5642566.
[8] 彭宝淦,侯树勋,吴闻文,等.椎间盘内亚甲蓝注射治疗椎间盘源性下腰痛[J].中华医学杂志,2006,11(5): 782-784.
[9] Carragee EJ, Alamin TF, Carragee JM. Low -pressure positive discography in subjects asymptomatic of significant low back pain illness.Spine(phila pa 1976).2006;31(5): 505-509.
[10] Carragee EJ, Alamin TF, Miller JL, et al. Provocative discography in volunteer subjects with mild persistent ljow back pain.Spine J.2002;2(3):25-34.
[11] Carragee EJ, Lincoln T, Parmar VS, et al. A gold standard evaluation of the “discogenic pain”diagnosis as determined by provocative discography. Spine.2006;31(1):2115-2123.
[12] Buenaventure RM, Shah RV, Patel V, et al. Systematic review of discography as a diagnostic test for spinal pain:An update. Pain Physician.2007;10(1):147-164.
[13] Derby R, Howard MW, Grant JM, et al.The ability of pressurecontrolled discography to predict surgical and nonsurgical outcomes. Spine.1999;24(4):364-371.
[14] Derby R, Lee SH, Kim BJ, et al. Pressure -controlled lumbar discography in volunteers without low back symptoms. Pain Med. 2005 ;6(3):213-21;discussion 222-224.
[15] Peng B, Hao J, Hou S, et al. Possible pathogenesis of painful interverterbral disc degeneration. Spine.2006;31(5):560-566.
[16] Peng B, Hou S, Wu W, et al. The pathogenesis and clinical significance of high -intensity zone (HIZ)of lumbar intervertebral disc on MR imaging in the patient with discogenic low back pain. Eur Spine J.2006;15 (5):583-587.
[17] Peng B, Wu W, Hou S, et al. The pathogenesis of discogenic low back pain. J Bone Joint Surq(Br).2005;87(1):62-67.
[18] Eusebio EB, Graham J, Mody N. Treatment of intractable pruritusani. Dis Colon Rectum.1990;33(9):770-772.
[19] Fairbank JC, Couper J, Davies JB, et al. The Oswestry low back pain disability questionnaire. Physiotherapy.1980;66(8): 271-273.
[20] Farouk R, Lee WR. Intradermal methylene blue injection for the treatment of intractable idiopathic pruritus ani. Br J Surq. 1997;84(5):670.
[21] 刘春雨,彭宝淦,高春华,等.硬膜外腔注入亚甲蓝对大鼠腰椎脊髓及脊神经节功能的电生理影响[J].脊柱外科杂志,2012,10(5): 304-309.
[22] 乔三福,王立维,丁喜杰,等.鞘内注射亚甲蓝混合液对家兔的镇痛作用研究[J].中国疼痛医学杂志,2011,17(10):624-626.
[23] 刘春雨.硬膜外下腔注入亚甲蓝腰椎脊髓及神经根功能和结构影响的实验研究[C].北京:中华医学会第十四届骨科学术会议暨第七届COA国际学术大会,2012.
[24] 周晶.痔手术后多模式镇痛效果的临床观察[D].哈尔滨:哈尔滨医科大学,2010.
[25] 王燕,柯昌斌,周小峰,等.氯胺酮对糖尿病大鼠神经功能及神经病理痛的作用[J].徐州医学院学报,2009,29(5):316-318.
[26] 陶利军,孙永海,张宏亚.甲蓝磁性明胶微球在外磁场作用下对家兔痛阈及体感诱发电位的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(14):2631-2634.
[27] 张成武.盘内注射亚甲蓝治疗椎间盘源性下腰痛疗效观察[C]. 银川:第三届全国脊髓损伤治疗与康复研讨会,2012.
[28] 孙永海,张宏,王勇,等.亚甲蓝与阿霉素磁性明胶药物微球镇痛作用的比较[J].解放军医学杂志,2007,32(4):316-318.
[29] Peng B, Zheng Y, Hou S, et al. intradiscad methy Lene blue injectnon for the treatment of chronic discogenic low back pain. Eur Spine J.2007;16(1): 33-38. |