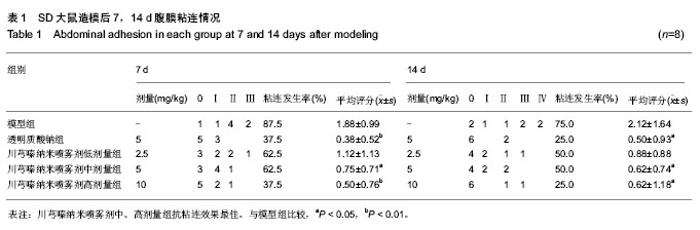
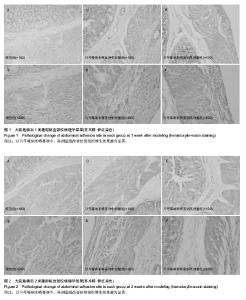
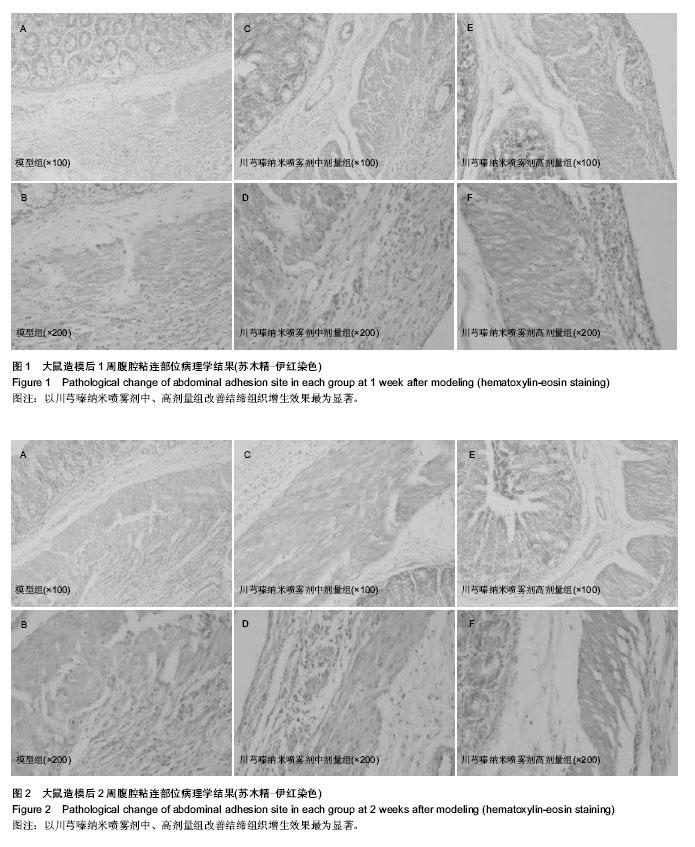
| [1] Rajab TK, Wallwiener M, Talukdar S,et al. Adhesion-related complications are common, but rarely discussed in preoperative consent: a multicenter study. World J Surg. 2009 Apr;33(4):748-750.
[2] Ten Broek RP, Kok-Krant N, Bakkum EA, et al. Different surgical techniques to reduce post-operative adhesion formation: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Hum Reprod Update. 2013 Jan-Feb;19(1):12-25
[3] Ouaïssi M, Gaujoux S, Veyrie N, .et al. Post-operative adhesions after digestive surgery: their incidence and prevention: review of the literature. J Visc Surg. 2012; 149(2):e104-14.
[4] Brochhausen C, Schmitt VH, Planck CN, et al. Current Strategies and Future Perspectives for Intraperitoneal Adhesion Prevention. J Gastrointest Surg. 2012;16(6): 1256-1274.
[5] Hamming JF, Bonsing BA. Adhesiolysis during abdominal surgery: substantial risks. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd.2013; 157(7): A5928.
[6] 曾莉,钱海华,赵群男,等.活血通腑方治疗术后粘连性肠梗阻56例临床观察[J].南京中医药大学学报,2010,26(3):346-348.
[7] 曾莉,凌立君,夏国守,等.活血通腑方对大鼠术后腹腔粘连的实验研究[J].中国中西医结合外科杂志,2005,(2):135-137.
[8] 凌立君,曾莉,陆茵,等.活血化瘀中药抗小鼠术后病理性腹腔粘连的实验研究[J].江苏中医药,2005,26(4):47-50.
[9] 杨雪梅.川芎嗪药理作用研究进展[J].中国生化药物杂志,2010, 31(3):215-217.
[10] 马清钧,王淑玲.常用中药现代研究与临床[M].天津科技翻译出版公司,1995:383-385
[11] 董秀清,阳晓,叶任高,等.川芎嗪抗腹膜间皮细胞损伤的实验研究[J].中国中西医结合肾病杂志,2001,2(8):441-443.
[12] 郝丽荣,王春梅,李春玲.川芎嗪防治腹膜纤维化作用的实验研究[J].中国血液净化,2006,5(8):437-439.
[13] 李战.纳米技术和纳米中药的研究进展[J].上海中医药杂志,2003, 37(1):61-63.
[14] 顾一男,祝文学,韩凤奎.纳米技术在中医药中的应用及发展[J].药业纵横,2008,17(2):22.
[15] 毛春芹,陆兔林,钱丽,等.正交试验法筛选川芎嗪纳米粒制备的最佳工艺[J].中成药,2013,35(8):1792-1794.
[16] 曾莉,凌立君,夏国守,等.术后病理性腹腔粘连大鼠模型制作的实验研究[J].医学研究生学报,2006,19(3):229-231.
[17] Bruggmann D, Tcha rtchian G, Wallwie ner M, et al. Intra-abdominal adhesions: definition, origin, significance in surgical practice, and treatment options.Dtsch Arzte bl Int. 2010;107:769-775.
[18] Cheong YC, Laird SM,Li TC,et al.Peritoneal healing and adhesion formation/reformation. Hum Reprod Update. 2001; 7(6):556-566.
[19] Xiao L, Du Y, Shen Y, et al. TGF-beta1 induced fibroblasts proliferation is mediated by the FGF-2/ERK pathway.Front Biosci.2012;17:2667-2674.
[20] ZhangYG,HuYC,MAOYY,et al.Transforming growth factor-β involved in urotensin 2-induced phenotypicdifferentiation of adventitial fibroblasts from rat aora.Chin Med J(Engl).2010; 123(24):3634-3639.
[21] 曾莉.腹腔粘连研究进展[J].南京中医药大学学报,2004, 22(2): 126-128.
[22] Gonzalez-Quintero VH,Cruz-Pachano FE.Preventing adhesions inobstetric and gynecologic surgical procedures. Rev Obstet Gynecol.2009,2(1):38-45.
[23] 吴志民,伦志军,刘迎春,等.透明质酸钠预防大鼠术后腹膜粘连的效果[J].中国老年学杂志,2011,7(31):2497-2498.
[24] 孙士营,马成立.透明质酸钠预防腹腔手术后粘连效果观察[J].山东医药,2006,46(17):99.
[25] 刘洪斌,李东华,郭世铎.腹腔粘连形成机制及治疗研究进展[J].中国中西医结合外科杂志,2005,11(1):84-86.
[26] 范玉香,杜进巧,王志芹,等.医用几丁糖预防剖宫产术后腹腔粘连临床观察[J].河北医药,2011,33(16):2448-2449.
[27] 左锋.几丁糖当归在肌腱粘连防治中的应用研究[J].亚太传统医药,2012,8(5):157-158.
[28] LeGrand EK,RodgersKE,GirgisW,et al.Comparative effica-cy of nonsteroidal ant-i inflammatory drugs and ant-i thromboxaneagentsin a rabbit adhesion-prevention model.J Invest Surg.1995;8(3):187
[29] Galili Y, Ben-Abraham R, Rabau M, et al. Reduction ofsurgery-induced peritoneal adhesions by methylene blue. Am JSurg.1998;38(6):555.
[30] Polat A,Nayci A,Polat G,et al. Dexamethasone down 2 regulatesendothelial expression of intercellular adhesion molecule and impairsthe healing of bowel anastomoses.Eur J Surg.2002;168(89):500-506.
[31] 刘宾.腹腔粘连的研究进展[J].中国现代医学,2013,51(5 ):24-25.
[32] 徐庆,曾莉.腹腔粘连的治疗进展[J].南京中医药大学学,2007, 23(5):335-337.
[33] 翁永强.转化生长因子-B多克隆抗体预防腹腔粘连的实验研究[J].中国普通外科杂志,2002,11(12):741.
[34] 裴海平,晏仲舒,伍韶斌.善得定对预防大鼠腹部手术后肠粘连的研究[J].中国普通外科杂志,2001,10(3):231-233.
[35] 张志清,康英,王育红.聚乳酸纳米粒给药系统研究进展[J].中国医院药学杂志,2002,22(9):555-557.
[36] 李争艳,毛春芹,曾莉,等.川芎嗪聚乳酸纳米粒的包封率测定[J].南京中医药大学学报,2011,27(1):77-79. |