Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (36): 5752-5757.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.36.003
Previous Articles Next Articles
Variation of tumor necrosis factor-alpha during acute rejection after liver transplantation in a rhesus monkey
Zhang Xi-bing, Ran Jiang-hua, Liu Jing, Zhang Sheng-ning, Li Lai-bang, Chen Yi-ming, Gao Yang, Li Wang, Li Li
- Department of Hepatopancreatobiliary Surgery, the Affiliated Ganmei Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Liver Transplantation Center of Organ Transplantation Institute of Yunnan Province, Kunming 650011, Yunnan Province, China
-
Revised:2014-07-11Online:2014-08-30Published:2014-08-30 -
Contact:Ran Jiang-hua, M.D., Professor, Master’s supervisor, Department of Hepatopancreatobiliary Surgery, the Affiliated Ganmei Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Liver Transplantation Center of Organ Transplantation Institute of Yunnan Province, Kunming 650011, Yunnan Province, China -
About author:Zhang Xi-bing, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Hepatopancreatobiliary Surgery, the Affiliated Ganmei Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Liver Transplantation Center of Organ Transplantation Institute of Yunnan Province, Kunming 650011, Yunnan Province, China -
Supported by:Major Program of Kunming Municipal Science and Technology Department, No. 08S100304
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Xi-bing, Ran Jiang-hua, Liu Jing, Zhang Sheng-ning, Li Lai-bang, Chen Yi-ming, Gao Yang, Li Wang, Li Li. Variation of tumor necrosis factor-alpha during acute rejection after liver transplantation in a rhesus monkey[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(36): 5752-5757.
share this article
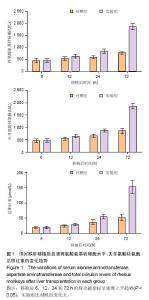
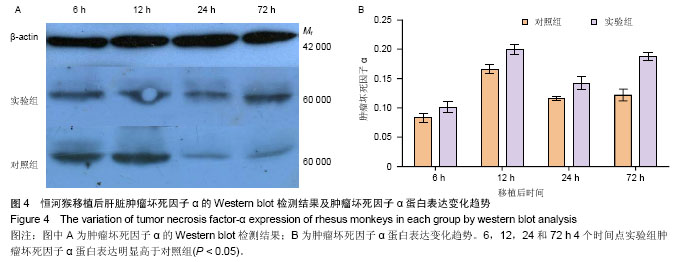
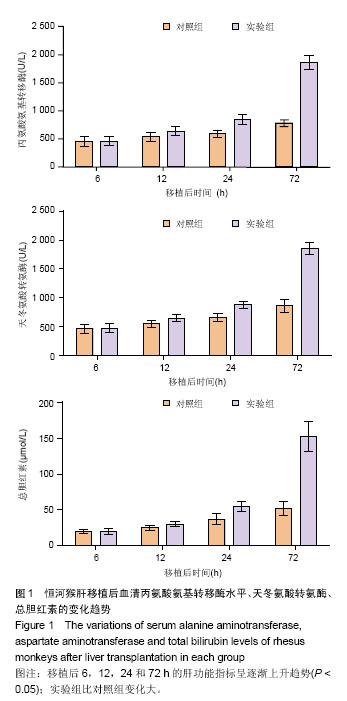
2.1 恒河猴肝移植后肝功能的变化 实验组和对照组分别于移植后同时点比较血清丙氨酸氨基转移酶、天冬氨酸转氨酶和总胆红素3个指标,其中实验组在移植后24,72 h明显高于对照组(P < 0.05),由于实验组未使用抗免疫排斥药物,而移植后也未使用激素等原因导致肝细胞受到机体炎性细胞的攻击损伤较对照组的严重。随着时间的延长,两组移植后丙氨酸氨基转移酶、天冬氨酸转氨酶和总胆红素,均呈增加趋势,其中6,12 h这3个指标水平比较接近,两组间比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。随着时间的延长,移植后6,12,24和72 h的肝功能呈逐渐上升趋势,因而两组组内比较,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。此外,实验组比对照组变化大,尤其在肝移植后24-72 h的变化趋势最为明显,见图1。"
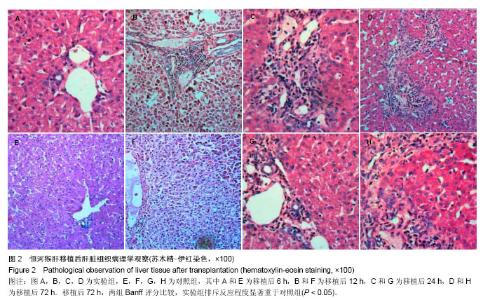
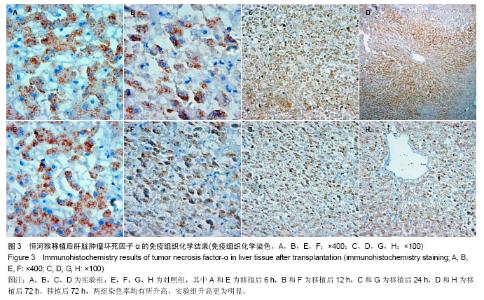
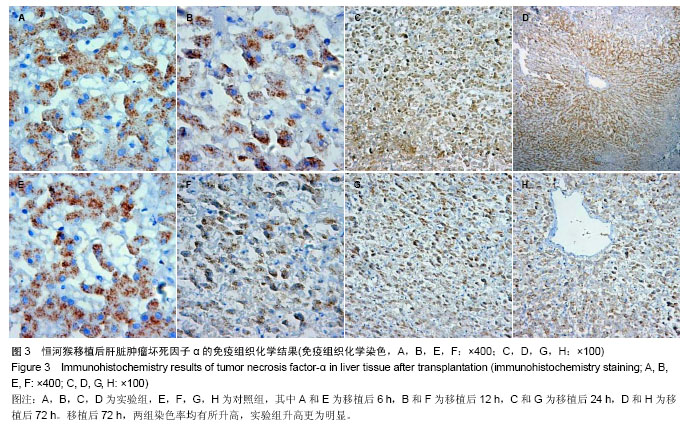
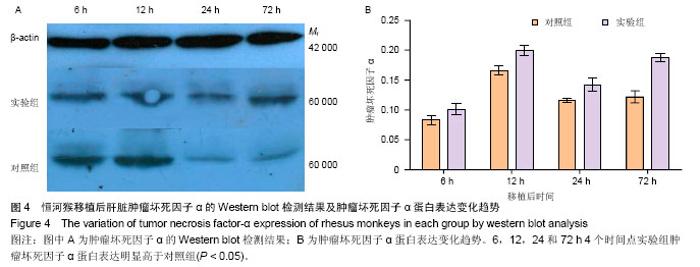
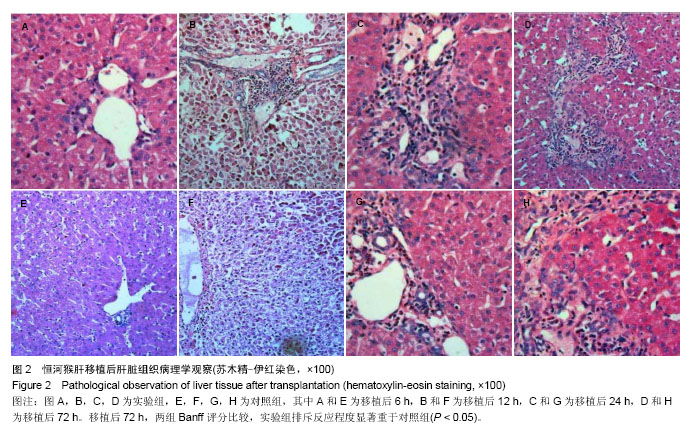
2.2 恒河猴肝移植后肝脏组织病理学观察结果 实验组和对照组在移植后6 h,镜下观察:肝组织基本正常,未见排斥反应,见图2中A、E。移植后12 h,苏木精-伊红染色镜下观察:实验组有轻度的排斥反应,Banff评分Ⅰ-Ⅱ级;对照组分级不明确,Banff评Ⅰ-Ⅱ级,见图2中B、F。移植后24 h,苏木精-伊红染色镜下观察:实验组有中度至重度排斥反应,Banff评分Ⅱ-Ⅲ级;对照组有轻度急性排斥反应,Banff评分0-Ⅰ级,见图2中C、G。移植后72 h,苏木精-伊红染色镜下观察:实验组有重度排斥反应,Banff评分Ⅲ级;对照组有轻度急性排斥反应,Banff评分0-Ⅰ级,且该时点两组Banff评分比较,实验组排斥反应程度重于对照组,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见图2中D、H。"
| [1] Goronzy JJ, Weyand CM. T-cell co-stimulatory pathways in autoimmunity. Arthritis Research and Therapy. 2008;10(1, article S3). [2] Alex Bishop G, Bertolino PD, Bowen DG,et al.Tolerance in liver transplantation.Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol.2012;26(1):73-84. [3] Rook M, Rand E.Predictors of long-term outcome after liver transplant.Curr Opin Organ Transplant.2011;16(5):499-504. [4] Li DH, Havell EA, Brown CL, et al.Woodchuck lymphotoxin-alpha, beta and tumor necrosis factor genes: structure, characterization and biological activity.Gene.2000 25;242(1-2):295-305. [5] Nedwin GE, Naylor SL, Sakaguelli AY, et al. Human lymphotoxin and tumorNecerosis factor genes: structure、homology and chromosomal localization. Nueleie Acids Res.1985;13(17):6361. [6] Bagul A.Ischaemic/reperfusion injury: Role of infliximab.World J Transplant.2012;2(3)35-40. [7] El-Gezawy EM, Eldin EN, Mohamed WS,et al.Tumor necrosis factor-alfa and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 gene polymorphisms in kidney transplant recipients.Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl.2013;24(4):688-695. [8] Roek CS,Lowry SF. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha.J Surg Res. 1991;51(5):434-445. [9] The Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China. Guidance Suggestions for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 2006-09-30. [10] Allain JE, Mahieu-Caputo D, Loux N, et al.Impronement of Orthotopic Liver Transplantation Model in Rhesus Monkey.Chin J Bases Clin General Surg.2010;3(4):212-219. [11] 冉江华,李铸,刘静,等.二袖套法建立恒河猴原位肝移植的稳定模型[J].中国组织工程研究,2011,15(5):62-768. [12] Busuttil RW, Lake JR.Role of tacrolimus in the evolution of liver transplantation. Transplantation.2004;77(9 suppl):S44-51. [13] Racusen LC,Halloran PF,Solez K.Banff 2003 meeting report:new diagnostic insights and standards.Am J Transplant.2004;4(10):1562-1566. [14] Solez K. History of the Banff classification of allograft pathology as it approaches its 20th year.Curr Opin Organ Transplant.2010;15(1):49-51. [15] Rüdiger T, Höfler H, Kreipe HH,et al.Quality assurance in immunohistochemistry: results of an interlaboratory trial involving172 pathologists.Am J Surg Pathol.2002;26(7): 873-882. [16] Dickson C.Protein techniques: immunoprecipitation, in vitro kinase assays, and Western blotting.Methods Mol Biol.2008;461:735-744. [17] Matsunaga K, Mashiba H. Augmentation of TNF-and lymphotoxin-mediated cytotoxic effect in the combined use of ACNU and involvement of oxygen free radicals.Gan To Kagaku Ryoho.1990;17(3pt2):452-458. [18] Matsubara N,Fuehimoto S,Orita K.Differing roles of Protein kinase C on the antiProliferative effects of tumor necrosis factor alpha and beta on LoVo cell.Pathobiology.1990;58(3):168-171. [19] Koga Y, Matsuzaki A, Suminoe A,al et.Neutrophil-derived TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL): a novel mechanism ofantitumor effect by neutrophils.Cancer Res. 2004; 64(3):1037-1043. [20] Futosi K, Fodor S, Mócsai A. Neutrophil cell surface receptors and their intracellular signal transduction pathways. Int Immunopharmacol.2013;17(3):638-650. [21] Bradley JR. TNF-mediated inflammatory disease. J Pathol. 2008;214(2):149-160. [22] Girnita DM, Webber SA, Zeevi A. Clinical impact of cytokine and growth factor genetic polymorphisms in thoracic organ transplantation.Clin Lab Med.2008;28(3):423-440. [23] Cardoni RL, Prigoshin N, Tambutti ML. Regulatory cytokines in the response to the allogeneic renal transplant. Medicina (B Aires).2005;65(1):54-62. [24] Kita Y, Iwaki Y, Noguehi K, et al. Daily serum infianunatory cytokine (turnor necrosis factor-a, interleukin-6) monitoring in liver transplantation focusing on all graft rejection:a five-case report. Transplant Proc.1996;28(3):1237. [25] Heidt S, San Segundo D, Shankar S.Peripheral blood sampling for the detection of allograft rejection: biomarker identification and validation.Transplantation.2011;92(1):1-9. [26] Imagawa DK, Millis JM, Olthoff KM, et al.The role of tumor necrosis factor in allograft rejection. TransPlantation.1990; 50(2): 219-225. [27] Pascher A, Klupp J.Biologics in the treatment of transplant rejection and ischemia/reperfusion injury: new applications for TNFalpha inhibitors? BioDrugs.2005;19(4):211-231. [28] Rokahr KL, MeCaughan GW, NaPoli J, et al. Quantitation of eytokine Mrna Expression in biopsies from human liver allograft by a novel reverse transeriptase/polymerase chain reaetion method. Trans Plant Proe.1995;27(3):2148. [29] Hoffmann MW, Wonigeit K, Steinlloff G, et al.Production of cytokines(TNF-α,IL-lβ)And endothelial cell aetivation in human liver allograft rejeetion.TransPlantation.1993;55(2):329-335. [30] Basista MH, Stieffenllofer A, Kim DG, et al. Proeoagulant aetivity and tumor necrosis factor in rat hepatic allograft rejection.HePatology.1991;14(5):883-887. [31] Adams DH, Garner C, Neuberger JM. Serum tumor necrosis factor alpha in Patients following liver transplantation. Trans Plant Proe.1990;22(5):2310. [32] Imagawa DK, Millis JM, Olthoff KM,et al.The role of tumor necrosis factor in allograft rejection. I. Evidence that elevated levels of tumor necrosis factor-alpha predict rejection following orthotopic liver transplantation.Transplantation.1990;50(2):219-225. [33] Fugger R, Hamilton G, Steininger R, et al. Intra operative estimation of endotoxin,TNF-a,and IL-6 in orthotopic liver transplantation and the irrelation to rejection and post operative infection. TransPlantation.1991;52(2):302. [34] Bathgate AJ, Praviea V, Perrey C, et al. The effect of polymorphisms in tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-10, and transforming growth factor beta genes in acut hepatic allograft rejeetion. Transplantation.2000;69(7):1514. [35] Flach R, Speidel N, Flohé S, et al. Analysis of intragraft cytokine expression during early reperfusion after liver transplantation using semi-quantitative RT-PCR.Cytokine.1998;10(6):445-451. |
| [1] | Jiang Xin, Qiao Liangwei, Sun Dong, Li Ming, Fang Jun, Qu Qingshan. Expression of long chain non-coding RNA PGM5-AS1 in serum of renal transplant patients and its regulation of human glomerular endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 741-745. |
| [2] | Li Liqiang, Jiao Longxing, Zhang Wu, Yan Wentao, Li Jian, Li Minghao. Effect of immature dendritic cells derived from bone marrow on rejection of orthotopic liver transplantation in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(13): 2025-2029. |
| [3] | Yang Feng, Chang Lipu, Huang Changshan, Gong Xiaoguang, Chang Shunwu. Macrolide antibiotics protects against ischemia-reperfusion injury after liver transplantation in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(26): 4176-4182. |
| [4] | Liu Mengyuan1, Fang Fang2. Risk factors for multi-drug resistant organisms infection after liver transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(7): 1109-1114. |
| [5] | Gao Hongqiang, Liu Jing, Li Zhiqiang, Wang Hailei, Zhao Xiongqi, Zhang Shengning, Ran Jianghua, Li Li . Ulinastatin improves rat liver metabolism after reduced-size liver transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(3): 435-440. |
| [6] | Chen Jun1, Lin Jie2, Zhao Zhongsheng2, Huang Yanfeng2, Wu Guangwen3. Effect of Wutou Decoction on TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway in synovial tissue of rat models with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(27): 4381-4386. |
| [7] | Liu Wenhua, Liang Jinfeng, Deng Shaojie. Resveratrol reduces tumor nuclear factor-α expression in wear-particle-treated macrophages by regulating the level of intracellular oxidative stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(26): 4115-4120. |
| [8] | Yang Baokuan, Huang Rui, Shi Xinghui. Bracketless invisible orthodontic appliance for treating adult periodontal disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(22): 3451-3455. |
| [9] | Liang Weidong, Ren Zhouliang, Sheng Jun, Cao Rui, Sheng Weibin. Interleukin-1beta, interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibit expression of type II collagen in nucleus pulposus cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(21): 3410-3417. |
| [10] | Cai Qiucheng, Fan Hongkai, Xiong Rihui, Jiang Yi. Intravenous administration of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells protects liver function following fatty liver transplantation from donors after cardiac death [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(17): 2625-2629. |
| [11] | Zhao Ying-peng, Li Li, Chen Gang, Bai Jian-hua, Liu Qi-yu. Reduced-size liver transplantation with fatty liver donors in a rat model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(4): 582-586. |
| [12] | Ding Chen1, Jiang Yi2, Pan Fan2, Cai Qiucheng2. Lipid metabolism after autologous orthotopic liver transplantation in rat models of fatty liver [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(36): 5821-5827. |
| [13] | Liu Li-ye1, Zhao De-fang2, Gao Fei1, Zhang Tong2, Dong Qin2. Schisandra extract regulates Th17 cells and regulatory T cell imbalance in dogs undergoing liver transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(20): 3213-3217. |
| [14] | Chen Rong, Jiang Tao, Yang Ai-zhen, Zhang Dong-hua, Wang Xuan. Clinical application of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells in liver transplantation patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(17): 2665-2671. |
| [15] | Lin Jing-xia, Su Fan, Luo Hong-shan. Transfusion of blood components in liver transplantation and abdominal multiple organ transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(33): 4957-4962. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||