Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (36): 5741-5746.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.36.001
Single-center experience of perioperative treatment of liver transplantation for acute hepatic failure
Pei Li-juan1, Xu Hong-bin2, Jin Xin1, Shi Xian-jie2
- 1Department of General Surgery, the 304 Affiliated Hospital, General Hospital of PLA, Beijing 100037, China
2Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, General Hospital of PLA, Beijing 100853, China
-
Revised:2014-07-01Online:2014-08-30Published:2014-08-30 -
Contact:Shi Xian-jie, M.D., Ph.D., Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, General Hospital of PLA, Beijing 100853, China -
About author:Pei Li-juan, Physician, Department of General Surgery, the 304 Affiliated Hospital, General Hospital of PLA, Beijing 100037, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Pei Li-juan, Xu Hong-bin, Jin Xin, Shi Xian-jie. Single-center experience of perioperative treatment of liver transplantation for acute hepatic failure[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(36): 5741-5746.
share this article
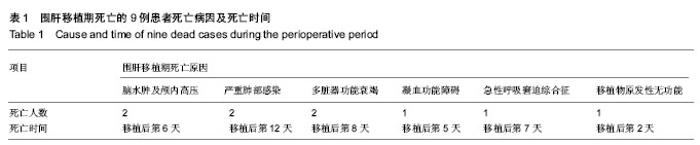
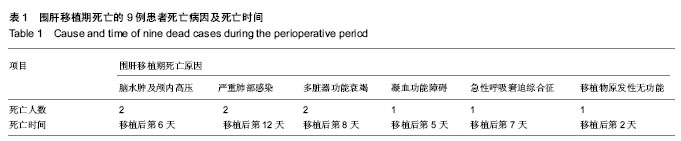
2.1 参与者数量分析 纳入患者38例,生存时间为13- 1 740 d,中位生存时间为634 d。患者的围肝移植期存活率为76%,1年存活率为63%,2年存活率为58%,全部进入结果分析。 2.2 肝移植后并发症及预后 肝移植后早期31例患者发生不同程度的肺部并发症,包括肺部感染、肺不张、胸腔积液、肺水肿、急性呼吸窘迫综合征等。其中有10例气管插管超过72 h行气管切开,4例死亡(1例痰培养证实新型隐球菌感染),其余6例经治疗后拔除气切套管、痊愈出院。余单纯肺部感染患者,移植后根据药敏试验结果联合应用抗生素治疗后痊愈出院12例患者出现肾功不全患者经药物治疗及血液净化治疗后10例恢复,2例患者因出现多脏器功能衰竭死亡。 4例患者于移植后2-5 d出现神经系统并发症,表现为昏迷、躁狂、幻觉、焦虑、失眠等,其中3例经对症治疗后,症状均获得有效的改善与控制,1例昏迷者头颅CT检查证实有颅内出血,抢救无效后死亡。 23例移植前合并乙型病毒性肝炎,其中有8例(8/23)在移植后1年内出现乙肝复发,复发的原因多为病毒变异,加用阿德福韦治疗后[18],6例复查 HBeAg转阴,HBV DNA<103拷贝/mL,肝功能正常,B超示肝脏形态正常。7例出现血管、胆道并发症行介入治疗后恢复良好,4例移植后12-24个月内出现胆管狭窄及胆泥淤积等再次手术治疗。 围手术期死亡患者9例,其死亡原因及死亡时间见表1。24例远期生存患者中,15例生活质量良好,重返工作岗位。药物因素所致急性肝功能衰竭行肝移植后的围手术期生存率为100%,明显高于非药物因素所致的急性肝衰竭行肝移植后的围手术期存活率为69%(χ2=9.129,P =0.003)。"
| [1] Polson J, Lee WM. American Association for the Study of Liver Disease. AASLD position paper: The management of Acute hepatic failure. Hepatology.2005;41(5):1179-1197. [2] Bernal W, Wendon J. Liver transplantation in adults with acute liver failure. J Hepatol.2004;40(2):192-197. [3] 中华医学会感染病学分会肝衰竭与人工肝学组、中华医学会肝病学分会重型肝病与人工肝学组.肝衰竭诊疗指南[J].中华肝脏病杂志,2006,14:643-646. [4] Satin SK, Kumar A, Almeida JA, et al. Acute-on-chronic liver failure:consensus recommendations ofthe Asian Pacific Associationfor the study ofthe liver(APASL). Hepatol Int.2009; 3:269-282. [5] Lee WM, Stravitz RT, Larson AM. Introduction to the revised American Association for the study of Liver Diseases Position Paper on acute fiver failure 2011. Hepatology.2012;55: 965-967. [6] AASLD Position Paper: The Management of Acute Liver Failure:Up-date 2011[EB/OL] (2011-09)E2011-01-02]. http://www.aasld.org/practiceguidelines/Documents/AcuteLiverFailureUpdate2011. [7] 中华医学会感染病学分会肝衰竭与人工肝学组、中华医学会肝病学分会重型肝病与人工肝学组.肝衰竭诊疗指南(2012版) [J].中华肝脏病杂志,2013,21:177-183. [8] Sass DA. Shakil AO. Fulminant hepatic failure.Liver Transpl. 2005;11:594-605. [9] Bretheriek AD, Craig DG, Masterton G, et al. Acute liver failure in Scotland between 1992 and 2009:incidence,aetiology and outcome.OJM.2011;104:945-956. [10] 王建锋,李霄,韩炜,等.急性肝衰竭的治疗进展[J].中华肝胆外科杂志,2012,18(12):957-960. [11] Achilles A, Robert S, Ronald W, et al. Prospective, randomized, multicenter, controlled trial of a bioartifical liver in treat acute liver failure.Ann of Surg,2004;239(5):660-670. [12] Olyaei AJ, deMattos AM, Bennett WM. Nephrotoxicity of immunosuppressive drugs : new insight and preventive strategies. Curr Opin Crit Care.2001;7(6):384-389. [13] Shin HS, Kim SP, Han SH, et al. Prognostic indicators for acute liver failure development and mortality in patients with hepatitis a: consecutive case analysis. Yonsei Med J.2014; 55(4):953-959. [14] Han YS, Lee SK, Joh JW, et al. outcomes of hepatitis B virus recurrence after liver transplantation. Transplant Proc. 2006; 38(7):2123-2124. [15] Blei AT, Cordoba J. Practice Parameters Committee ofthe American College of Gastroenterology.Hepatic Encephalopathy. Am J Gastroenteml.2001;96:1968-1976. [16] Pugh RN, MurrayLyon IM, Dawson JL, et al.Transection of the oesophagus for bleeding oesophageal varices.Br J Surg. 1973; 60:646-649. [17] Kamath PS, Wiesner RH, Malinchoc M, et al A model tO predict survival in patients with end-stage liver disease.Hepatology.2001;33:464-470. [18] Dhiman RK, Seth AK, Jain S, et al. Prognositic evaluation of early indicators in fulminant hepatic failure by multivariate analysis.Dig Dis Sci.1998;43:1311. [19] 李兰娟.肝衰竭临床治疗中的难点和热点[J].中华肝脏病杂志,2012,20(6):405-407. [20] Voigt MD. Predicting Death in Patients With Acetamin-ophen-Induced Acute Liver Failure:The King’s College Hospital Model Is on the SOFA,Not the Mat.Liver Transpl.2012;18:384-386. [21] Kamath PS, Kim WR. The model for end-stage 1iver disease (MELD). Hepatology.2007;45:797-805. [22] Mochida S.Indication criteria for liver transplantation for acute fiver failure in Japan.Hepatol Res.2008;38 Suppl l:S52-55. [23] 饶慧瑛,郭芳,魏来.2005年美国肝病学会急性肝衰竭诊治和肝移植患者评价指南简介[J].中华肝脏病杂志,2006,14(2):154-156. [24] Jain S, Pendyala P, Varma S, et al.Effect of renal dysfunction in fulminant hepatic failure. Trop Gastro.2000;21(3):118-120. [25] Patrono D, Brunati A, Romagnoli R, et al. Liver transplantation after severe hepatic trauma: a sustainable practice. A single-center experience and review of the literature.Clin Transplant.2013;27(4):E528-37. [26] Davenport A, Will EJ, Davidson AM. Improved cardiovascular stability during continuous modes of renal replacement therapy in critically ill patients with acute hepatic and renal failure. Crit Care Med.1993;21(3):328-338. [27] Ostapowicz GA, Fontana RJ, Schi odt FV, et al. Results of a prospective study of acute liver failure at 17 tertiary care centers in the United States. Ann Intern Med.2002;137(12): 947-954. [28] Karidis NP, Kouraklis G, Theocharis SE. Platelet activating factor in liver injury: a relational scope. World J Gastroenter ol. 2006;12(23):3695-3706. [29] Jung O, Asbe Vollkopf A, Betz C, et al. Long term therapy of acute liver failure to successful transplantation with an extra corporealliver support system. Gastroenterol.2007; 45(1):21. [30] Steadman RH, Van Rensburg A, KrRnler DJ. Transplantation for acute liver failure:perioperative management.Curt Opin Organ Transplant.2010;15:368-373. [31] Mochida S.Indication criteria for liver transplantation for acute fiver failure in Japan.Hepatol Res.2008;38 Suppl l:S52-55. [32] Ling Q, Xu X, Wei Q, et al. Downgrading MELD improves the outcomes after liver transplantation in patients with acute-on-chronic hepatitis B liver failure.PLoS One.2012;7: e30322. [33] Fontana RJ, Ellerbe C, Durkalski VE, et al.Two-year outcomes in initial survivors with acute liver failure: results from a prospective, multicentre study. Liver Int. 2014 Jul 12.[Epub ahead of print] [34] Manka P, Olliges V, Bechmann LP,et al.Low levels of blood lipids are associated with etiology and lethal outcome in acute liver failure.PLoS One. 2014;9(7):e102351. [35] Sampaio MS, Martin P, Bunnapradist S.Renal Dysfunction in End-Stage Liver Disease and Post-Liver Transplant.Clin Liver Dis. 2014;18(3):543-560. [36] Shin HS, Kim SP, Han SH,et al.Prognostic indicators for acute liver failure development and mortality in patients with hepatitis a: consecutive case analysis.Yonsei Med J. 2014; 55(4): 953-959. [37] Kaido T, Tomiyama K, Ogawa K,et al.Section 12. Living donor liver transplantation for patients with high model for end-stage liver disease scores and acute liver failure.Transplantation. 2014; 97 Suppl 8:S46-7. [38] Wu FL, Shi KQ, Chen YP,et al.Scoring systems predict the prognosis of acute-on-chronic hepatitis B liver failure: an evidence-based review.Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014;8(6):623-632. [39] Koch A, Zimmermann HW, Gassler N, et al.Clinical relevance and cellular source of elevated soluble urokinase plasminogen activator receptor (suPAR) in acute liver failure. Liver Int. 2014 Feb 28. [Epub ahead of print]. [40] Zheng YB, Huang ZL, Wu ZB,et al.Dynamic changes of clinical features that predict the prognosis of acute-on-chronic hepatitis B liver failure: a retrospective cohort study.Int J Med Sci. 2013;10(12):1658-1664. |
| [1] | Cao Linlin, Ding Kaiyang, Song Hao, Wu Guolin, Hu Maogui, Fan Dandan, Zhou Chenyang, Wang Cuicui, Feng Yuanyuan. Efficacy and influencing factors of autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in the treatment of malignant lymphoma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(13): 1993-1998. |
| [2] | Li Liqiang, Jiao Longxing, Zhang Wu, Yan Wentao, Li Jian, Li Minghao. Effect of immature dendritic cells derived from bone marrow on rejection of orthotopic liver transplantation in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(13): 2025-2029. |
| [3] | Yang Feng, Chang Lipu, Huang Changshan, Gong Xiaoguang, Chang Shunwu. Macrolide antibiotics protects against ischemia-reperfusion injury after liver transplantation in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(26): 4176-4182. |
| [4] | Liu Mengyuan1, Fang Fang2. Risk factors for multi-drug resistant organisms infection after liver transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(7): 1109-1114. |
| [5] | Gao Hongqiang, Liu Jing, Li Zhiqiang, Wang Hailei, Zhao Xiongqi, Zhang Shengning, Ran Jianghua, Li Li . Ulinastatin improves rat liver metabolism after reduced-size liver transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(3): 435-440. |
| [6] | Jin Wenhu, Zhou Aiting, Wu Zhonghuan, Fan Zhenhai, Wang Dali, Wei Zairong. Vascular endothelial growth factor gene modified human amnion-derived mesenchymal stem cells promote the survival of ultra-long random skin flap [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(21): 3349-3356. |
| [7] | Cai Qiucheng, Fan Hongkai, Xiong Rihui, Jiang Yi. Intravenous administration of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells protects liver function following fatty liver transplantation from donors after cardiac death [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(17): 2625-2629. |
| [8] | Zhao Ying-peng, Li Li, Chen Gang, Bai Jian-hua, Liu Qi-yu. Reduced-size liver transplantation with fatty liver donors in a rat model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(4): 582-586. |
| [9] | Ding Chen1, Jiang Yi2, Pan Fan2, Cai Qiucheng2. Lipid metabolism after autologous orthotopic liver transplantation in rat models of fatty liver [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(36): 5821-5827. |
| [10] | Liu Li-ye1, Zhao De-fang2, Gao Fei1, Zhang Tong2, Dong Qin2. Schisandra extract regulates Th17 cells and regulatory T cell imbalance in dogs undergoing liver transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(20): 3213-3217. |
| [11] | Huang Shao-dai, Chen Peng, Wu Chao, Hu Dan, Peng Jiang, Tian Jian-wei. Isolation and culture of neonatal rat cardiomyocytes growing in sheets [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(24): 3875-3880. |
| [12] | Chen Rong, Jiang Tao, Yang Ai-zhen, Zhang Dong-hua, Wang Xuan. Clinical application of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells in liver transplantation patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(17): 2665-2671. |
| [13] | Lin Jing-xia, Su Fan, Luo Hong-shan. Transfusion of blood components in liver transplantation and abdominal multiple organ transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(33): 4957-4962. |
| [14] | Zhao Gao-ping1, 2, Deng Shao-ping1, Huang Xiao-lun2, Yang Mao-zhu2, Wei Ling-ling2, Li Shu-rong2, Wei liang2. Effects of pre-vascularization of tissue-engineered constructs on the survival of transplanted pancreatic islets [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(24): 3562-3567. |
| [15] | Bai Jian-hua, Chen Gang, Zhu Xin-feng, Wang Fan, Zhao Ying-peng, Liu Qi-yu, Li Li. Techniques and improvements of establishing orthotopic liver transplantation rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(40): 6526-6530. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||